关于决策树的简介可以参考: http://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/78880934
在 https://machinelearningmastery.com/implement-decision-tree-algorithm-scratch-python/ 中给出了CART(Classification and Regression Trees,分类回归树算法,简称CART)算法的Python实现,采用的数据集为Banknote Dataset,关于此数据集的介绍可以参考:http://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/78624358 ,这里在原作者的基础上,进行了略微改动,使其可以直接执行,code如下:
# reference: https://machinelearningmastery.com/implement-decision-tree-algorithm-scratch-python/
# http://zhuanlan.51cto.com/art/201702/531945.htm
# using CART(Classification and Regression Trees,分类回归树算法,简称CART算法)) for classification
# CART on the Bank Note dataset
from random import seed
from random import randrange
from csv import reader
# Load a CSV file
def load_csv(filename):
file = open(filename, "r")
lines = reader(file)
dataset = list(lines)
return dataset
# Convert string column to float
def str_column_to_float(dataset, column):
for row in dataset:
row[column] = float(row[column].strip())
# Split a dataset into k folds
def cross_validation_split(dataset, n_folds):
dataset_split = list()
dataset_copy = list(dataset)
fold_size = int(len(dataset) / n_folds)
for i in range(n_folds):
fold = list()
while len(fold) < fold_size:
index = randrange(len(dataset_copy))
fold.append(dataset_copy.pop(index))
dataset_split.append(fold)
return dataset_split
# Calculate accuracy percentage
def accuracy_metric(actual, predicted):
correct = 0
for i in range(len(actual)):
if actual[i] == predicted[i]:
correct += 1
return correct / float(len(actual)) * 100.0
# Evaluate an algorithm using a cross validation split
def evaluate_algorithm(dataset, algorithm, n_folds, *args):
folds = cross_validation_split(dataset, n_folds)
scores = list()
for fold in folds:
train_set = list(folds)
train_set.remove(fold)
train_set = sum(train_set, [])
test_set = list()
for row in fold:
row_copy = list(row)
test_set.append(row_copy)
row_copy[-1] = None
predicted = algorithm(train_set, test_set, *args)
actual = [row[-1] for row in fold]
accuracy = accuracy_metric(actual, predicted)
scores.append(accuracy)
return scores
# Split a dataset based on an attribute and an attribute value
def test_split(index, value, dataset):
left, right = list(), list()
for row in dataset:
if row[index] < value:
left.append(row)
else:
right.append(row)
return left, right
# Calculate the Gini index for a split dataset
def gini_index(groups, classes):
# count all samples at split point
n_instances = float(sum([len(group) for group in groups])) # 计算总的样本数
# sum weighted Gini index for each group
gini = 0.0
for group in groups:
size = float(len(group))
# avoid divide by zero
if size == 0:
continue
score = 0.0
# score the group based on the score for each class
for class_val in classes:
p = [row[-1] for row in group].count(class_val) / size # row[-1]指每个样本(一行)中最后一列即类别
score += p * p
# weight the group score by its relative size
gini += (1.0 - score) * (size / n_instances)
return gini
# Select the best split point for a dataset
def get_split(dataset):
class_values = list(set(row[-1] for row in dataset)) # class_values的值为: [0, 1]
b_index, b_value, b_score, b_groups = 999, 999, 999, None
for index in range(len(dataset[0])-1): # index的值为: [0, 1, 2, 3]
for row in dataset:
groups = test_split(index, row[index], dataset)
gini = gini_index(groups, class_values)
if gini < b_score:
b_index, b_value, b_score, b_groups = index, row[index], gini, groups
return {'index':b_index, 'value':b_value, 'groups':b_groups} # 返回字典数据类型
# Create a terminal node value
def to_terminal(group):
outcomes = [row[-1] for row in group]
return max(set(outcomes), key=outcomes.count)
# Create child splits for a node or make terminal
def split(node, max_depth, min_size, depth):
left, right = node['groups']
del(node['groups'])
# check for a no split
if not left or not right:
node['left'] = node['right'] = to_terminal(left + right)
return
# check for max depth
if depth >= max_depth:
node['left'], node['right'] = to_terminal(left), to_terminal(right)
return
# process left child
if len(left) <= min_size:
node['left'] = to_terminal(left)
else:
node['left'] = get_split(left)
split(node['left'], max_depth, min_size, depth+1)
# process right child
if len(right) <= min_size:
node['right'] = to_terminal(right)
else:
node['right'] = get_split(right)
split(node['right'], max_depth, min_size, depth+1)
# Build a decision tree
def build_tree(train, max_depth, min_size):
root = get_split(train)
split(root, max_depth, min_size, 1)
return root
# Make a prediction with a decision tree
def predict(node, row):
if row[node['index']] < node['value']:
if isinstance(node['left'], dict):
return predict(node['left'], row)
else:
return node['left']
else:
if isinstance(node['right'], dict):
return predict(node['right'], row)
else:
return node['right']
# Classification and Regression Tree Algorithm
def decision_tree(train, test, max_depth, min_size):
tree = build_tree(train, max_depth, min_size)
predictions = list()
for row in test:
prediction = predict(tree, row)
predictions.append(prediction)
return(predictions)
# Test CART on Bank Note dataset
seed(1)
# load and prepare data
filename = '../../../data/database/BacknoteDataset/data_banknote_authentication.csv'
dataset = load_csv(filename)
# convert string attributes to integers
for i in range(len(dataset[0])):
str_column_to_float(dataset, i) # dataset为嵌套列表的列表,类型为float
# evaluate algorithm
n_folds = 5
max_depth = 5
min_size = 10
scores = evaluate_algorithm(dataset, decision_tree, n_folds, max_depth, min_size)
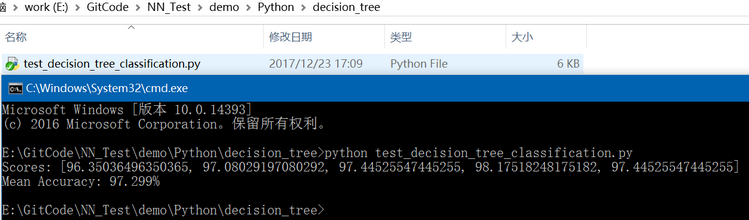
print('Scores: %s' % scores)
print('Mean Accuracy: %.3f%%' % (sum(scores)/float(len(scores))))























 808
808











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








