书接上回,我们既然直接运行例程成功了,接下来就是了解如何实现例程中的每个环节。当然,我们先从简单的做起,一般编程语言都会找个helloworld例子,而我们的显卡是不会说话的,只能做一些简单的加减乘除运算。所以,CUDA程序的helloworld,我想应该最合适不过的就是向量加了。
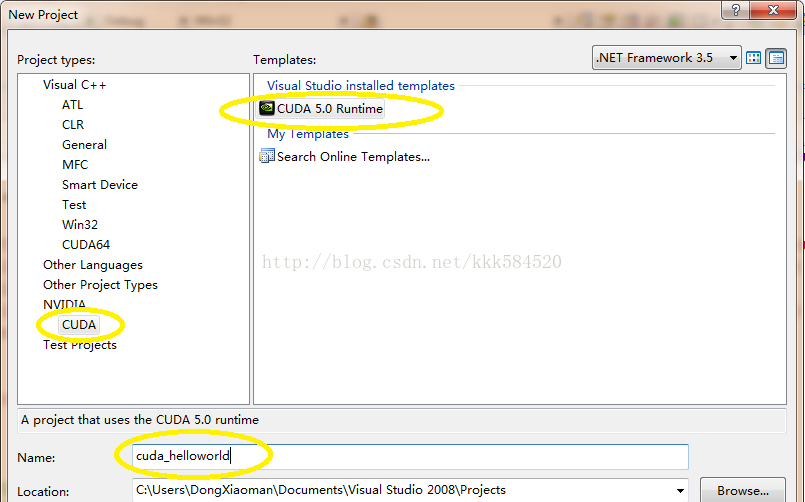
打开VS2008,选择File->New->Project,弹出下面对话框,设置如下:
之后点OK,直接进入工程界面。
工程中,我们看到只有一个.cu文件,内容如下:
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include <stdio.h>
cudaError_t addWithCuda(int *c, const int *a, const int *b, size_t size);
__global__ void addKernel(int *c, const int *a, const int *b)
{
int i = threadIdx.x;
c[i] = a[i] + b[i];
}
int main()
{
const int arraySize = 5;
const int a[arraySize] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
const int b[arraySize] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
int c[arraySize] = { 0 };
// Add vectors in parallel.
cudaError_t cudaStatus = addWithCuda(c, a, b, arraySize);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "addWithCuda failed!");
return 1;
}
printf("{1,2,3,4,5} + {10,20,30,40,50} = {%d,%d,%d,%d,%d}\n",
c[0], c[1], c[2], c[3], c[4]);
// cudaThreadExit must be called before exiting in order for profiling and
// tracing tools such as Nsight and Visual Profiler to show complete traces.
cudaStatus = cudaThreadExit();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaThreadExit failed!");
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// Helper function for using CUDA to add vectors in parallel.
cudaError_t addWithCuda(int *c, const int *a, const int *b, size_t size)
{
int *dev_a = 0;
int *dev_b = 0;
int *dev_c = 0;
cudaError_t cudaStatus;
// Choose which GPU to run on, change this on a multi-GPU system.
cudaStatus = cudaSetDevice(0);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaSetDevice failed! Do you have a CUDA-capable GPU installed?");
goto Error;
}
// Allocate GPU buffers for three vectors (two input, one output) .
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_c, size * sizeof(int));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_a, size * sizeof(int));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_b, size * sizeof(int));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!");
goto Error;
}
// Copy input vectors from host memory to GPU buffers.
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_a, a, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_b, b, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
}
// Launch a kernel on the GPU with one thread for each element.
addKernel<<<1, size>>>(dev_c, dev_a, dev_b);
// cudaThreadSynchronize waits for the kernel to finish, and returns
// any errors encountered during the launch.
cudaStatus = cudaThreadSynchronize();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaThreadSynchronize returned error code %d after launching addKernel!\n", cudaStatus);
goto Error;
}
// Copy output vector from GPU buffer to host memory.
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(c, dev_c, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
}
Error:
cudaFree(dev_c);
cudaFree(dev_a);
cudaFree(dev_b);
return cudaStatus;
}
可以看出,CUDA程序和C程序并无区别,只是多了一些以"cuda"开头的一些库函数和一个特殊声明的函数:
__global__ void addKernel(int *c, const int *a, const int *b)
{
int i = threadIdx.x;
c[i] = a[i] + b[i];
}
这个函数就是在GPU上运行的函数,称之为核函数,英文名Kernel Function,注意要和操作系统内核函数区分开来。
我们直接按F7编译,可以得到如下输出:
1>------ Build started: Project: cuda_helloworld, Configuration: Debug Win32 ------
1>Compiling with CUDA Build Rule...
1>"C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v5.0\\bin\nvcc.exe" -G -gencode=arch=compute_10,code=\"sm_10,compute_10\" -gencode=arch=compute_20,code=\"sm_20,compute_20\" --machine 32 -ccbin "C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio 9.0\VC\bin" -Xcompiler "/EHsc /W3 /nologo /O2 /Zi /MT " -I"C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v5.0\\include" -maxrregcount=0 --compile -o "Debug/kernel.cu.obj" kernel.cu
1>tmpxft_000000ec_00000000-8_kernel.compute_10.cudafe1.gpu
1>tmpxft_000000ec_00000000-14_kernel.compute_10.cudafe2.gpu
1>tmpxft_000000ec_00000000-5_kernel.compute_20.cudafe1.gpu
1>tmpxft_000000ec_00000000-17_kernel.compute_20.cudafe2.gpu
1>kernel.cu
1>kernel.cu
1>tmpxft_000000ec_00000000-8_kernel.compute_10.cudafe1.cpp
1>tmpxft_000000ec_00000000-24_kernel.compute_10.ii
1>Linking...
1>Embedding manifest...
1>Performing Post-Build Event...
1>copy "C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v5.0\\bin\cudart*.dll" "C:\Users\DongXiaoman\Documents\Visual Studio 2008\Projects\cuda_helloworld\Debug"
1>C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v5.0\\bin\cudart32_50_35.dll
1>C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v5.0\\bin\cudart64_50_35.dll
1>已复制 2 个文件。
1>Build log was saved at "file://c:\Users\DongXiaoman\Documents\Visual Studio 2008\Projects\cuda_helloworld\cuda_helloworld\Debug\BuildLog.htm"
1>cuda_helloworld - 0 error(s), 105 warning(s)
========== Build: 1 succeeded, 0 failed, 0 up-to-date, 0 skipped ==========
可见,编译.cu文件需要利用nvcc工具。该工具的详细使用见后面博客。
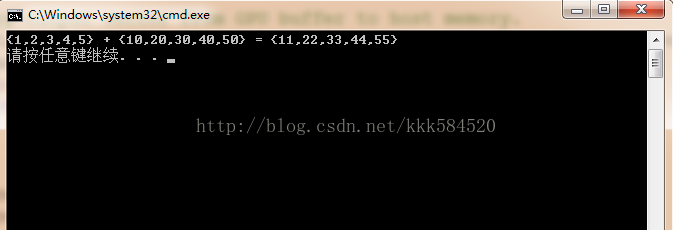
直接运行,可以得到结果图如下:
如果显示正确,那么我们的第一个程序宣告成功!
























 738
738

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








