一、比较字符串strcmp
函数原型:
int strcmp(const char *s1,const char*s2);
返回值:
负数:s1<s2
0:s1=s2
正数:s1>s2
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char test[] = "huang\0hah";
printf("%s\n", test);//huang
char command[16];
printf("Enter a Command:");
scanf("%s", command);
if (strcmp(command, "Quit") == 0)
{
printf("The command was Quit\n");//从键盘输入Quit\0hah时,不相等
}
else
{
printf("The command was not Quit\n");
}
printf("%d\n", strcmp("Quit", "Quit\0hah"));//输出0,表示相等。
}
字符串比较时不正确的写法:
char command[16];
printf("Enter a Command:\n");
scanf("%s", command);
if (command == "Quit")
{
//...
}这样会得到假,因为这样比较的是command的地址和字符串字面量的地址。
二、复制字符串strcpy
函数原型声明
char* strcpy(char *s1,const char *s2);
将s2所指字符串拷贝至s1所指向的字符串,拷贝的时候,连通'\0'一起拷贝过去。返回s1字符串的起始地址。
char a[10] = "huangyang";
char b[3] = "lc";
strcpy(a, b);
printf("%s\n", a);//lc字符串复制的一个应用:
有一类常见的应用程序会读入一系列字符串,挨个存入占据内存最少的数组。要实现这一点,可以创建一个长度足以容纳用户可能输入的最长字符串的数组,并且把字符串读入这个数组。有了读入的字符串,我们就能分配合适的内存。基本的方法是这样的:
(1)用一个很长的char数组读入字符串
(2)用malloc分配恰好容纳字符串的适量内存
(3)用strcpy把字符串复制到动态分配的内存中。
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char name[30];
char *names[200];
int count = 0;
for (count = 0; count < 200; count++)
{
printf("please input the %d value\n", count);
scanf("%s", name);
names[count] = (char *)malloc(strlen(name) + 1);
strcpy(names[count], name);
count++;
}
return 0;
}
插入:两个指针可以同时指向同一个字符串
char *pageHeaders[300];
pageHeaders[12] = "Amorphous Compounds";
pageHeaders[13] = pageHeaders[12];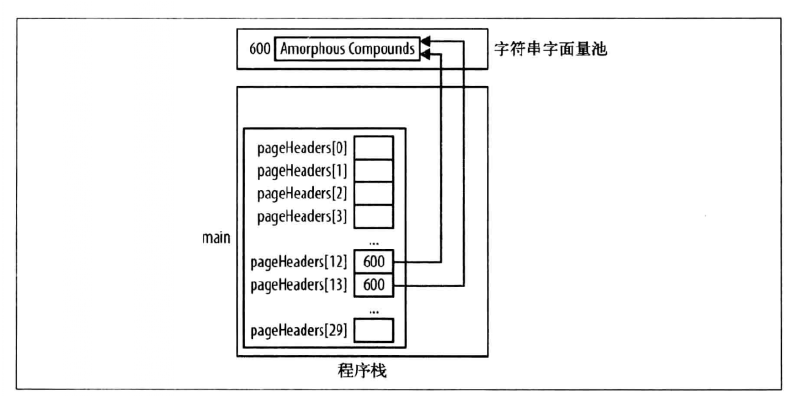
三、拼接字符串strcat
char *strcat(char *s1,const char *s2);
把第二个字符串拼接到第一个字符串的结尾,第一个字符串必须足够长,能够容纳拼接后的结果。函数的返回值的地址跟第一个参数的地址一样。
拼接的时候,把第一个字符串的\0覆盖,第二个字符串的\0复制过来。
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char *error = "ERROR: ";
char *errorMessage = "Not enough memory";
char *buffer = (char *)malloc(strlen(error) + strlen(errorMessage) + 1);
strcpy(buffer, error);
strcpy(buffer, errorMessage);
printf("%s\n", buffer);
printf("%s\n", error);
printf("%s\n", errorMessage);
return 0;
}
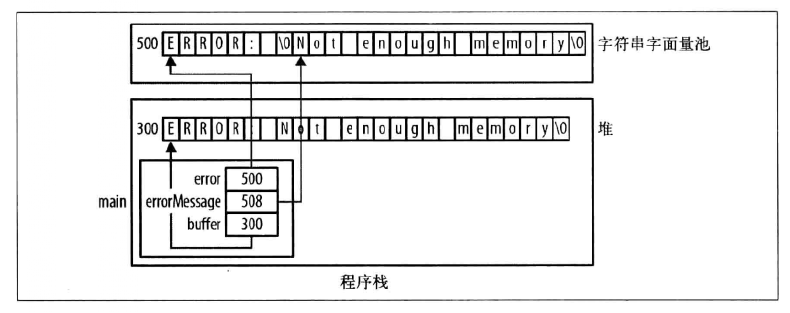
不正确的字符串连接1
char *error = "ERROR: ";
char *errorMessage = "Not enough memory";
strcat(error, errorMessage);
printf("%s\n", error);
printf("%s\n", errorMessage);不正确的字符串连接2
char error[] = "ERROR: ";
char errorMessage[] = "Not enough memory";
strcat(error, errorMessage);//报错
//error = strcat(error, errorMessage);错误,error为指针常量四、计算字符串长度
#include<stdio.h>
int stringLength(char *string)
{
int length = 0;
while (*(string++))//注意这里写法
{
length++;
}
return length;
}
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", stringLength("Hello"));//5
return 0;
}






















 1173
1173











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








