1指针常量
int*constptr;
指针常量,即不可以将ptr修改为指向内存中另一处的地址,但可以用它来改变它所指向的地址处的数据内容。
//const.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
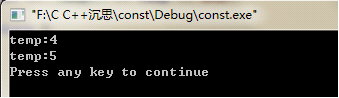
int temp = 4;
cout << temp << endl;
//ptr被const修饰 定义时必须初始化
int *const ptr = &temp;
*ptr = 5;
cout << temp << endl;
return 0;
}程序运行截图:
2常量指针
constint*ptr;(常量指针的另一种写法intconst*ptr)
常量指针,即可以将ptr修改为指向内存中另一处的地址,但不可以用它来改变它所指向的地址处的数据内容。
//const.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int temp1 = 4;
int temp2 = 5;
const int *ptr;
ptr = &temp1;
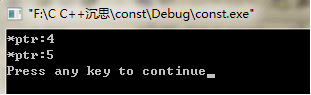
cout << "*ptr:" << *ptr << endl;
ptr = &temp2;
cout << "*ptr:" << *ptr << endl;
return 0;
}程序运行截图:
3指向const常量的const指针
constint*constptr;(另一种写法intconst*constptr)
指向const常量的const指针,即ptr所指向的内存地址和所指向的地址处的数据内容都不能被修改
PS:const离谁比较近,则谁的值不能被改变
二const与函数
1const修饰函数的参数
const使该参数在函数中不能被改变
voidcopy(char*strDes,constchar*strsrc);
即strsrc指针所指向的值在copy函数中不能被改变,如果意外的改动该指针,编译器会报错
注意:
不用将“值传递”的方式(voidcopy(intx,iny))加const修饰,因为函数会自动产生临时变量用于复制该参数,参数本来就不需要保护。
2const修饰函数的返回值
constint*add(intx,inty);
即add函数的返回值(即指针)的内容不能被修改,该返回值只能被赋值给加const修饰的同类型指针
constint*p=add(3,5);
注意:
如果函数返回值是“值传递方式”(intadd(intx,inty)),由于函数会把返回值复制到外部临时的存储单元中,加const修饰没有意义。
3const成员函数
任何不会修改类的数据成员(即函数中的变量)的函数都应该声明为const类型。在编写const成员函数时,如果不小心修改了数据成员,或者调用了其他非const成员函数,编译器会报错,这种做法将大大提高程序的健壮性。
//test.cpp
class test
{
public:
void set(int);
//const成员函数
int get()const;
private:
int value;
};
int test::get()const
{
//编译错误 修改数据成员value
++value;
//编译错误 调用了非const函数
set(5);
return value;
}



















 165
165

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








