决策树是一种基本的分类回归方法。是类似于if else的思想。
重点:通过信息增益值来不断形成树的分叉
决策树参考API:
class sklearn.tree.DecisionTreeRegressor(*, criterion=‘mse’, splitter=‘best’, max_depth=None, min_samples_split=2, min_samples_leaf=1, min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, max_features=None, random_state=None, max_leaf_nodes=None, min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None, presort=‘deprecated’, ccp_alpha=0.0)
-
1.criterion gini or entropy 衡量标准—————选择熵值还是gini系数作为衡量标准
-
2.splitter best or random 切分点的选择 ———— 前者是在所有特征中找最好的切分点 后者是在部分特征中(数据量大的时候)默认参数是best
-
3.max_depth 最大深度 ———— 数据少或者特征少的时候可以不管这个值,如果模型样本量多,特征也多的情况下,可以for循环尝试限制下
-
4.min_samples_split 最小样本数 ———— 如果某节点的样本数少于min_samples_split,则不会继续再尝试选择最优特征来进行划分如果样本量不大,不需要管这个值。如果样本量数量级非常大,则推荐增大这个值。
-
5.min_samples_leaf 最小叶子节点 ———— 这个值限制了叶子节点最少的样本数,如果某叶子节点数目小于样本数,则会和兄弟节点一起被剪枝,如果样本量不大,不需要管这个值,大些如10W可是尝试下5
-
6.min_weight_fraction_leaf 最小权重值————这个值限制了叶子节点所有样本权重和的最小值,如果小于这个值,则会和兄弟节点一起被剪枝默认是0,就是不考虑权重问题。一般来说,如果我们有较多样本有缺失值,或者分类树样本的分布类别偏差很大,就会引入样本权重,这时我们就要注意这个值了。
-
7.max_leaf_nodes 最大叶子节点数————通过限制最大叶子节点数,可以防止过拟合,默认是"None”,即不限制最大的叶子节点数。如果加了限制,算法会建立在最大叶子节点数内最优的决策树。如果特征不多,可以不考虑这个值,但是如果特征分成多的话,可以加以限制具体的值可以通过交叉验证得到。
-
8.class_weight 指定样本各类别的的权重————主要是为了防止训练集某些类别的样本过多导致训练的决策树过于偏向这些类别。这里可以自己指定各个样本的权重如果使用“balanced”,则算法会自己计算权重,样本量少的类别所对应的样本权重会高。
-
9.n_estimators:要建立树的个数
经典案例:
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier, export_graphviz
def decision_iris():
"""
用决策树对鸢尾花进行分类
:return:
"""
# 1)获取数据集
iris = load_iris()
# 2)划分数据集
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(iris.data, iris.target, random_state=22)
# 3)决策树预估器
estimator = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion="entropy")
estimator.fit(x_train, y_train)
# 4)模型评估
# 方法1:直接比对真实值和预测值
y_predict = estimator.predict(x_test)
print("y_predict:\n", y_predict)
print("直接比对真实值和预测值:\n", y_test == y_predict)
# 方法2:计算准确率
score = estimator.score(x_test, y_test)
print("准确率为:\n", score)
# 可视化决策树
export_graphviz(estimator, out_file="iris_tree.dot", feature_names=iris.feature_names)
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 代码4:用决策树对鸢尾花进行分类
decision_iris()
数据集介绍:
特征值名称:
['sepal length (cm)', 'sepal width (cm)', 'petal length (cm)', 'petal width (cm)']
目标值:
['setosa' 'versicolor' 'virginica']
数据集的描述
.. _iris_dataset:
Iris plants dataset
--------------------
**Data Set Characteristics:**
:Number of Instances: 150 (50 in each of three classes)
:Number of Attributes: 4 numeric, predictive attributes and the class
:Attribute Information:
- sepal length in cm
- sepal width in cm
- petal length in cm
- petal width in cm
- class:
- Iris-Setosa
- Iris-Versicolour
- Iris-Virginica
:Summary Statistics:
============== ==== ==== ======= ===== ====================
Min Max Mean SD Class Correlation
============== ==== ==== ======= ===== ====================
sepal length: 4.3 7.9 5.84 0.83 0.7826
sepal width: 2.0 4.4 3.05 0.43 -0.4194
petal length: 1.0 6.9 3.76 1.76 0.9490 (high!)
petal width: 0.1 2.5 1.20 0.76 0.9565 (high!)
============== ==== ==== ======= ===== ====================
:Missing Attribute Values: None
:Class Distribution: 33.3% for each of 3 classes.
:Creator: R.A. Fisher
:Donor: Michael Marshall (MARSHALL%PLU@io.arc.nasa.gov)
:Date: July, 1988
The famous Iris database, first used by Sir R.A. Fisher. The dataset is taken
from Fisher's paper. Note that it's the same as in R, but not as in the UCI
Machine Learning Repository, which has two wrong data points.
This is perhaps the best known database to be found in the
pattern recognition literature. Fisher's paper is a classic in the field and
is referenced frequently to this day. (See Duda & Hart, for example.) The
data set contains 3 classes of 50 instances each, where each class refers to a
type of iris plant. One class is linearly separable from the other 2; the
latter are NOT linearly separable from each other.
.. topic:: References
- Fisher, R.A. "The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems"
Annual Eugenics, 7, Part II, 179-188 (1936); also in "Contributions to
Mathematical Statistics" (John Wiley, NY, 1950).
- Duda, R.O., & Hart, P.E. (1973) Pattern Classification and Scene Analysis.
(Q327.D83) John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-22361-1. See page 218.
- Dasarathy, B.V. (1980) "Nosing Around the Neighborhood: A New System
Structure and Classification Rule for Recognition in Partially Exposed
Environments". IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence, Vol. PAMI-2, No. 1, 67-71.
- Gates, G.W. (1972) "The Reduced Nearest Neighbor Rule". IEEE Transactions
on Information Theory, May 1972, 431-433.
- See also: 1988 MLC Proceedings, 54-64. Cheeseman et al"s AUTOCLASS II
conceptual clustering system finds 3 classes in the data.
- Many, many more ...
```简而言之:鸢尾花数据集包括sepal length (cm)', 'sepal width (cm)', 'petal length (cm)', 'petal width (cm)'这四个特征值和'setosa' 'versicolor' 'virginica'这三个目标值
结果如下
[0 2 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 0 2 1 2 2 0 2 1 1 1 1 0 2 0 1 2 0 2 2 2 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0
0]
直接比对真实值和预测值:
[ True True True True True True True False True True True True
True True True True True True False True True True True True
True True True True True False True True True True True True
True True]
准确率为:
0.9210526315789473
可视化:通过
# 可视化决策树
export_graphviz(estimator, out_file="iris_tree.dot", feature_names=iris.feature_names)
这条语句生成.dot文件,再将.dot文件内容复制到:http://www.webgraphviz.com/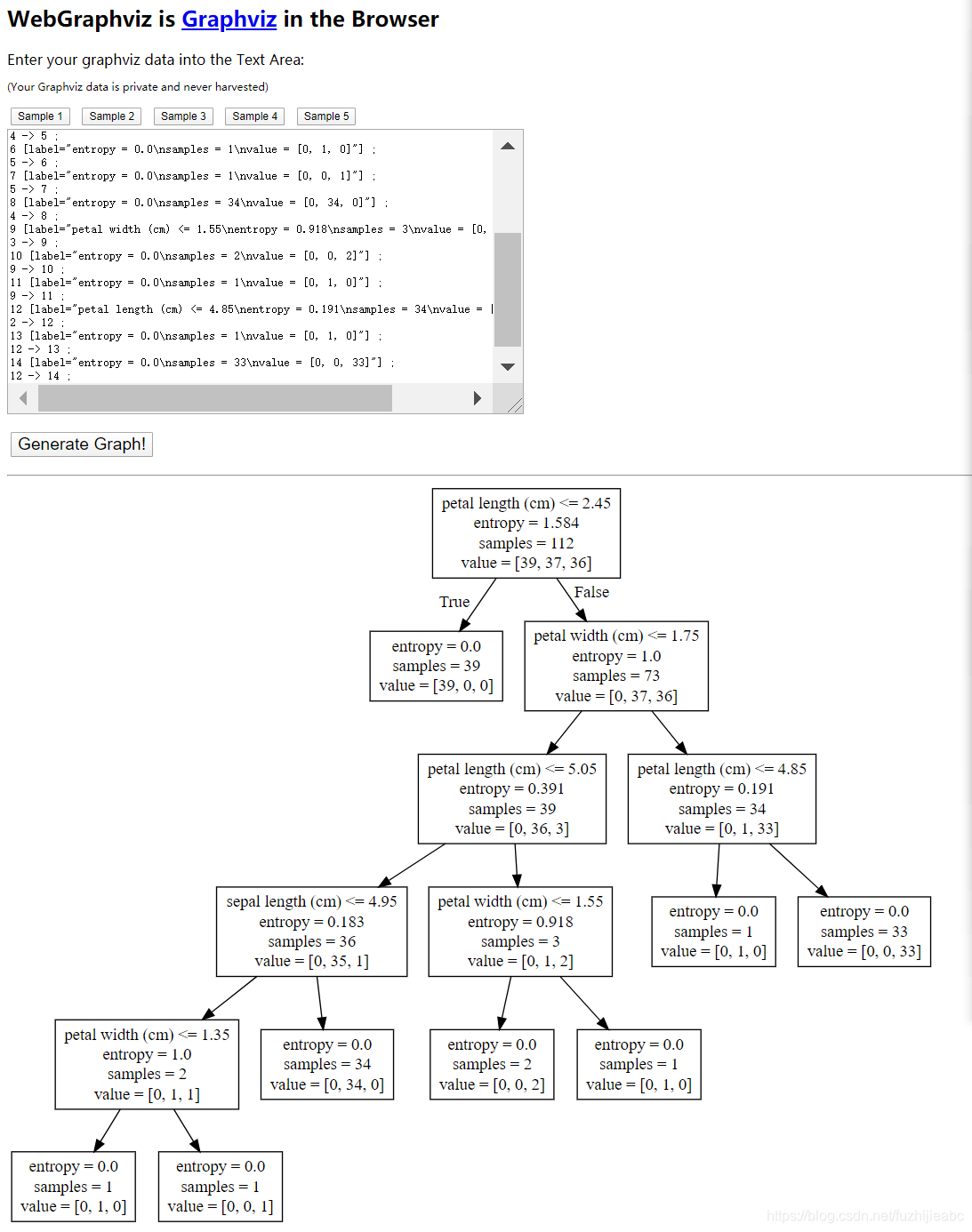





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








