本章介绍了字符串、向量Vector、数组之间的关系,相通而且相互类似,加上指针迭代器的加持显得更加灵活,另外C++和C之间string的标准库的区别和相同也做了一些介绍,本章依然是基础干活满满。
一、概述


二、内容题干
3.1 命名空间using声明
using生命无须专门的前缀(命名空间::)也能使用所需的名字。 using namespace::name;
#include <iostream>
// using declarations for names from the standard library
using std::cin;
using std::cout; using std::endl;
int main()
{
cout << "Enter two numbers:" << endl;
int v1, v2;
cin >> v1 >> v2;
cout << "The sum of " << v1 << " and " << v2
<< " is " << v1 + v2 << endl;
return 0;
}


3.2、 标准库string
#inculude <string> using std::string;


#include <string>
using std::string;
#include <iostream>
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main()
{
string s; // empty string
cin >> s; // read a whitespace-separated string into s
cout << s << endl; // write s to the output
return 0;
}
#include <string>
using std::string;
#include <iostream>
using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::endl;
int main()
{
string s1, s2;
cin >> s1 >> s2; // read first input into s1, second into s2
cout << s1 << s2 << endl; // write both strings
return 0;
}

#include <iostream>
using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::endl;
#include <string>
using std::string;
int main()
{
string word;
while (cin >> word) // read until end-of-file
cout << word << endl; // write each word followed by a new line
return 0;
}


string 的empty 和size操作

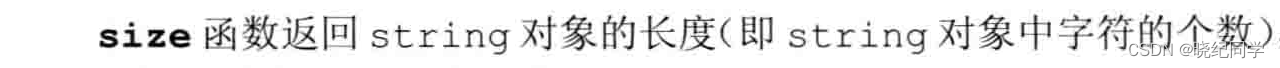
#include <string>
using std::string; using std::getline;
#include <iostream>
using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::endl;
int main()
{
string line;
// read input a line at a time and discard blank lines
while (getline(cin, line))
if (!line.empty())
cout << line << endl;
return 0;
}
#include <string>
using std::string;
#include <iostream>
using std::cout; using std::endl;
string st1; // empty string
string st2(st1); // st2 is a copy of st1
int main()
{
string st("The expense of spirit\n");
cout << "The size of " << st << "is " << st.size()
<< " characters, including the newline" << endl;
return 0;
}
#include <cstddef>
using std::size_t;
#include <string>
using std::string; using std::getline;
#include <iostream>
using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::endl;
int main()
{
string line;
// read input a line at a time and print lines that are longer than 80 characters
while (getline(cin, line))
if (line.size() > 80)
cout << line << endl;
return 0;
}
string::size_type类型

比较string对象


string相加
#include <iostream>
using std::cout; using std::endl;
#include <string>
using std::string;
int main()
{
string s1 = "hello, ", s2 = "world\n";
string s3 = s1 + s2; // s3 is hello, world\n
cout << s1 << s2 << s3 << endl;
s1 += s2; // equivalent to s1 = s1 + s2
cout << s1;
string s4 = "hello", s5 = "world"; // no punctuation in s4 or s2
string s6 = s4 + ", " + s5 + '\n';
cout << s4 << s5 << "\n" << s6 << endl;
return 0;
}




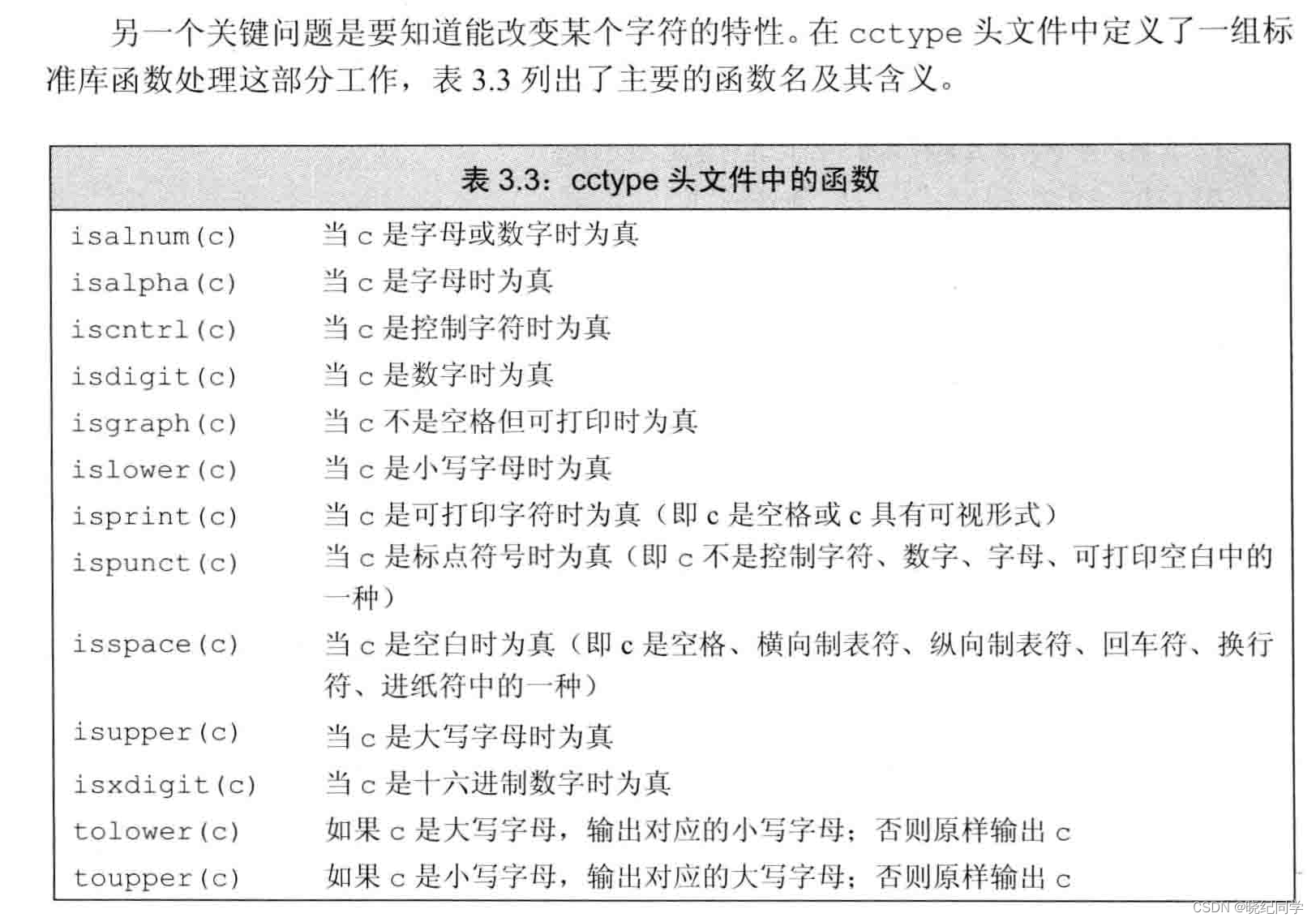
处理string对象中的字符

#include <string>
using std::string;
#include <cctype>
using std::isupper; using std::toupper;
using std::islower; using std::tolower;
using std::isalpha; using std::isspace;
#include <iostream>
using std::cout; using std::endl;
int main()
{
string s("Hello World!!!");
// punct_cnt has the same type that s.size returns
decltype(s.size()) punct_cnt = 0;
// count the number of punctuation characters in s
for (auto c : s) // for every char in s
if (ispunct(c)) // if the character is punctuation
++punct_cnt; // increment the punctuation counter
cout << punct_cnt
<< " punctuation characters in " << s << endl;
// convert s to uppercase
string orig = s;
for (auto &c : s) // for every char in s (note: c is a reference)
// c is a reference, so this assignment changes the char in s
c = toupper(c);
cout << s << endl;
// convert first word in s to uppercase
s = orig; // restore s to original case
decltype(s.size()) index = 0;
// process characters in s until we run out of characters
// or we hit a whitespace
while (index != s.size() && !isspace(s[index])) {
// s[index] returns a reference so we can change
// the underlying character
s[index] = toupper(s[index]);
// increment the index to look at the next character
// on the next iteration
++index;
}
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}



#include <iostream>
using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::endl;
#include <string>
using std::string;
#include <cstddef>
using std::size_t;
int main()
{
const string hexdigits = "0123456789ABCDEF"; // possible hex digits
cout << "Enter a series of numbers between 0 and 15"
<< " separated by spaces. Hit ENTER when finished: "
<< endl;
string result; // will hold the resulting hexify'd string
string::size_type n; // hold numbers from the input
while (cin >> n)
if (n < hexdigits.size()) // ignore invalid input
result += hexdigits[n]; // fetch the indicated hex digit
cout << "Your hex number is: " << result << endl;
return 0;
}


3.3、标准库vector
Vector属于类模板,模板本身不是类或者函数,相反可以看作是编译器生成类或者函数编写的一份说明,编译器根据模板创建类或者函数的过程成为实例化,编译器应指出类或者函数实例化为何种类型

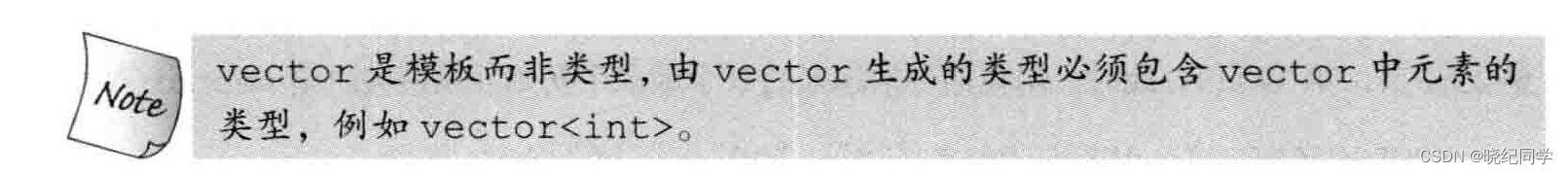

定义或者初始化vector对象

#include "Version_test.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout; using std::endl;
#include <string>
using std::string;
#include <vector>
using std::vector;
#include "Sales_item.h"
#ifndef LIST_INIT
#include <iterator>
using std::begin; using std::end;
#endif
int main()
{
#ifdef LIST_INIT
// list initialization, articles has 3 elements
vector<string> articles = {"a", "an", "the"};
#else
string temp[] = {"a", "an", "the"};
vector<string> articles(begin(temp), end(temp));
#endif
vector<string> svec; // default initialization; svec has no elements
vector<int> ivec; // ivec holds objects of type int
vector<Sales_item> Sales_vec; // holds Sales_items
vector<vector<string>> file; // vector whose elements are vectors
vector<vector<int>> vecOfvec; // each element is itself a vector
// all five vectors have size 0
cout << svec.size() << " " << ivec.size() << " "
<< Sales_vec.size() << " "
<< file.size() << " " << vecOfvec.size() << endl;
vector<int> ivec2(10); // ten elements, each initialized to 0
vector<int> ivec3(10, -1); // ten int elements, each initialized to -1
vector<string> svec2(10); // ten elements, each an empty string
vector<string> svec3(10, "hi!"); // ten strings; each element is "hi!"
cout << ivec2.size() << " " << ivec3.size() << " "
<< svec2.size() << " " << svec3.size() << endl;
// 10 is not a string, so cannot be list initialization
vector<string> v1(10); // construct v1 with ten value-initialized elements
#ifdef LIST_INIT
vector<string> v2{10}; // ten elements value-initialized elements
#else
vector<string> v2(10);
#endif
vector<string> v3(10, "hi"); // ten elements with value "hi"
#ifdef LIST_INIT
// again list initialization is not viable, so ordinary construction
vector<string> v4{10, "hi"}; // ten elements with values "hi"
#else
vector<string> v4(10, "hi"); // ten elements with values "hi"
#endif
// all four vectors have size ten
cout << v1.size() << " " << v2.size()
<< " " << v3.size() << " " << v4.size() << endl;
#ifdef LIST_INIT
vector<string> vs1{"hi"}; // list initialization: vs1 has 1 element
vector<string> vs2{10}; // ten default-initialized elements
vector<string> vs3{10, "hi"}; // has ten elements with value "hi"
#else
vector<string> vs1;
vs1.push_back("hi"); // explicitly add the element; vs1 has 1 element
vector<string> vs2(10); // don't use curlies;
// vs2 has ten default-initialized elements
vector<string> vs3(10, "hi"); // don't use curlies;
// vs3 has ten elements with value "hi"
#endif
cout << vs1.size() << " " << vs2.size() << " " << vs3.size() << endl;
vector<int> v5(10, 1); // ten elements with value 1
#ifdef LIST_INIT
vector<int> v6{10, 1}; // two elements with values 10 and 1
#else
vector<int> v6;
v6.push_back(10);
v6.push_back(1);
#endif
cout << v5.size() << " " << v6.size() << endl;
#ifdef LIST_INIT
// intention is clearer
vector<int> alt_v3 = {10}; // one element with value 10
vector<int> alt_v4 = {10, 1}; // two elements with values 10 and 1
#else
vector<int> alt_v3;
alt_v3.push_back(10); // one element with value 10
vector<int> alt_v4;
alt_v4.push_back(10);
alt_v4.push_back(1); // two elements with values 10 and 1
#endif
cout << alt_v3.size() << " " << alt_v4.size() << endl;
return 0;
}




列表初始化和元素数量


向 Vector对象添加元素


{
#ifdef LIST_INIT
vector<int> v = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
#else
int temp[] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
vector<int> v(begin(temp), end(temp));
#endif
auto sz = v.size();
decltype(sz) i = 0;
// duplicate contents of v onto the back of v
while (i != sz) {
v.push_back(*v.begin() + i);
++i;
}
// prints 0...9 0...9
for (auto it : v)
cout << it << " ";
cout << endl;
#ifdef LIST_INIT
// alternative way to stop when we get to the original last element
vector<int> alt_v = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; // vector with values 0...9
#else
vector<int> alt_v(begin(temp), end(temp)); // copy the array into alt_v
#endif
for (decltype(alt_v.size()) i = 0, sz = alt_v.size(); i != sz; ++i)
alt_v.push_back(alt_v[i]);
// prints 0...9 0...9
for (auto it : alt_v)
cout << it << " ";
cout << endl;
#ifdef LIST_INIT
vector<int> v2 = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; // vector with values 0...9
#else
vector<int> v2(begin(temp), end(temp));
#endif
decltype(v2.size()) ix = 0; // we'll use ix to index the vector
// set the elements with values less than 5 to 0
while (ix != v2.size() && v2[ix] < 5) {
v2[ix] = 0; // changes the value of the element in v
++ix; // increment the index so the next iteration fetches the next element
}
// print the elements using subscripts
for (unsigned i = 0; i != v2.size(); ++i)
cout << v2[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
#ifdef LIST_INIT
// equivalent but using iterators
vector<int> alt_v2 = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; // vector with values 0 ...9
#else
vector<int> alt_v2(begin(temp), end(temp));
#endif
// set the elements to 0 up to the first one that is 5 or greater
auto it = alt_v2.begin();
while (it != alt_v2.end() && *it < 5) {
*it = 0; // changes the value of the element in alt_v2
++it; // advance the iterator to denote the next element
}
for (auto it = alt_v2.begin(); // it denotes first element in alt_v2
it != alt_v2.end(); // so long as it denotes an element
++it) // increment the iterator to next element
cout << *it << " "; // print element denoted by it from alt_v2
cout << endl;
return 0;
}


#include <string>
using std::string;
#include <vector>
using std::vector;
#include <iostream>
using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::endl;
int main()
{
// hold the grades we read from the standard input
vector<unsigned> grades;
// count the number of grades by clusters of ten:
// 0--9, 10--19, . .. 90--99, 100
vector<unsigned> scores(11, 0); // 11 buckets, all initially 0
unsigned grade;
while (cin >> grade) { // read the grades
if (grade <= 100) // handle only valid grades
grades.push_back(grade);
++scores[grade/10]; // increment the counter for the current cluster
}
cout << "grades.size = " << grades.size() << endl;
for (auto it : grades)
cout << it << " " ;
cout << endl;
cout << "scores.size = " << scores.size() << endl;
for (auto it : scores)
cout << it << " " ;
cout << endl;
// equivalent program using iterators instead of subscripts
vector<unsigned> alt_scores(11, 0); // 11 buckets, all initially 0
// for each grade in the input
for (auto it = grades.begin(); it != grades.end(); ++it) {
unsigned i = *it;
// increment the counter for the current cluster
++(*(alt_scores.begin() + i/10));
}
cout << "alt_scores.size = " << alt_scores.size() << endl;
for (auto it = alt_scores.begin(); it != alt_scores.end(); ++it)
cout << *it << " " ;
cout << endl;
}


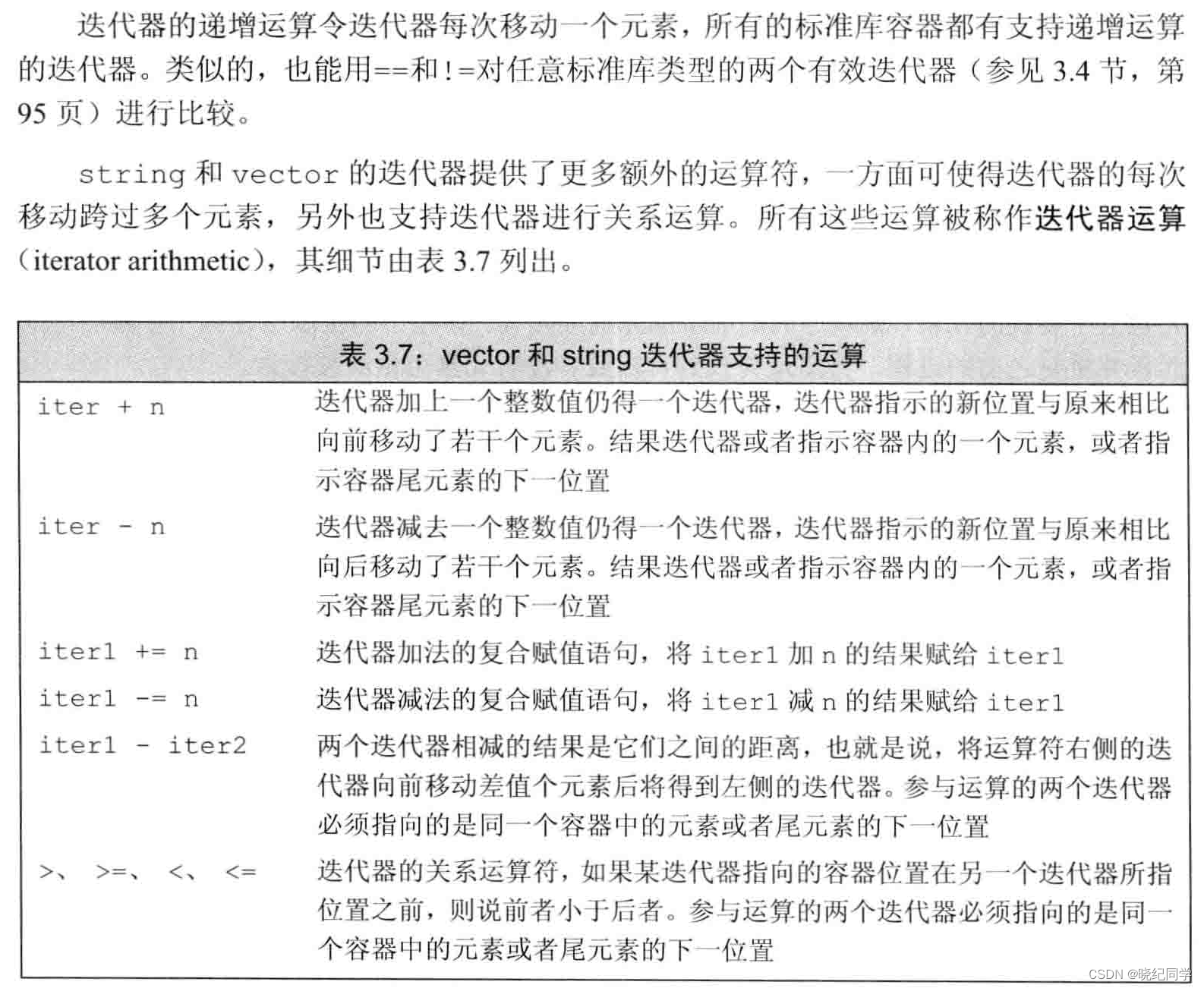
3.4 、迭代器的介绍












迭代器的运算


include "Version_test.h"
#include <string>
using std::string;
#include <vector>
using std::vector;
#include <iostream>
using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::endl;
#ifndef LIST_INIT
#include <iterator>
using std::begin; using std::end;
#endif
int main()
{
#ifdef LIST_INIT
vector<int> v = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
#else
int temp[] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
vector<int> v(begin(temp), end(temp));
#endif
auto sz = v.size();
decltype(sz) i = 0;
// duplicate contents of v onto the back of v
while (i != sz) {
v.push_back(*v.begin() + i);
++i;
}
// prints 0...9 0...9
for (auto it : v)
cout << it << " ";
cout << endl;
#ifdef LIST_INIT
// alternative way to stop when we get to the original last element
vector<int> alt_v = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; // vector with values 0...9
#else
vector<int> alt_v(begin(temp), end(temp)); // copy the array into alt_v
#endif
for (decltype(alt_v.size()) i = 0, sz = alt_v.size(); i != sz; ++i)
alt_v.push_back(alt_v[i]);
// prints 0...9 0...9
for (auto it : alt_v)
cout << it << " ";
cout << endl;
#ifdef LIST_INIT
vector<int> v2 = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; // vector with values 0...9
#else
vector<int> v2(begin(temp), end(temp));
#endif
decltype(v2.size()) ix = 0; // we'll use ix to index the vector
// set the elements with values less than 5 to 0
while (ix != v2.size() && v2[ix] < 5) {
v2[ix] = 0; // changes the value of the element in v
++ix; // increment the index so the next iteration fetches the next element
}
// print the elements using subscripts
for (unsigned i = 0; i != v2.size(); ++i)
cout << v2[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
#ifdef LIST_INIT
// equivalent but using iterators
vector<int> alt_v2 = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; // vector with values 0 ...9
#else
vector<int> alt_v2(begin(temp), end(temp));
#endif
// set the elements to 0 up to the first one that is 5 or greater
auto it = alt_v2.begin();
while (it != alt_v2.end() && *it < 5) {
*it = 0; // changes the value of the element in alt_v2
++it; // advance the iterator to denote the next element
}
for (auto it = alt_v2.begin(); // it denotes first element in alt_v2
it != alt_v2.end(); // so long as it denotes an element
++it) // increment the iterator to next element
cout << *it << " "; // print element denoted by it from alt_v2
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
3.5、数组










#include "Version_test.h"
#include <vector>
using std::vector;
#include <iostream>
using std::cout; using std::endl;
#ifndef LIST_INIT
#include <iterator>
using std::begin; using std::end;
#endif
int main()
{
#ifdef LIST_INIT
vector<int> v{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
#else
int temp[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
vector<int> v(begin(temp), end(temp));
#endif
for (auto &i : v) // for each element in v (note: i is a reference)
i *= i; // square the element value
for (auto i : v) // for each element in v
cout << i << " "; // print the element
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
指针和数组







c语言风格字符串

#include <string>
using std::string;
#include <iostream>
using std::cout; using std::endl;
#include <cstring>
#include <cstddef>
using std::size_t;
int main() {
string s1 = "A string example";
string s2 = "A different string";
if (s1 < s2) // false: s2 is less than s1
cout << s1 << endl;
else
cout << s2 << endl;
const char ca1[] = "A string example";
const char ca2[] = "A different string";
if (strcmp(ca1, ca2) < 0) // same effect as string comparison s1 < s2
cout << ca1 << endl;
else
cout << ca2 << endl;
const char *cp1 = ca1, *cp2 = ca2;
cout << strcmp(cp1, cp2) << endl; // output is positive
cout << strcmp(cp2, cp1) << endl; // output is negative
cout << strcmp(cp1, cp1) << endl; // output is zero
cout << strlen(cp1) << endl; // prints 16; strlen ignores the null
const unsigned sz = 16 + 18 + 2;
char largeStr[sz]; // will hold the result
// disastrous if we miscalculated the size of largeStr
strcpy(largeStr, ca1); // copies ca1 into largeStr
strcat(largeStr, " "); // adds a space at the end of largeStr
strcat(largeStr, ca2); // concatenates ca2 onto largeStr
// prints A string example A different string
cout << largeStr << endl;
strncpy(largeStr, ca1, sz); // size to copy includes the null
if (strlen(ca1) > sz)
largeStr[sz-1] = '\0';
strncat(largeStr, " ", 2); // pedantic, but a good habit
strncat(largeStr, ca2, sz - strlen(largeStr));
cout << largeStr << endl;
// initialize large_string as a concatenation of s1, a space, and s2
string large_string = s1 + " " + s2;
cout << large_string << endl;
return 0;
}




3.6多维数组







#include "Version_test.h"
#include <iterator>
using std::begin; using std::end;
#include <vector>
using std::vector;
#include <iostream>
using std::cout; using std::endl;
#include <cstddef>
using std::size_t;
int main()
{
// array of size 3; each element is an array of 4 uninitailzed ints
int ia1[3][4];
// array of size 10; each element is a 20-element array
// whose elements are arrays of 30 ints
int arr[10][20][30] = {0}; // initialize all elements to 0
// assigns the first element of arr to the last element
// in the last row of ia
ia1[2][3] = arr[0][0][0];
// binds row to the second four-element array in ia
int (&row)[4] = ia1[1];
// three elements, each element is an array of size 4
int ia2[3][4] = {
{0, 1, 2, 3}, // initializers for the row indexed by 0
{4, 5, 6, 7}, // initializers for the row indexed by 1
{8, 9, 10, 11} // initializers for the row indexed by 2
};
// equivalent initialization without the optional
// nested braces for each row
int ia3[3][4] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11};
// explicitly initialize only element 0 in each row
int ia4[3][4] = {{ 0 }, { 4 }, { 8 }};
// explicitly initialize row 0; the remaining elements
// are value initialized
int ix[3][4] = {0, 3, 6, 9};
// prints 9 0 0
cout << ix[0][3] << ' ' << ix[1][0] << ' ' << ix[2][0] << endl;
#ifdef CONSTEXPR_VARS
constexpr size_t rowCnt = 3, colCnt = 4;
#else
const size_t rowCnt = 3, colCnt = 4;
#endif
int ia[rowCnt][colCnt]; // 12 uninitialized elements
// for each row
for (size_t i = 0; i != rowCnt; ++i) {
// for each column within the row
for (size_t j = 0; j != colCnt; ++j) {
// assign the element's positional index as its value
ia[i][j] = i * colCnt + j;
}
}
// four ways to print the contents of ia
// 1. using nested range for loops
for (const auto &row : ia) // for every element in the outer array
for (auto col : row) // for every element in the inner array
cout << col << endl; // print the element's value
cout << ia[0][0] << ' ' << ia[2][3] << endl; // prints 0 11
// 2. using pointers and a traditional for loop
// with pointer arithmetic to calculate the end pointers
for (auto p = ia; p != ia + rowCnt; ++p) {
// q points to the first element of an array of four ints;
// that is, q points to an int
for (auto q = *p; q != *p + colCnt; ++q)
cout << *q << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
// 3. using pointers and a traditional for loop
// with the library begin and end functions to manage the pointers
for (auto p = begin(ia); p != end(ia); ++p) {
// q points to the first element in an inner array
for (auto q = begin(*p); q != end(*p); ++q)
cout << *q << ' '; // prints the int value to which q points
cout << endl;
}
// 4. using a type alias to declare the loop control variable
#ifdef TYPE_ALIAS_DECLS
using int_array = int[4]; // new style type alias declaration
#else
typedef int int_array[4]; // equivalent typedef declaration
#endif
for (int_array *p = ia; p != ia + 3; ++p) {
for (int *q = *p; q != *p + 4; ++q)
cout << *q << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
// alternative way to assign positional index to elements
// in a two-dimensional array
int alt_ia[rowCnt][colCnt]; // 12 uninitialized elements
size_t cnt = 0;
for (auto &row : alt_ia) // for every element in the outer array
for (auto &col : row) { // for every element in the inner array
col = cnt; // give this element the next value
++cnt; // increment cnt
}
// now print the value of the array
for (const auto &row : alt_ia) // for every element in the outer array
for (auto col : row) // for every element in the inner array
cout << col << endl;
return 0;
}
3.7、小结

3.8、术语表
























 6万+
6万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








