该文翻译整理自:selective search for object detection(c++ / python)
一、目标检测 VS 目标识别
目标识别(objec recognition)是指明一幅输入图像中包含那类目标。其输入为一幅图像,输出是该图像中的目标属于哪个类别(class probability)。而目标检测(object detection)除了要告诉输入图像中包含了哪类目前外,还要框出该目标的具体位置(bounding boxes)。
在目标检测时,为了定位到目标的具体位置,通常会把图像分成许多子块(sub-regions / patches),然后把子块作为输入,送到目标识别的模型中。分子块的最直接方法叫滑动窗口法(sliding window approach)。滑动窗口的方法就是按照子块的大小在整幅图像上穷举所有子图像块。这种方法产生的数据量想想都头大。和滑动窗口法相对的是另外一类基于区域(region proposal)的方法。selective search就是其中之一!
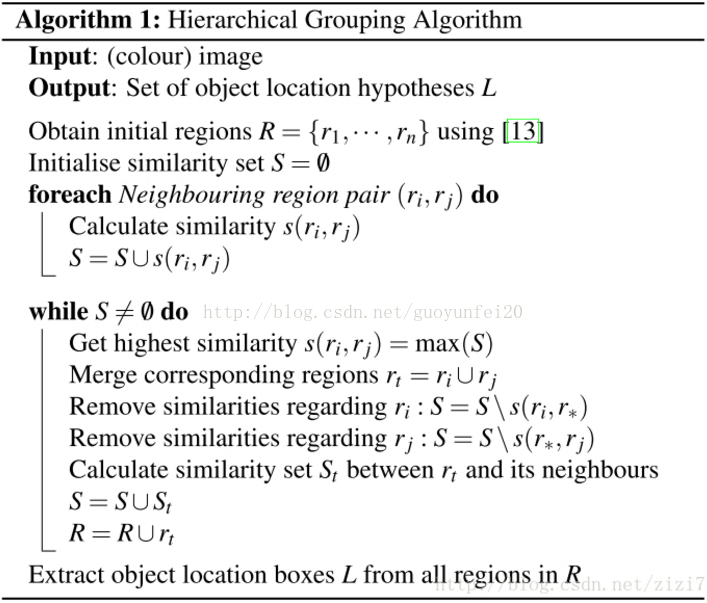
二、selective search算法流程
step0:生成区域集R,具体参见论文《Efficient Graph-Based Image Segmentation》
step1:计算区域集R里每个相邻区域的相似度S={s1,s2,…}
step2:找出相似度最高的两个区域,将其合并为新集,添加进R
step3:从S中移除所有与step2中有关的子集
step4:计算新集与所有子集的相似度
step5:跳至step2,直至S为空
三、相似度计算
论文考虑了颜色、纹理、尺寸和空间交叠这4个参数。
3.1、颜色相似度(color similarity)
将色彩空间转为HSV,每个通道下以bins=25计算直方图,这样每个区域的颜色直方图有25*3=75个区间。 对直方图除以区域尺寸做归一化后使用下式计算相似度:
3.2、纹理相似度(texture similarity)
论文采用方差为1的高斯分布在8个方向做梯度统计,然后将统计结果(尺寸与区域大小一致)以bins=10计算直方图。直方图区间数为8*3*10=240(使用RGB色彩空间)。

其中, 是直方图中第
是直方图中第 个bin的值。
个bin的值。
3.3、尺寸相似度(size similarity)

保证合并操作的尺度较为均匀,避免一个大区域陆续“吃掉”其他小区域。
例:设有区域a-b-c-d-e-f-g-h。较好的合并方式是:ab-cd-ef-gh -> abcd-efgh -> abcdefgh。 不好的合并方法是:ab-c-d-e-f-g-h ->abcd-e-f-g-h ->abcdef-gh -> abcdefgh。
3.4、交叠相似度(shape compatibility measure)

3.5、最终的相似度

四、OpenCV 3.3 实现了selective search
在OpenCV的contrib模块中实现了selective search算法。类定义为:
cv::ximgproc::segmentation::SelectiveSearchSegmentation
#include "opencv2/ximgproc/segmentation.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::ximgproc::segmentation;
static void help() {
std::cout << std::endl <<
"Usage:" << std::endl <<
"./ssearch input_image (f|q)" << std::endl <<
"f=fast, q=quality" << std::endl <<
"Use l to display less rects, m to display more rects, q to quit" << std::endl;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
// If image path and f/q is not passed as command
// line arguments, quit and display help message
if (argc < 3) {
help();
return -1;
}
// speed-up using multithreads
// void cv::setUseOptimized(bool onoff), Enables or disables the optimized code.
setUseOptimized(true);
setNumThreads(4);
// read image
Mat im = imread(argv[1]);
// resize image
int newHeight = 200;
int newWidth = im.cols*newHeight/im.rows;
resize(im, im, Size(newWidth, newHeight));
// create Selective Search Segmentation Object using default parameters
Ptr<SelectiveSearchSegmentation> ss = createSelectiveSearchSegmentation();
// set input image on which we will run segmentation
ss->setBaseImage(im);
// Switch to fast but low recall Selective Search method
if (argv[2][0] == 'f') {
ss->switchToSelectiveSearchFast();
}
// Switch to high recall but slow Selective Search method
else if (argv[2][0] == 'q') {
ss->switchToSelectiveSearchQuality();
}
// if argument is neither f nor q print help message
else {
help();
return -2;
}
// run selective search segmentation on input image
std::vector<Rect> rects;
ss->process(rects);
std::cout << "Total Number of Region Proposals: " << rects.size() << std::endl;
// number of region proposals to show
int numShowRects = 100;
// increment to increase/decrease total number of reason proposals to be shown
int increment = 50;
while(1) {
// create a copy of original image
Mat imOut = im.clone();
// itereate over all the region proposals
for(int i = 0; i < rects.size(); i++) {
if (i < numShowRects) {
rectangle(imOut, rects[i], Scalar(0, 255, 0));
}
else {
break;
}
}
// show output
imshow("Output", imOut);
// record key press
int k = waitKey();
// m is pressed
if (k == 109) {
// increase total number of rectangles to show by increment
numShowRects += increment;
}
// l is pressed
else if (k == 108 && numShowRects > increment) {
// decrease total number of rectangles to show by increment
numShowRects -= increment;
}
// q is pressed
else if (k == 113) {
break;
}
}
return 0;
}







 本文介绍 Selective Search 算法,一种用于目标检测的任务,在计算机视觉领域有着广泛应用。该算法通过图像分割和区域合并的方式生成候选区域,进而为后续的目标识别提供可能的位置信息。
本文介绍 Selective Search 算法,一种用于目标检测的任务,在计算机视觉领域有着广泛应用。该算法通过图像分割和区域合并的方式生成候选区域,进而为后续的目标识别提供可能的位置信息。
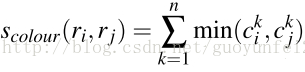

















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








