1 算法来源
- 典型相关分析是数据分析领域中非常常用的统计分析方法,而清华大学的林中林将CCA应用到了SSVEP中,并得到了较好的结果,成为SSVEP识别的经典算法。
- Z. Lin, C. Zhang, W. Wu and X. Gao, “Frequency recognition based on canonical correlation analysis for SSVEP-based BCIs,” in IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, vol. 54, no. 6, pp. 1172-1176, June 2007, doi: 10.1109/TBME.2006.889197.
2 算法原理
-
确定所需频率
-
用对应频率构造sin-cos信号
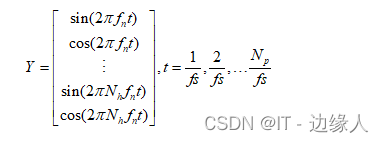
其中fn代表第n个刺激频率,fs表示采样频率。 -
获取一段脑电信号,与2中构造的信号进行相关计算,得到一个相关系数(特征)序列,从序列中选取最大相关系数的索引值对应的频率作为该段脑电信号预测出的结果。
3 算法实现
3.1 测试数据
清华大学脑机接口研究组-Benchmark Dataset
网址:http://bci.med.tsinghua.edu.cn/
3.2 MainForCCA.m
% Main for CCA[1]
%
% Dataset (Sx.mat):
% A 40-target SSVEP dataset recorded from a single subject. The stimuli
% were generated by the joint frequency-phase modulation (JFPM) [3]
% - Stimulus frequencies : 8.0 - 15.8 Hz with an interval of 0.2 Hz
% - Stimulus phases : 0pi, 0.5pi, 1.0pi, and 1.5pi
% - # of channels : 9 (1: Pz, 2: PO5,3: PO3, 4: POz, 5: PO4,
% 6: PO6, 7: O1, 8: Oz, and 9: O2)
% - # of recording blocks : 6
% - Data length of epochs : 5 [seconds]
% - Sampling rate : 250 [Hz]
% - Data format : # channels, # points, # targets, # blocks
%
clear
clc
name =1;
filename1 = ['F:\BenchmarkDataset\S',num2str(name),'.mat','\S',num2str(name),'.mat'];
filename2 = 'F:\BenchmarkDataset\Freq_Phase.mat';
load (filename1)
load (filename2)
%% -----------handle the raw data---------------
fs=250;
% number of targets
NumTarget=40;
% chanels
eeg=data([48 54:58 61:63], :, 1:NumTarget, :);
% latency is 140 ms, dataLength is time window
dataLength=1.5;
eeg1=eeg(:,0.64*250:(0.64+dataLength)*250-1,:,:);
% channels*points*targets*blocks -> channels*points*blocks*targets
eeg1=permute(eeg1,[1,2,4,3]);
eeg2=[];
for i=1:NumTarget
% (channels,points,blocks,targets) -> (channels,points,trials)
eeg2=cat(3,eeg2,eeg1(:,:,:,i));
end
[Numchannel, ~, NumTrial] = size(eeg2);
%% ----------design bandpass filter from 8Hz to 90Hz--------------
Wp = [8/fs*2, 90/fs*2];
Ws = [4/fs*2, 100/fs*2];
% [N, Wn]=cheb1ord(Wp, Ws, 3, 40);
[N, Wn]=cheb1ord(Wp, Ws, 3, 60);
[b, a] = cheby1(N, 0.5, Wn);
for i=1:NumTrial
for j=1:Numchannel
eeg3(j,:,i)=filtfilt(b,a,eeg2(j,:,i));
end
end
% labels assignment
labels=[];
freqs = freqs(1:NumTarget);
for i=1:NumTarget
labels=cat(2,labels,ones(1,6)*freqs(i));
end
%% --------------CCA-------------------
tic
for i = 1:NumTrial
[outputlabels(i)] = CCA(eeg3(:,:,i),freqs);
%outputlabels(i) = MSI(eeg3(:,:,i),freqs);
end
t=toc;
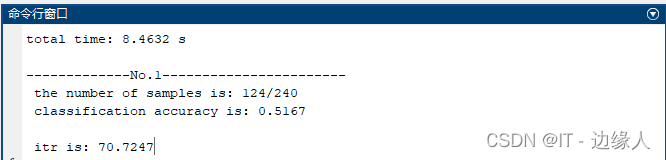
disp(['total time: ',num2str(t),' s']);
TrueNum = sum((outputlabels-labels)==0);
ACC(name) = TrueNum/length(labels);
ITR(name) = itr(40,ACC(name),dataLength);
%% --------------data visualization------------
%fprintf('\n-----------------------------------------')
fprintf('\n-------------No.%d-----------------------',name)
fprintf('\n the number of samples is: %d/%d',TrueNum, NumTrial)
fprintf('\n classification accuracy is: %.4f\n',ACC(name))
fprintf('\n itr is: %.4f\n',ITR(name))
3.3 itr.m
function [ itr ] = itr(n, p, t)
% Calculate information transfer rate (ITR) for brain-computer interface
% (BCI) [2]
% function [ itr ] = itr(n, p, t)
%
% Input:
% n : # of targets
% p : Target identification accuracy (0 <= p <= 1)
% t : Averaged time for a selection [s]
%
% Output:
% itr : Information transfer rate [bits/min]
%
% Reference:
% [1] M. Cheng, X. Gao, S. Gao, and D. Xu,
% "Design and Implementation of a Brain-Computer Interface With High
% Transfer Rates",
% IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 49, 1181-1186, 2002.
%
% Masaki Nakanishi, 22-Dec-2017
% Swartz Center for Computational Neuroscience, Institute for Neural
% Computation, University of California San Diego
% E-mail: masaki@sccn.ucsd.edu
if nargin < 3
error('stats:itr:LackOfInput', 'Not enough input arguments.'); end
if p < 0 || 1 < p
error('stats:itr:BadInputValue',...
'Accuracy need to be between 0 and 1.');
elseif p < 1/n
warning('stats:itr:BadInputValue',...
'The ITR might be incorrect because the accuracy < chance level.');
itr = 0;
elseif p == 1
itr = log2(n)*60/t;
else
itr = (log2(n) + p*log2(p) + (1-p)*log2((1-p)/(n-1)))*60/t;
end
3.4 CCA.m
function [output1,output2] = CCA(EEG,freqs)
% where EEG: channels*point
% frequency is the stimulus frequency,used to construct reference signal
% output1: recognized frequency
% output2: correlation coefficient for each frequency
X=EEG;
N = 5;
fs=250;
[~,T]= size(EEG);
t=1/fs:1/fs:T/fs;
f=freqs;
for k1=1:length(f)
%compute reference signal
Y=[];
for k2=1:N %number of harmonic
%Y=cat(1,Y,cat(1,0.8*sin(2*pi*f(k1)*k2*t),0.8*cos(2*pi*f(k1)*k2*t)));
Y=cat(1,Y,cat(1,sin(2*pi*f(k1)*k2*t),cos(2*pi*f(k1)*k2*t)));
end
%compute covariance matrix
meanx=mean(X,2);%channels*1
meany=mean(Y,2);%2N*1
s11=0;s22=0;s12=0;s21=0;
for i1=1:T
s11=s11+(X(:,i1)-meanx)*(X(:,i1)-meanx)';
s22=s22+(Y(:,i1)-meany)*(Y(:,i1)-meany)';
s12=s12+(X(:,i1)-meanx)*(Y(:,i1)-meany)';
s21=s21+(Y(:,i1)-meany)*(X(:,i1)-meanx)';
end
s11=s11/(T-1);
s22=s22/(T-1);
s12=s12/(T-1);
s21=s21/(T-1);
%compute eigvalue and eigvector
%namely correlation coefficient and canonical covariance
[ta,eigvaluea]=eig(inv(s11)*s12*inv(s22)*s21);
[tb,eigvalueb]=eig(inv(s22)*s21*inv(s11)*s12);
[evaluea, esorta] = sort(-diag(eigvaluea));
evaluea=-evaluea;
[evalueb, esortb] = sort(-diag(eigvalueb));
evalueb=-evalueb;
%correlation coefficient
output2(k1)=max(sqrt(evaluea));
%use canonical covariance to reduce dimension
%didn't use
U=0;V=0;
for i=1:length(X(:,1))
U(i,1:T)=ta(:,esorta(i))'*(X-meanx*ones(1,size(X,2)));
end
for i=1:length(Y(:,1))
V(i,1:T)=tb(:,esortb(i))'*(Y-meany*ones(1,size(Y,2)));
end
end
%output
[value,index]=max(output2);
output1 = f(index);
end
4 算法测试























 1064
1064











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










