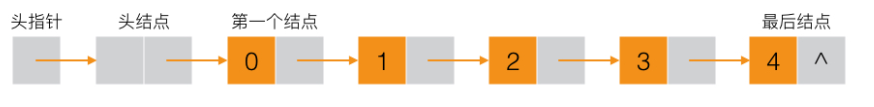
单链表算是一种很基础的数据结构了,下图是单链表的一般图示。
上学那会儿没怎么实际应用,对其功能和实现都是一知半解。
下面是以java来实现单链表的一些基本操作。
首先是结点类,每个结点包括数据域和指针域,数据域存放数据,指针域指向下个结点,也就是存放下个结点的地址。
/**
* 结点类
*/
class Node {
private String data; // 数据域
private Node next; // 指针域,指向下个结点
public Node(String data, Node next) {
super();
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(String data) {
super();
this.data = data;
}
public String getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(String data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
public void destroy() {
this.data = null;
this.next = null;
}
}接着是单链表类
/**
* 单链表类
*/
class List {
private Node head; // 头结点
public int length; // 长度
public List() {
init();
}
private void init() {
head = new Node("head", null);
}
public Node getHead() {
return head;
}
public void setHead(Node head) {
this.head = head;
}
/**
* 头插法---插入结点
*
* @param node
*/
public boolean insertToHead(Node node) {
Node n = head.getNext(); // 得到第一个结点
if (n == null) { // 如果是空的话,直接插入头结点之后
head.setNext(node);
} else {
node.setNext(n);
head.setNext(node);
}
length++;
return true;
}
/**
* 尾插法---插入结点
* @param node
* @return
*/
public boolean insertToTail(Node node) {
Node n = head.getNext();
if(n == null) {
insertToHead(node);
return true;
}
while(true) {
if(n.getNext() == null){
break;
}
n = n.getNext();
}
// insert
n.setNext(node);
length++;
return true;
}
/**
* 插入结点到指定位置(从0开始)
*
* @param index
*/
public boolean insertToIndex(int index, Node p) {
if (index < 0 || index > length) {
System.out.println("超出范围");
return false;
}
if (index == 0) { // 插入到头结点之后
insertToHead(p);
} else if(index ==length) {
insertToTail(p);
} else {
Node node = head;
for (int i = -1; i < length - 1; i++) { // -1 to 3
if (i + 1 == index) {
p.setNext(node.getNext());
node.setNext(p);
length++;
break;
}
node = node.getNext();
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* 结点编号是否在范围之内 (从0开始)
*
* @param index
* @return
*/
public boolean findNode(int index) {
if (index >= length || index < 0) {
System.out.println("结点超出范围");
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 删除指定编号的结点(从0开始)
*
* @param index
* @return
*/
public boolean deleteNode(int index) {
if (!findNode(index)) {
return false;
}
Node node = head;
// i从-1 到 length-2,判断其后的结点编号是否是待删除的结点
for (int i = -1; i < length - 1; i++) {
if (i + 1 == index) {
// 如果其后的结点正是要删除的,赋值给p
Node p = node.getNext();
// 跳过此结点p
node.setNext(p.getNext());
// 销毁结点p
p.destroy();
}
node = node.getNext();
}
length--;
return true;
}
/**
* 根据数据域删除结点
*
* @param data
* @return
*/
public boolean deleteNode(String data) {
boolean isExist = false;
Node n = head;
while (n != null) {
if (n.getNext() != null && data.equals(n.getNext().getData())) {
isExist = true;
//
n.setNext(n.getNext().getNext());
length--;
break;
}
n = n.getNext();
}
System.out.print(isExist ? "" : String
.format("数据为\"%s\"的结点不存在\n", data));
return isExist;
}
/**
* 输出整个单链表
*/
public void printList() {
Node n = head;
while (n != null) {
System.out.print(n.getData());
n = n.getNext();
System.out.print(n == null ? "" : "-->");
}
System.out.println("\n长度为:" + length);
}
}代码中主要实现了单链表的插入(头插法,尾插法和指定位置插入),删除(根据数据和位置的删除)。
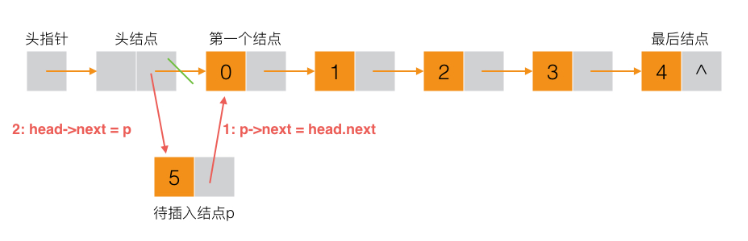
下面是头插法的算法图:
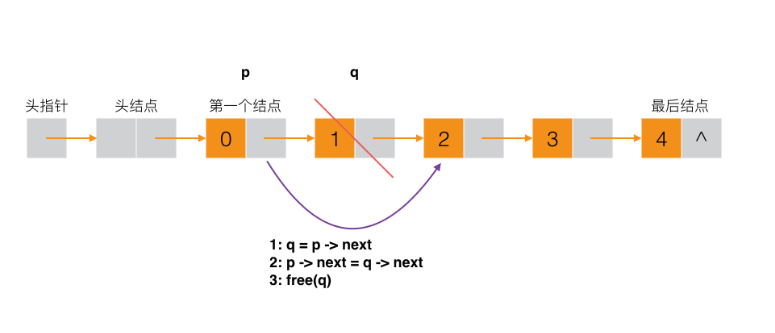
接下来是删除的图:
最后,附上测试类
/**
* 测试类
*/
public class SinglyLinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new List();
// 头插法插入6个结点
list.insertToHead(new Node("1"));
list.insertToHead(new Node("2"));
list.insertToHead(new Node("3"));
list.insertToHead(new Node("4"));
list.insertToHead(new Node("5"));
list.insertToHead(new Node("6"));
// 输出整个单链表
list.printList();
System.out.println("****************************");
// 头插法插入"99"
System.out.println("头插法插入99");
list.insertToHead(new Node("99"));
list.printList();
System.out.println("****************************");
// 尾插法插入"77"
System.out.println("尾插法插入77");
list.insertToTail(new Node("77"));
list.printList();
System.out.println("****************************");
// 删除编号3的结点,从0开始
System.out.println("删除第三个结点");
list.deleteNode(3);
// 输出整个单链表
list.printList();
System.out.println("****************************");
System.out.println("删除数据为\"111\"的结点");
list.deleteNode("111");
list.printList();
System.out.println("****************************");
// 在目标索引位置插入结点,从0开始
System.out.println("在位置3插入数据为\"88\"的结点");
list.insertToIndex(3, new Node("88"));
// 输出整个单链表
list.printList();
}最后是测试结果
head-->6-->5-->4-->3-->2-->1
长度为:6
****************************
头插法插入99
head-->99-->6-->5-->4-->3-->2-->1
长度为:7
****************************
尾插法插入77
head-->99-->6-->5-->4-->3-->2-->1-->77
长度为:8
****************************
删除第三个结点
head-->99-->6-->5-->3-->2-->1-->77
长度为:7
****************************
删除数据为"111"的结点
数据为"111"的结点不存在
head-->99-->6-->5-->3-->2-->1-->77
长度为:7
****************************
在位置3插入数据为"88"的结点
head-->99-->6-->5-->88-->3-->2-->1-->77
长度为:8





















 717
717

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








