1.序言
牵引车-半挂车的车辆结构与普通的车辆相比增加了一个半挂车,它们之间通过鞍座相连接,为了分析半挂牵引车运动过程中的位姿和状态,本文将基于车辆的机械结构建立对应的运动学模型,该模型基于以下假设:
- 车辆行驶过程中,道路平坦且无凸凹;
- 车辆低速行驶,且运行过程中车身无侧倾和俯仰运动;
- 车辆行驶过程中,轮胎无形变,无侧向滑动,且无侧向力;
- 牵引车和半挂车均满足阿克曼转向几何原理;
- 牵引车与半挂车不会发现折叠。
2. 运动学模型及推导
牵引车带挂前向运动是开环稳定的,其对应的自行车模型如下所示:
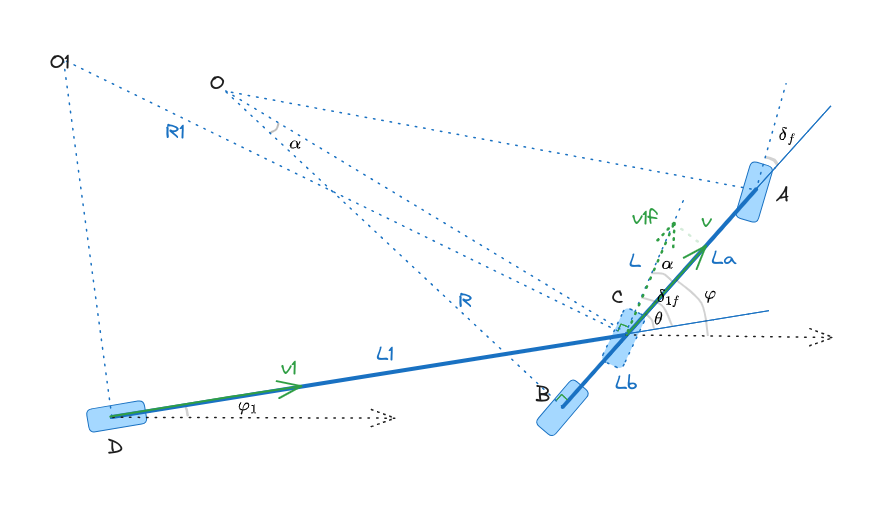
其中:
- A A A:牵引车的前轮中心点,其坐标为 ( x f , y f ) (x_f,y_f) (xf,yf);
- B B B:牵引车后轮中心点,其坐标为 ( x r , y r ) (x_r,y_r) (xr,yr);
- C C C:牵引车与半挂车的铰接点,也是半挂车的等效前轮中心点,其坐标为 ( x 1 f , y 1 f ) (x_{1f},y_{1f}) (x1f,y1f);
- D D D:半挂车后轮中心点,其坐标为 ( x 1 r , y 1 r ) (x_{1r},y_{1r}) (x1r,y1r);
- L L L:牵引车的轴距;
- L a L_a La:铰接点 C C C到 A A A的距离;
- L b L_b Lb:铰接点 C C C到 B B B的距离;
- L 1 L1 L1:半挂车的轴距;
- δ f \delta_f δf:牵引车前轮转角;
- δ 1 f \delta_{1f} δ1f:半挂车虚拟前轮转角;
- φ \varphi φ:牵引车航向角;
- φ 1 \varphi_1 φ1:半挂车的航向角;
- θ \theta θ:铰接角,即牵引车与半挂车的航向的夹角;
- v v v:牵引车的纵向速度;
- v 1 v_1 v1:半挂车的纵向速度;
- v 1 f v_{1f} v1f:挂车虚拟前轮速度;
- α \alpha α:挂车虚拟前轮与牵引车航向的夹角。
结合我们前面车辆运动学方程推导和代码实现的推导,可得牵引车的运动学模型如下
{
x
r
˙
=
v
cos
φ
y
r
˙
=
v
sin
φ
φ
˙
=
v
tan
δ
f
L
(1)
\begin{cases} \dot{x_r}=v\cos{\varphi}\\ \dot{y_r}=v\sin{\varphi}\\ \dot{\varphi}=\frac{v\tan\delta_f}{L} \end{cases}\tag{1}
⎩
⎨
⎧xr˙=vcosφyr˙=vsinφφ˙=Lvtanδf(1)
对于半挂车我们也把其等效为自行车模型,则其也有
{
x
1
r
˙
=
v
1
cos
φ
1
y
1
r
˙
=
v
1
sin
φ
1
φ
1
˙
=
v
1
tan
δ
1
f
L
1
(2)
\begin{cases} \dot{x_{1r}}=v_1\cos{\varphi_1}\\ \dot{y_{1r}}=v_1\sin{\varphi_1}\\ \dot{\varphi_1}=\frac{v_1\tan\delta_{1f}}{L_1} \end{cases}\tag{2}
⎩
⎨
⎧x1r˙=v1cosφ1y1r˙=v1sinφ1φ1˙=L1v1tanδ1f(2)
根据图中几何关系,可得挂车虚拟前轮速度
v
1
f
v_{1f}
v1f与纵向速度
v
1
v_1
v1的关系有
v
1
=
v
1
f
cos
δ
1
f
=
v
1
f
cos
(
α
+
θ
)
(3)
v_1=v_{1f}\cos\delta_{1f}=v_{1f}\cos(\alpha+\theta)\tag{3}
v1=v1fcosδ1f=v1fcos(α+θ)(3)
其中
θ
=
φ
−
φ
1
\theta=\varphi-\varphi_1
θ=φ−φ1。
由于牵引车与挂车是通过挢接点进行动力牵引的,所以半挂车虚拟前轮的速度与牵引车的纵向速度存在以下等式关系:
v
1
f
=
v
cos
α
(4)
v_{1f}=\frac{v}{\cos\alpha} \tag{4}
v1f=cosαv(4)
由公式3、4可得
v
1
=
v
1
f
cos
δ
1
f
=
v
cos
(
α
+
θ
)
cos
α
(5)
v_1=v_{1f}\cos\delta_{1f}=\frac{v\cos(\alpha+\theta)}{\cos\alpha}\tag{5}
v1=v1fcosδ1f=cosαvcos(α+θ)(5)
结合上图和阿克曼转向原理可得
R
=
L
tan
δ
f
R
1
=
L
1
tan
δ
1
f
(6)
R=\frac{L}{\tan\delta_f}\\ R_1=\frac{L_1}{\tan\delta_{1f}} \tag{6}
R=tanδfLR1=tanδ1fL1(6)
注:具体推导可参考历史文章:车辆运动学方程推导和代码实现
由图中的几何关系可得
tan
α
=
L
b
R
=
L
b
tan
δ
f
L
(7)
\tan\alpha=\frac{L_b}{R}=\frac{L_b\tan\delta_f}{L}\tag{7}
tanα=RLb=LLbtanδf(7)
由5、7可得
v
1
=
v
cos
(
α
+
θ
)
cos
α
=
v
(
cos
θ
−
tan
α
sin
θ
)
=
v
(
cos
θ
−
L
b
tan
δ
f
L
sin
θ
)
(8)
v_1=\frac{v\cos(\alpha+\theta)}{\cos\alpha} =v(\cos\theta-\tan\alpha\sin\theta) =v(\cos\theta-\frac{L_b\tan\delta_f}{L}\sin\theta) \tag{8}
v1=cosαvcos(α+θ)=v(cosθ−tanαsinθ)=v(cosθ−LLbtanδfsinθ)(8)
由2、7和8可得
φ
1
˙
=
v
1
tan
δ
1
f
L
1
=
v
(
cos
θ
−
L
b
tan
δ
f
L
sin
θ
)
L
1
tan
δ
1
f
=
v
(
cos
θ
−
L
b
tan
δ
f
L
sin
θ
)
L
1
tan
φ
+
tan
θ
1
−
tan
φ
tan
θ
=
v
(
cos
θ
−
L
b
tan
δ
f
L
sin
θ
)
L
1
L
b
tan
δ
f
L
+
tan
θ
1
−
L
b
tan
δ
f
L
tan
θ
=
v
(
cos
θ
−
L
b
tan
δ
f
L
sin
θ
)
L
1
L
b
tan
δ
f
+
L
tan
θ
L
−
L
b
tan
δ
f
tan
θ
=
v
L
1
(
sin
θ
+
L
b
tan
δ
f
cos
θ
L
)
(9)
\begin{equation} \begin{split} \dot{\varphi_1} &=\frac{v_1\tan\delta_{1f}}{L_1}\\ &=\frac{v(\cos\theta-\frac{L_b\tan\delta_f}{L}\sin\theta)}{L_1}\tan\delta_{1f}\\ &=\frac{v(\cos\theta-\frac{L_b\tan\delta_f}{L}\sin\theta)}{L_1}\frac{\tan\varphi+\tan\theta}{1-\tan\varphi\tan\theta}\\ &=\frac{v(\cos\theta-\frac{L_b\tan\delta_f}{L}\sin\theta)}{L_1} \frac{\frac{L_b\tan\delta_f}{L}+\tan\theta}{1-\frac{L_b\tan\delta_f}{L}\tan\theta}\\ &=\frac{v(\cos\theta-\frac{L_b\tan\delta_f}{L}\sin\theta)}{L_1} \frac{L_b\tan\delta_f+L\tan\theta}{L-L_b\tan\delta_f\tan\theta}\\ &=\frac{v}{L_1}(\sin\theta+\frac{L_b\tan\delta_f\cos\theta}{L})\\ \end{split} \end{equation} \tag{9}
φ1˙=L1v1tanδ1f=L1v(cosθ−LLbtanδfsinθ)tanδ1f=L1v(cosθ−LLbtanδfsinθ)1−tanφtanθtanφ+tanθ=L1v(cosθ−LLbtanδfsinθ)1−LLbtanδftanθLLbtanδf+tanθ=L1v(cosθ−LLbtanδfsinθ)L−LbtanδftanθLbtanδf+Ltanθ=L1v(sinθ+LLbtanδfcosθ)(9)
结合上图几何关系,可得挂车的后轴中心坐标为
{
x
1
r
=
x
r
+
L
b
cos
φ
−
L
1
cos
φ
1
y
1
r
=
y
r
+
L
b
sin
φ
−
L
1
sin
φ
1
(10)
\begin{cases} x_{1r}=x_r+L_b\cos\varphi-L_1\cos\varphi_1\\ y_{1r}=y_r+L_b\sin\varphi-L_1\sin\varphi_1\\ \end{cases} \tag{10}
{x1r=xr+Lbcosφ−L1cosφ1y1r=yr+Lbsinφ−L1sinφ1(10)
综上,带挂牵引车的运动学模型方程如下所示:
{ x r ˙ = v cos φ y r ˙ = v sin φ φ ˙ = v tan δ f L φ 1 ˙ = v L 1 ( sin θ + L b tan δ f cos θ L ) θ = φ − φ 1 (11) \begin{cases} \dot{x_r}=v\cos{\varphi}\\ \dot{y_r}=v\sin{\varphi}\\ \dot{\varphi}=\frac{v\tan\delta_f}{L}\\ \dot{\varphi_1}=\frac{v}{L_1}(\sin\theta+\frac{L_b\tan\delta_f\cos\theta}{L})\\ \theta=\varphi-\varphi_1\\ \end{cases} \tag{11} ⎩ ⎨ ⎧xr˙=vcosφyr˙=vsinφφ˙=Lvtanδfφ1˙=L1v(sinθ+LLbtanδfcosθ)θ=φ−φ1(11)
3. 代码实现
semi_truck_fwd_model.py
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import imageio.v2 as imageio
class VehicleParamInfo:
# 牵引车(车头)
L = 3.0 # 轴距
W = 2.0 # 宽度
LF = 3.8 # 后轴中心到车头距离
LB = 0.8 # 后轴中心到车尾距离
MAX_STEER = 0.6 # 最大前轮转角
TR = 0.5 # 轮子半径
TW = 0.5 # 轮子宽度
WD = W # 轮距
LENGTH = LB + LF # 车辆长度
La = 2.7 # 铰接点到牵引车前轴中心的距离
Lb = 0.3 # 铰接点到牵引车后轴中心的距离
# 挂车
L1 = 7 # 挂车轴距
LF1 = 8.0 # 挂车后轴中心到车头距离
LB1 = 1.0 # 挂车后轴中心到车尾距离
def normalize_angle(angle):
a = math.fmod(angle + np.pi, 2 * np.pi)
if a < 0.0:
a += (2.0 * np.pi)
return a - np.pi
class Vehicle:
def __init__(self, x=0.0, y=0.0, yaw=0.0, v=0.0, dt=0.1, vehicle_param_info=VehicleParamInfo):
# 牵引车
self.steer = 0
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.yaw = yaw
self.v = v
self.dt = dt
self.vehicle_param_info = vehicle_param_info
self.x_front = self.x + self.vehicle_param_info.L * math.cos(self.yaw)
self.y_front = self.y + self.vehicle_param_info.L * math.sin(self.yaw)
# 挂车
self.yaw1 = yaw
self.x_front1 = self.x + self.vehicle_param_info.Lb * math.cos(self.yaw)
self.y_front1 = self.y + self.vehicle_param_info.Lb * math.sin(self.yaw)
self.x1 = self.x_front1 - self.vehicle_param_info.L1 * math.cos(self.yaw1)
self.y1 = self.y_front1 - self.vehicle_param_info.L1 * math.sin(self.yaw1)
def update(self, a, delta, max_steer=None):
if max_steer is None:
max_steer = self.vehicle_param_info.MAX_STEER
delta = np.clip(delta, -max_steer, max_steer)
self.steer = delta
hitchAngle = normalize_angle(self.yaw-self.yaw1)
self.x += self.v * math.cos(self.yaw) * self.dt
self.y += self.v * math.sin(self.yaw) * self.dt
self.x_front = self.x + self.vehicle_param_info.L * math.cos(self.yaw)
self.y_front = self.y + self.vehicle_param_info.L * math.sin(self.yaw)
self.x_front1 = self.x + self.vehicle_param_info.Lb * math.cos(self.yaw)
self.y_front1 = self.y + self.vehicle_param_info.Lb * math.sin(self.yaw)
self.x1 = self.x_front1 - self.vehicle_param_info.L1 * math.cos(self.yaw1)
self.y1 = self.y_front1 - self.vehicle_param_info.L1 * math.sin(self.yaw1)
self.yaw += self.v / self.vehicle_param_info.L * math.tan(delta) * self.dt
self.yaw = normalize_angle(self.yaw)
self.v += a * self.dt
self.yaw1 += self.v / self.vehicle_param_info.L1 * (
math.sin(hitchAngle) + self.vehicle_param_info.Lb * math.tan(self.steer) * math.cos(
hitchAngle) / self.vehicle_param_info.L) * self.dt
self.yaw1 = normalize_angle(self.yaw1)
def draw_vehicle_trailer(x, y, yaw,x1, y1, yaw1, steer, ax, vehicle_param_info=VehicleParamInfo, color='black'):
vehicle_outline = np.array([
[-vehicle_param_info.LB, vehicle_param_info.LF, vehicle_param_info.LF, -vehicle_param_info.LB, -vehicle_param_info.LB],
[vehicle_param_info.W / 2, vehicle_param_info.W / 2, -vehicle_param_info.W / 2, -vehicle_param_info.W / 2, vehicle_param_info.W / 2]
])
vehicle_outline1 = np.array([
[-vehicle_param_info.LB1, vehicle_param_info.LF1, vehicle_param_info.LF1, -vehicle_param_info.LB1,
-vehicle_param_info.LB1],
[vehicle_param_info.W / 2, vehicle_param_info.W / 2, -vehicle_param_info.W / 2, -vehicle_param_info.W / 2,
vehicle_param_info.W / 2]
])
wheel = np.array([
[-vehicle_param_info.TR, vehicle_param_info.TR, vehicle_param_info.TR, -vehicle_param_info.TR, -vehicle_param_info.TR],
[vehicle_param_info.TW / 2, vehicle_param_info.TW / 2, -vehicle_param_info.TW / 2, -vehicle_param_info.TW / 2, vehicle_param_info.TW / 2]
])
rr_wheel = wheel.copy() # 右后轮
rl_wheel = wheel.copy() # 左后轮
fr_wheel = wheel.copy() # 右前轮
fl_wheel = wheel.copy() # 左前轮
rr_wheel1 = wheel.copy() # 挂车右后轮
rl_wheel1 = wheel.copy() # 挂车左后轮
rr_wheel[1, :] += vehicle_param_info.WD / 2
rl_wheel[1, :] -= vehicle_param_info.WD / 2
rr_wheel1[1, :] += vehicle_param_info.WD / 2
rl_wheel1[1, :] -= vehicle_param_info.WD / 2
# 前轮旋转
rot1 = np.array([
[np.cos(steer), -np.sin(steer)],
[np.sin(steer), np.cos(steer)]
])
# yaw旋转矩阵
rot2 = np.array([
[np.cos(yaw), -np.sin(yaw)],
[np.sin(yaw), np.cos(yaw)]
])
# yaw1旋转矩阵
rot3 = np.array([
[np.cos(yaw1), -np.sin(yaw1)],
[np.sin(yaw1), np.cos(yaw1)]
])
fr_wheel = np.dot(rot1, fr_wheel)
fl_wheel = np.dot(rot1, fl_wheel)
fr_wheel += np.array([[vehicle_param_info.L], [-vehicle_param_info.WD / 2]])
fl_wheel += np.array([[vehicle_param_info.L], [vehicle_param_info.WD / 2]])
fr_wheel = np.dot(rot2, fr_wheel)
fr_wheel[0, :] += x
fr_wheel[1, :] += y
fl_wheel = np.dot(rot2, fl_wheel)
fl_wheel[0, :] += x
fl_wheel[1, :] += y
rr_wheel = np.dot(rot2, rr_wheel)
rr_wheel[0, :] += x
rr_wheel[1, :] += y
rl_wheel = np.dot(rot2, rl_wheel)
rl_wheel[0, :] += x
rl_wheel[1, :] += y
vehicle_outline = np.dot(rot2, vehicle_outline)
vehicle_outline[0, :] += x
vehicle_outline[1, :] += y
rr_wheel1 = np.dot(rot3, rr_wheel1)
rr_wheel1[0, :] += x1
rr_wheel1[1, :] += y1
rl_wheel1 = np.dot(rot3, rl_wheel1)
rl_wheel1[0, :] += x1
rl_wheel1[1, :] += y1
vehicle_outline1 = np.dot(rot3, vehicle_outline1)
vehicle_outline1[0, :] += x1
vehicle_outline1[1, :] += y1
ax.plot(fr_wheel[0, :], fr_wheel[1, :], color)
ax.plot(rr_wheel[0, :], rr_wheel[1, :], color)
ax.plot(fl_wheel[0, :], fl_wheel[1, :], color)
ax.plot(rl_wheel[0, :], rl_wheel[1, :], color)
ax.plot(rr_wheel1[0, :], rr_wheel1[1, :], color)
ax.plot(rl_wheel1[0, :], rl_wheel1[1, :], color)
ax.plot(vehicle_outline[0, :], vehicle_outline[1, :], color)
ax.plot(vehicle_outline1[0, :], vehicle_outline1[1, :], color)
if __name__ == "__main__":
vehicle = Vehicle(x=0.0, y=0.0, yaw=np.pi/3, v=0.0, dt=0.1)
vehicle.v = 1
trajectory_x = []
trajectory_y = []
trailer_trajectory_x = []
trailer_trajectory_y = []
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
image_list = [] # 存储图片
for i in range(1120):
ax.cla()
ax.set_aspect('equal', adjustable='box')
delta = -np.pi / 10.0 if i > 560 else np.pi / 10.0
vehicle.update(0, delta)
draw_vehicle_trailer(vehicle.x, vehicle.y, vehicle.yaw, vehicle.x1, vehicle.y1, vehicle.yaw1, vehicle.steer, ax)
trajectory_x.append(vehicle.x)
trajectory_y.append(vehicle.y)
trailer_trajectory_x.append(vehicle.x1)
trailer_trajectory_y.append(vehicle.y1)
ax.plot(trajectory_x, trajectory_y, 'blue')
ax.plot(trailer_trajectory_x, trailer_trajectory_y, 'green')
ax.set_xlim(-22, 20)
ax.set_ylim(-20, 18)
plt.pause(0.001)
# plt.savefig("temp.png")
# i += 1
# if (i % 30) == 0:
# image_list.append(imageio.imread("temp.png"))
#
# imageio.mimsave("display.gif", image_list, duration=0.2)
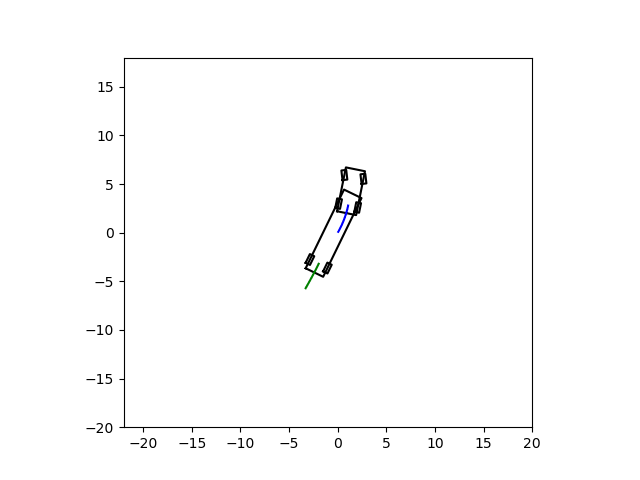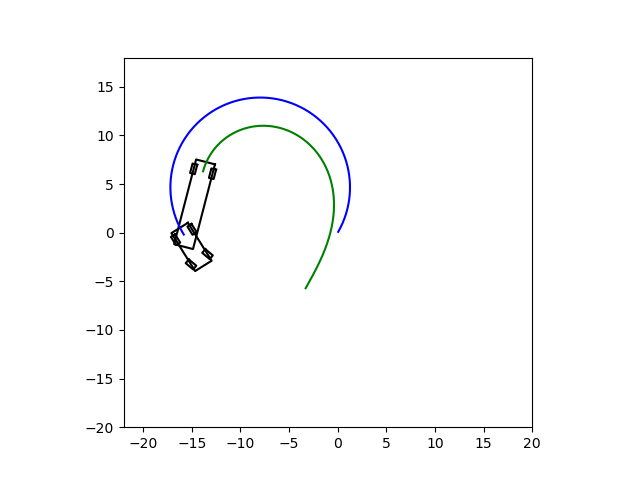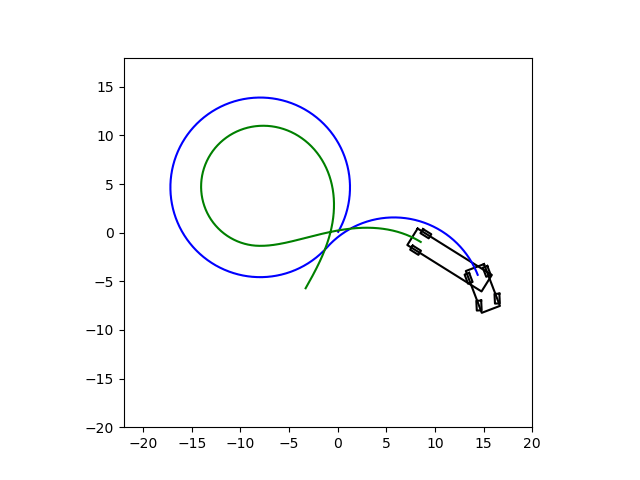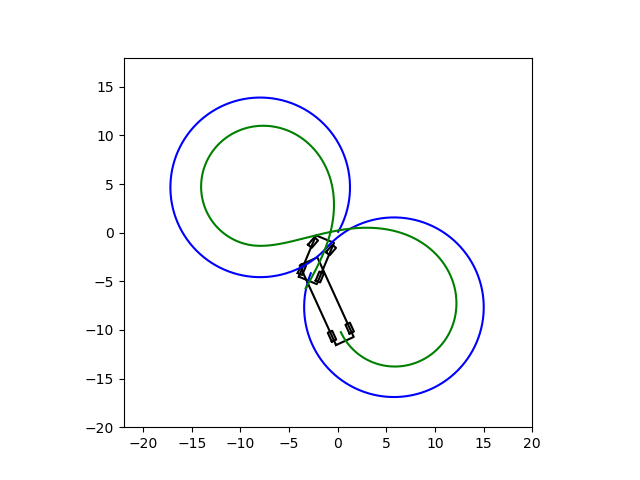
运行效果如下:
参考文献
[1]贾生超.半挂牵引车自动泊车路径规划与运动控制方法研究[D].燕山大学,2023.


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










