文章目录
1、环境安装
1.1 运行环境
1.1.1 Conda虚拟环境
创建ppai
conda create -n ppai python=3.7
激活环境
conda activate ppai
1.1.2 PyTorch
Python3.7推荐版本:
pytorch1.13.1 + torchvision0.14.1 + torchaudio0.13.1 + cuda11.7
conda install pytorch==1.13.1 torchvision==0.14.1 torchaudio==0.13.1 pytorch-cuda=11.7 -c pytorch -c nvidia
安装遇到疑难参考 这里
1.1.3 Tensorflow
Python3.7推荐版本:
tensorflow-gpu 1.15
pip install tensorflow-gpu==1.15 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
安装遇到疑难参考 这里
1.2 Paddle核心框架
1.2.1 安装Paddle框架
- CPU 版本
pip install paddlepaddle - GPU 版本
飞桨官网点这里
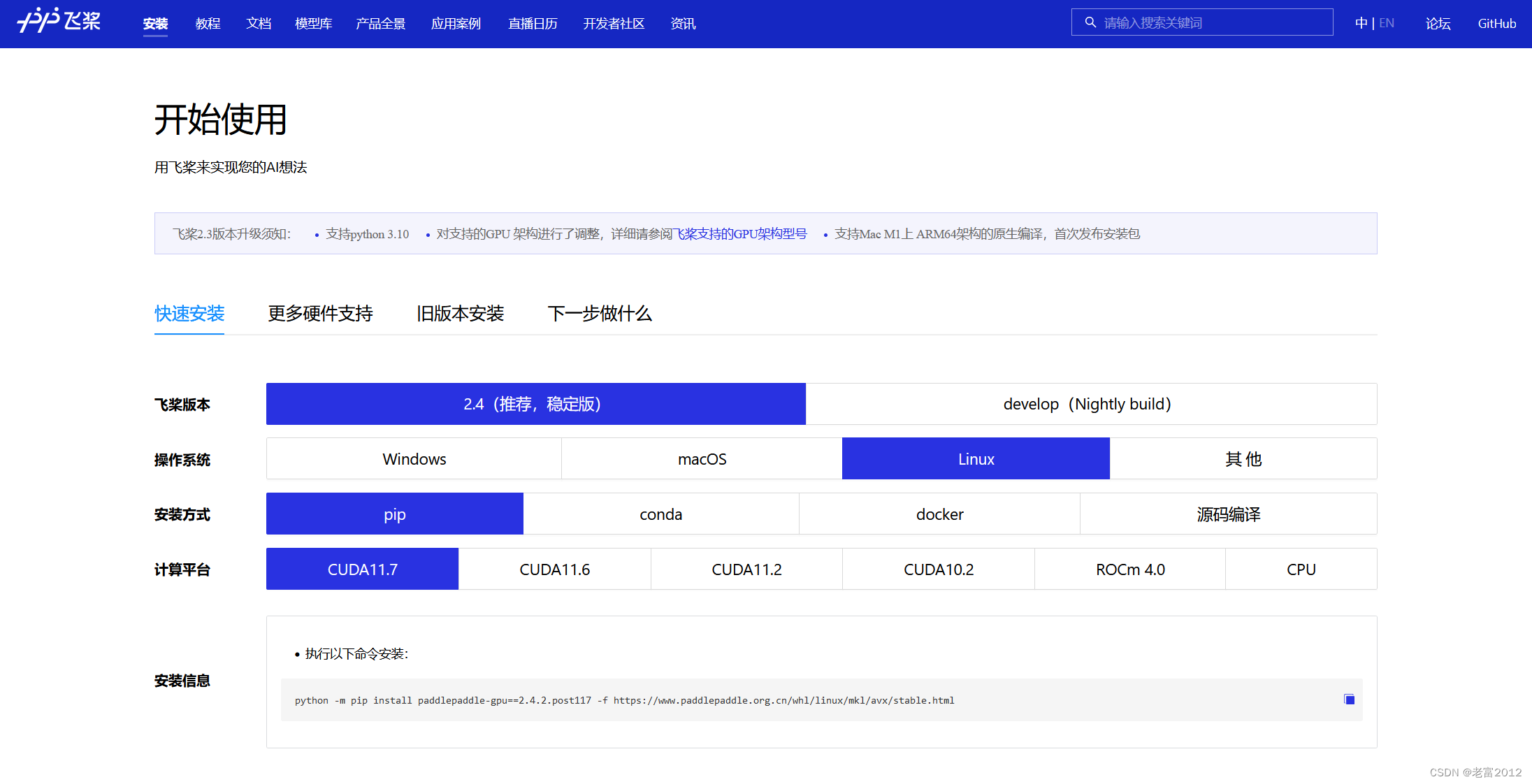
- 安装与你GPU匹配的版本
python -m pip install paddlepaddle-gpu==2.4.2.post117 -f https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/whl/linux/mkl/avx/stable.html
1.2.2 验证框架是否安装成功
python -c "import paddle; print(paddle.__version__)"
(ppai) xf@VP01:~/ai/tts$ python -c "import paddle; print(paddle.__version__)"
2.4.2
python -c "import paddle;paddle.utils.run_check()"
(ppai) xf@VP01:~/ai/tts$ python -c "import paddle;paddle.utils.run_check()"
Running verify PaddlePaddle program ...
W0502 07:43:23.693028 1278 gpu_resources.cc:61] Please NOTE: device: 0, GPU Compute Capability: 8.9, Driver API Version: 12.1, Runtime API Version: 11.7
W0502 07:43:23.701891 1278 gpu_resources.cc:91] device: 0, cuDNN Version: 8.8.
PaddlePaddle works well on 1 GPU.
PaddlePaddle works well on 1 GPUs.
PaddlePaddle is installed successfully! Let's start deep learning with PaddlePaddle now.
1.3 PaddleSpeech 语音服务
1.3.1 安装paddlespeech
pip install paddlespeech
1.3.2 Git下载源码包
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSpeech
(ppai) xf@VP01:~/ai/tts$ git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSpeech
Cloning into 'PaddleSpeech'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 44486, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (968/968), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (616/616), done.
remote: Total 44486 (delta 379), reused 789 (delta 295), pack-reused 43518
Receiving objects: 100% (44486/44486), 69.56 MiB | 16.05 MiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (28721/28721), done.
Updating files: 100% (3558/3558), done.
(ppai) xf@VP01:~/ai/tts$ cd paddlespeech
(ppai) xf@VP01:~/ai/tts/paddlespeech$ ls
LICENSE README.md audio demos docs paddlespeech setup.cfg tests tools
MANIFEST.in README_cn.md dataset docker examples runtime setup.py third_party utils
2、语音服务器
2.1 启用CLI 语音服务
2.1.1 application.yaml服务器配置
服务器配置application.yaml,在PaddleSpeech/paddlespeech/server/conf目录下:
engine_list: ['asr_python', 'tts_python', 'cls_python', 'text_python', 'vector_python']
engine_list 表示开启的服务类型
- asr_python(语音识别)
- tts_python(语音合成)
- cls_python(声音分类)
- text_python(标点恢复)
- vector_python (声纹向量提取)
2.1.2 运行server命令
paddlespeech_server start --config_file /home/xf/ai/tts/paddlespeech/paddlespeech/server/conf/application.yaml
(ppai) xf@VP01:~/ai/tts/paddlespeech$ paddlespeech_server start --config_file paddlespeech/server/conf/application.yaml
[2023-05-02 07:16:34,644] [ INFO] - start to init the engine
[2023-05-02 07:16:34,644] [ INFO] - asr : python engine.
W0502 07:16:37.497296 1187 gpu_resources.cc:61] Please NOTE: device: 0, GPU Compute Capability: 8.9, Driver API Version: 12.1, Runtime API Version: 11.7
W0502 07:16:37.502528 1187 gpu_resources.cc:91] device: 0, cuDNN Version: 8.8.
2023-05-02 07:16:38.195 | INFO | paddlespeech.s2t.modules.embedding:__init__:153 - max len: 5000
[2023-05-02 07:16:39,064] [ INFO] - Initialize ASR server engine successfully on device: gpu:0.
[2023-05-02 07:16:39,064] [ INFO] - tts : python engine.
...
[2023-05-02 07:16:55] [INFO] [on.py:61] Application startup complete.
INFO: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8090 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
[2023-05-02 07:16:55] [INFO] [server.py:212] Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8090 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
服务成功运行在http://127.0.0.1:8090 端口。
2.2 自定义CLI快捷启动Shell
2.2.1 自定义Shell目标
在home目录创建shell,不用进入层层目录,快捷启动PaddleSpeech语音服务器:
- 自动启用conda环境
- 自动cd到paddlespeech目录
- 自动输入cli命令及config_file
cd ~
vim mypss
自行修改当中的文件路径和conda环境名
#!/bin/bash
source /home/xf/anaconda3/bin/activate ppai
cd /home/xf/ai/tts/PaddleSpeech
paddlespeech_server start --config_file paddlespeech/server/conf/application.yaml
2.2.2 快捷启动
在mypss目录输入
. mypss
3、客户端语音使用的几种方法
3.1 命令行cli调用
(ppai) xf@VP01:~/ai/tts/paddlespeech$ paddlespeech_client tts --server_ip 127.0.0.1 --port 8090 --input "您好,这是命令行cli生成语音。" --output ./output/output_tts_cli.wav
[2023-05-02 08:53:42,265] [ INFO] - Save synthesized audio successfully on ./output/output_tts_cli.wav.
[2023-05-02 08:53:42,266] [ INFO] - Audio duration: 2.575000 s.
[2023-05-02 08:53:42,266] [ INFO] - Response time: 0.491946 s.
3.2 客户端直接调用
创建xf_tts_class.py
# 客户端直接调用
from paddlespeech.cli.tts.infer import TTSExecutor
tts = TTSExecutor()
res = tts(
text="这是class生成语音。",
output="./output/output_tts_class.wav"
)
print(res)
(ppai) xf@VP01:~/ai/tts/paddlespeech$ python xf_tts_class.py
/home/xf/anaconda3/envs/ppai/lib/python3.7/site-packages/librosa/core/constantq.py:1059: DeprecationWarning: `np.complex` is a deprecated alias for the builtin `complex`. To silence this warning, use `complex` by itself. Doing this will not modify any behavior and is safe. If you specifically wanted the numpy scalar type, use `np.complex128` here.
Deprecated in NumPy 1.20; for more details and guidance: https://numpy.org/devdocs/release/1.20.0-notes.html#deprecations
dtype=np.complex,
/home/xf/anaconda3/envs/ppai/lib/python3.7/site-packages/_distutils_hack/__init__.py:33: UserWarning: Setuptools is replacing distutils.
warnings.warn("Setuptools is replacing distutils.")
[2023-05-02 08:58:16,097] [ INFO] - Already cached /home/xf/.paddlenlp/models/bert-base-chinese/bert-base-chinese-vocab.txt
[2023-05-02 08:58:16,114] [ INFO] - tokenizer config file saved in /home/xf/.paddlenlp/models/bert-base-chinese/tokenizer_config.json
[2023-05-02 08:58:16,114] [ INFO] - Special tokens file saved in /home/xf/.paddlenlp/models/bert-base-chinese/special_tokens_map.json
W0502 08:58:16.274096 1806 gpu_resources.cc:61] Please NOTE: device: 0, GPU Compute Capability: 8.9, Driver API Version: 12.1, Runtime API Version: 11.7
W0502 08:58:16.279990 1806 gpu_resources.cc:91] device: 0, cuDNN Version: 8.8.
Building prefix dict from the default dictionary ...
[2023-05-02 08:58:23] [DEBUG] [__init__.py:113] Building prefix dict from the default dictionary ...
Loading model from cache /tmp/jieba.cache
[2023-05-02 08:58:23] [DEBUG] [__init__.py:133] Loading model from cache /tmp/jieba.cache
Loading model cost 0.282 seconds.
[2023-05-02 08:58:23] [DEBUG] [__init__.py:165] Loading model cost 0.282 seconds.
Prefix dict has been built successfully.
[2023-05-02 08:58:23] [DEBUG] [__init__.py:166] Prefix dict has been built successfully.
/mnt/d/develop/ubuntu/tts/paddlespeech/output/output_tts_class.wav
3.3 客户端API请求
创建xf_tts_client.py
# 客户端API请求
from paddlespeech.server.bin.paddlespeech_client import TTSClientExecutor
import json
ttsclient_executor = TTSClientExecutor()
res = ttsclient_executor(
input="这是API客户端生成的语音。 ",
server_ip="127.0.0.1",
port=8090,
spk_id=0,
speed=1.0,
volume=1.0,
sample_rate=0,
output="./output/output_tts_client.wav")
response_dict = res.json()
print(response_dict["message"])
print("Save synthesized audio successfully on %s." % (response_dict['result']['save_path']))
print("Audio duration: %f s." %(response_dict['result']['duration']))
(ppai) xf@VP01:~/ai/tts/paddlespeech$ python xf_tts_client.py
{'description': 'success.'}
Save synthesized audio successfully on ./output/output_tts_client.wav.
Audio duration: 2.125000 s.
3.4 客户端Requests构建API请求
3.4.1 示例
创建xf_tts_api.py
# Requests构建 API 请求
import requests
import base64
import json
import soundfile
import io
# 定义paddlespeech_request函数
def paddlespeech_request(url, data):
res = requests.post(
url=url,
data=json.dumps(data)
)
if res.status_code == 200:
res = res.json()
else:
print("请求失败,错误代码:", res.status_code)
res = None
return res
# API 请求
tts_url = "http://127.0.0.1:8090/paddlespeech/tts"
## 请求数据包
data = {
"text": "这个音频是由Requests构建 API 请求生成的!",
"spk_id": 0,
"speed": 1.0,
"volume": 1.0,
"sample_rate": 0,
# 这里先不保存,演示如何将base64编码还原成wav音频
"save_path": None
}
## 发送请求
res = paddlespeech_request(tts_url, data)
print(res['success'])
# 将res中的base64还原成wav
wav_base64 = res['result']['audio']
audio_data_byte = base64.b64decode(wav_base64)
## 重新读取sample
samples, sample_rate = soundfile.read(
io.BytesIO(audio_data_byte), dtype='float32')
## 保存成audio
outfile = "./output/output_tts_api.wav"
soundfile.write(outfile, samples, sample_rate)
print(outfile)
(ppai) xf@VP01:~/ai/tts/paddlespeech$ python xf_tts_api.py
True
./output/output_tts_api.wav
3.4.2 API响应返回格式
正常情况下都会返回HTTP 200状态码,application/json格式。
| 字段 | 必选 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| success | 是 | bool | 表示请求成功与否 |
| code | 是 | int | 错误码。success=true 的时候,code 必然为 0。success=false 的时候,code 为具体的错误码。 |
| message | 是 | json | 用来描述错误信息 |








 本文详细介绍了如何搭建PaddleSpeech API语音服务器,包括环境安装(Conda、PyTorch、Tensorflow和Paddle框架)、PaddleSpeech的安装与配置、服务器启动与自定义CLI、客户端调用方法,以及解决运行中遇到的问题。通过这个指南,读者将能够成功运行并使用PaddleSpeech语音服务。
本文详细介绍了如何搭建PaddleSpeech API语音服务器,包括环境安装(Conda、PyTorch、Tensorflow和Paddle框架)、PaddleSpeech的安装与配置、服务器启动与自定义CLI、客户端调用方法,以及解决运行中遇到的问题。通过这个指南,读者将能够成功运行并使用PaddleSpeech语音服务。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 671
671

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








