1、协作型过滤(collaborative filtering)
一个协作型过滤算法通常的做法是对一大群人进行搜索,并从中找出与我们品味相近的一小群人。算法会对这些人所偏爱的其他内容进行考查,并将它们组合起来构造出一个经过排序的推荐列表。
2、搜索偏好
第一件事情,寻找一种表达不同人及其偏好的方法,使用嵌套字典。
# A dictionary of movie critics and their ratings of a small
# set of movies
#一个涉及影评者以及对几部影片评分情况的字典
critics={'Lisa Rose': {'Lady in the Water': 2.5, 'Snakes on a Plane': 3.5,
'Just My Luck': 3.0, 'Superman Returns': 3.5, 'You, Me and Dupree': 2.5,
'The Night Listener': 3.0},
'Gene Seymour': {'Lady in the Water': 3.0, 'Snakes on a Plane': 3.5,
'Just My Luck': 1.5, 'Superman Returns': 5.0, 'The Night Listener': 3.0,
'You, Me and Dupree': 3.5},
'Michael Phillips': {'Lady in the Water': 2.5, 'Snakes on a Plane': 3.0,
'Superman Returns': 3.5, 'The Night Listener': 4.0},
'Claudia Puig': {'Snakes on a Plane': 3.5, 'Just My Luck': 3.0,
'The Night Listener': 4.5, 'Superman Returns': 4.0,
'You, Me and Dupree': 2.5},
'Mick LaSalle': {'Lady in the Water': 3.0, 'Snakes on a Plane': 4.0,
'Just My Luck': 2.0, 'Superman Returns': 3.0, 'The Night Listener': 3.0,
'You, Me and Dupree': 2.0},
'Jack Matthews': {'Lady in the Water': 3.0, 'Snakes on a Plane': 4.0,
'The Night Listener': 3.0, 'Superman Returns': 5.0, 'You, Me and Dupree': 3.5},
'Toby': {'Snakes on a Plane':4.5,'You, Me and Dupree':1.0,'Superman Returns':4.0}}
3、寻找相近的用户
将每个人与所有其他人进行对比,并计算他们的相似度评价值。将介绍两套计算相似度评价值的体系:欧几里得距离和皮尔逊相关度。
欧几里德距离评价
以经过人们一致评价的物品为坐标轴,然后将参与评价的人绘制到图上,并考查他们彼此间的距离远近,如图所示:

def get_score_by_movie(prefs,movie1,movie2):
for item in prefs:
movie_list = prefs[item]
if ( movie1 in movie_list ) and (movie2 in movie_list):
name_list = item.split()
if len(name_list) > 1:
name = name_list[1]
else:
name = name_list[0]
print "%s=(%0.2f,%0.2f)" % (name,critics[item][movie1],critics[item][movie2])
get_score_by_movie(critics,'You, Me and Dupree','Snakes on a Plane')输出:
Matthews=(3.50,4.00)
LaSalle=(2.00,4.00)
Puig=(2.50,3.50)
Rose=(2.50,3.50)
Toby=(1.00,4.50)
Seymour=(3.50,3.50)
from math import sqrt
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def get_score_by_movie(prefs,movie1,movie2):
fig = plt.figure()
fig.suptitle('Preference Movie', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
fig.subplots_adjust(top=0.85)
ax.set_xlabel(movie1)
ax.set_ylabel(movie2)
for item in prefs:
movie_list = prefs[item]
if ( movie1 in movie_list ) and (movie2 in movie_list):
name_list = item.split()
if len(name_list) > 1:
name = name_list[1]
else:
name = name_list[0]
x = critics[item][movie1]
y = critics[item][movie2]
ax.text(x,y,name)
print "%s=(%0.2f,%0.2f)" % (name,x,y)
#起到关键作用,调整坐标轴size,默认为[0,1]
ax.axis([0, 5, 0, 5])
plt.savefig("test.png")输出的结果:

不做ax.axis([0, 5, 0, 5]) ,输出结果如下:

欧几里德距离定义
欧几里得度量定义欧几里得空间中,点 x = (x1,...,xn) 和 y = (y1,...,yn) 之间的距离为

向量 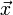 的自然长度,即该点到原点的距离为
的自然长度,即该点到原点的距离为
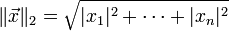
它是一个纯数值。在欧几里得度量下,两点之间直线最短。
from math import sqrt
def sim_distance(prefs,person1,person2): si = {}
for item in prefs[person1]:
if item in prefs[person2]:
si[item] = 1
if len(si) == 0 :return 0
//对同一部电影的喜好程度,构成上面 x = (x1,...,xn) 和 y = (y1,...,yn)
sum_of_squares = sum(pow( prefs[person1][item] - prefs[person2][item] , 2) for item in si) return 1/(1+sum_of_squares)
if __name__ == '__main__':
print sim_distance(critics,'Lisa Rose','Gene Seymour')输出结果为: 0.148148148148
皮尔逊相关度评价
它在数据不是很normalized的时候(影评者对影片的评价总是相对于平均水平偏离很大时),会倾向给出更好的结果。
如下图Mick LaSalle为Superman评了3分,而Gene Seymour则评了5分,故该影片对应的定位为(3,5):

在图上,还可以看到一条直线,其可能地靠近图上的所有坐标,被称作为最佳拟合线。
如果两位评论者对所有影片的评分情况都相同的话,那么这条直线将成为对角线,并且会与图上所有的坐标点都相交,从而得一个结果为1的理想相关度评价。
上图相关系数为0.4左右。下图相关系数为0.75:

在采用皮尔逊方法进行评价时,可以从图上发现一个值得注意的地方,就是它修正“夸大分值”的情况。虽然Jack总是倾向于给出比Lisa更高的分值,但最终的直线仍然是拟合的,这说明他们之间有很好的相关性。
对比欧几里得:
1、皮尔逊:如果某人总是倾向于给出比另一个人更高的分值,而二者的分值之差又始终保持一致,则他们依然可能存在很好的相关性
2、欧几里得:一个人的评价始终比另一个人的更好,从而导致评价始终相对偏低,得出两者不相近的结果。尽管他们的品味很相似也是如此。
假设有两个变量X、Y,那么两变量间的皮尔逊相关系数可通过以下公式计算:

皮尔逊相关度评价算法首先会找出两位评论者都曾评价过的物品,然后计算两者的评分总和与平方和,并求得评分的乘积之和。最后,算法利用这些计算结果计算出皮尔逊相关系数。
def sim_person(prefs,p1,p2):
si = {}
for item in prefs[p1]:
if item in prefs[p2]:
si[item] = 1
n = len(si)
if n == 0:return 0
sum1 = sum([prefs[p1][it] for it in si])
sum2 = sum([prefs[p2][it] for it in si])
sum1Sq = sum([pow(prefs[p1][it],2) for it in si])
sum2Sq = sum([pow(prefs[p2][it],2) for it in si])
pSum = sum([prefs[p1][it]*prefs[p2][it] for it in si])
num = pSum - sum1*sum2/n
den = sqrt((sum1Sq-pow(sum1,2)/n)*(sum2Sq-pow(sum2,2)/n))
if den == 0:
return 0
return num/den输出结果为:0.396059017191
该函数将返回介于-1与1之间的数值,值1表明两个人有一致的评价。
应该选用哪一种相似性度量方法
根据实际效果进行选择,皮尔逊、欧几里得距离等任何其他方法。
Jaccard系数或曼哈顿距离算法,作为相似度计算函数,只要满足如下条件:拥有同样的函数签名,以一个浮点数作为返回值,其数值越大代表相似度越大。
为评论者打分
使用上面的相似度计算函数,为影评者打分
def topMatches(prefs,person,n=5 ,similarity=sim_person):
scores = [(similarity(prefs,person,other),other) for other in prefs if other!=person]
scores.sort()
scores.reverse()
print scores
return scores[0:n]
topMatches(critics,'Lisa Rose')
[(0.9912407071619299, u'Toby'), (0.7470178808339965, u'Jack Matthews'), (0.5940885257860044, u'Mick LaSalle'), (0.5669467095138396, u'Claudia Puig'), (0.40451991747794525, u'Michael Phillips'), (0.39605901719066977, u'Gene Seymour')]






















 1403
1403

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








