sort(beg,end)
sort(beg,end,op)
stable(beg,end,)
stable(beg,end,op)
1.sort()与stable_sort()的上述第一形式,使用operator<对区间[beg,end)内的所有元素进行排序。
2.sort()与stable_sort()的上述第二形式,使用二元判断式op(elem1,elem2)作为排序准则,对区间[beg,end)内的所有元素进行排序。
3.sort()和stable_sort()的区别是,后者保证相等元素的原本相对次序在排序后保持不变。即stable_sort()是稳定排序。所谓稳定排序,是指对一个序列进行排序之后,如果两个元素的值相等,则原来乱序时在前面的元素现在(排好序之后)仍然排在前面。sort()没有这个承诺,而stable_sort()承诺了这一点。
4.不可以对list调用这些算法,因为list不支持随机存取迭代器,不过对于list,其自身带有成员函数,可以完成sort(),对其自身元素排序。
5.sort()的平均排序效能是nlogn,如果想避免可能出现的差情况,应该使用partial_sort()。
6.sort()内部使用快速排序,stable_sort()使用归并排序。
代码示例:
#include"fuzhu.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
deque<int> coll;
INSERT_ELEMENTS(coll,1,9);
INSERT_ELEMENTS(coll,1,9);
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll,"on entry: ");
sort(coll.begin(),coll.end()); // [beg,end) 默认less <
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll,"sorted: ");
sort(coll.begin(),coll.end(),greater<int>()); //[beg,end) greater >
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll,"sorted >: ");
system("pause");
return 0;
}运行结果:
#include"fuzhu.h"
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int value;
int index;
};
bool mycmp(const Node& a,const Node& b)
{
return a.value<b.value;
}
int main()
{
vector<Node> coll;
vector<Node>::iterator pos;
Node node;
int va;
for(int i=0;i<=8;i++)
{
cin>>va;
node.value=va;
node.index=i;
coll.push_back(node);
}
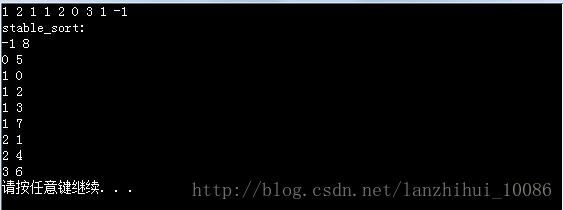
stable_sort(coll.begin(),coll.end(),mycmp);
//sort(coll.begin(),coll.end(),mycmp);
cout<<"stable_sort: "<<endl;
for(pos=coll.begin();pos!=coll.end();++pos)
{
cout<<pos->value<<" "<<pos->index<<endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}运行结果:

























 1575
1575

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








