
Neuroimage; 2021(Feb); reward; longitudinal stability;ICC; University of Pittsburgh; win>neutral
Curr Opin Behav Sci; 2021(Aug); extensive sampling; Kendrick
bioRixv; 2021; NSD dataset; Kendrick
01

Neuroimage的文章,使用了两个独立的longitudinal样本PMCP和PGS-E研究了奖赏加工大脑活动的stability。
文章最主要的结论:
Notably, results suggest that contrasts intended to map cognitive function and show robust group-level effects (i.e. Win > Loss) may be less effective in studies of individual differences and disease risk.
样本1: PMCP

样本2: PGS-E

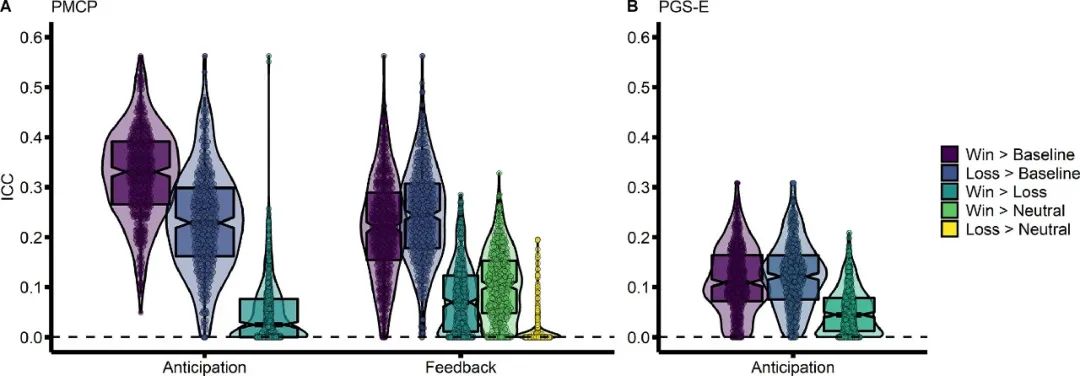
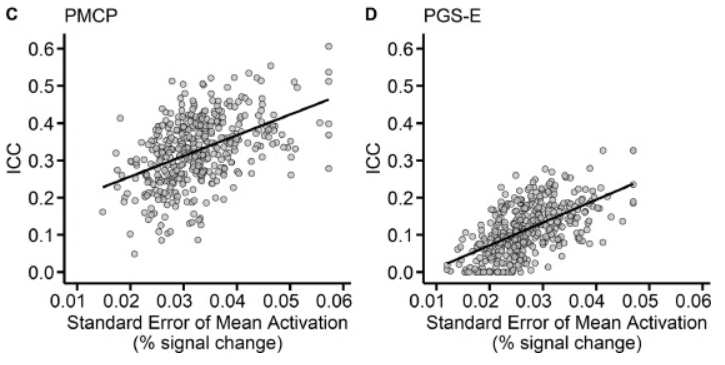
一个典型的test-retest (ICC)研究,简答说考察的是,在第一次测量的大脑活动,和随后的重测的大脑活动,能达到多少的相关。分别用了两个独立样本,一个成年人,一个是青少年,可以看到所有结果中,青少年样本的ICC都相对于成年人样本低,原因是青少年的大脑仍处于发育中,文章的讨论部分有专门对这一点进行讨论。推荐阅读原文,有很多ICC相关的文献。
结果
1. 使用了Schaefer atlas parcellations – 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, and 1,000 ROIs。发现parcellation中ROI的多少,不影响稳定性。
2. win>baseline比常用的win>loss的contrast有更高的ICC。基于任务条件之间的contrast有较低的稳定性,可能的原因是任务条件之间,比如win or loss之间存在较高的相关,相减之后稳定性下降。
3.Subcortical的区域来自于Harvard-Oxford subcortical atlas, 其中Schaefer atlas有其对应的Yeo 2011的几个network的标签。但是没有reward network,作者用Neurosynth👇寻找reward network是一个不错的idea! 用Neurosynth做meta-analysis找到reward的区域,ROI如果和这些区域有显著的重合(p<0.05),则将ROI划分为reward network。btw, Neurosynth也是一个不错的写introduction的资源。

结果表明limbic 和 reward network的ICC比cortical的要低。

4.有更多variability的区域有更高的ICC。一些任务的设计初衷就是诱发目标区域的活动,相比之下,某些非目标区域比如默认网络的稳定性更高。
These tasks are designed to elicit strong within-subject effects in targeted regions at a single time-point. This results in lower between-subject variance in targeted regions (Hedge et al., 2018), leading to reduced reliability.
02

来自Kendrick Kay和Thomas Naselaris的实验室。观点类的文章,也可以算作他们之后NSD数据库的Introduction。
由于fMRI并不便宜,进行实验时需要决定是要研究被试间差异还是被试内差异。大部分的研究都做的是被试间的采样,比如UKB有5万多人的采集了磁共振的数据(👇图),但是大部分被试都只做了一个session,平均下来每个被试的机时都很低。作者认为这样单纯堆叠样本量的做法会引入很多不必要的误差,意义不大。相比而言,对于数目有限的被试进行多次(extensive)的采样更有利于我们理解大脑如何处理复杂的信息。

作者列举了以下👇3个使用大样本+sampling individual variation的理由,
We might be concerned that what we observe to be true of one brain may not be true of others. 希望结果能更好的推广的其他被试上,而不仅限于我们采样的20或者30个被试。
We might want to increase the statistical power of our analyses by adding more subjects. 为了提高统计效力
We are actually interested in explaining individual variation (or variation across groups). 希望解释被试间的差异
随后从这几个角度进行了讨论:
Complete models of individuals are likely to generalize
More subjects = more ‘noise’
Complete models of individual brains may reveal the most interesting forms of individual variation
这里的complete model指的是通过对同一批被试进行大量的采样获得的结果/模型。
03

同样来自Kendrick Kay和Thomas Naselaris的实验室。一批高质量,被试内重复采样的7T数据即将共享,是做视觉和computational modeling不错的资源。简单看下有什么:
Using ultra-high-field fMRI (7T, whole-brain, T2*-weighted gradient-echo EPI, 1.8-mm resolution, 1.6-s TR), we measured BOLD responses while each of 8 participants viewed 9,000–10,000 distinct, color natural scenes (22,500–30,000 trials) in 30–40 weekly scan sessions over the course of a year.

Access似乎也比较容易,需要提交一个谷歌form。作者在文末提到要保留一部分数据作为held-out dataset用于data chanllenge。文章进行了不少分析,代码作者也会分享,其中做去噪的方法似乎值得了解一下。

目前大部分的研究关注的都是group level,group-to-individual generalization是当前psychology/neuroimaging领域面临的挑战之一。
推荐阅读:
①Hamaker, E. L. (2012). Why researchers should think "within-person": A paradigmatic rationale. In M. R. Mehl & T. S. Conner (Eds.), Handbook of research methods for studying daily life (p. 43–61). The Guilford Press.
the large-sample approach is not necessarily the only appropriate research approach in psychology
several alternatives to the standard large-sample approach that allow us to take a closer and more detailed look at the processes as they are occurring in daily life
②Poldrack, R. A., Laumann, T. O., Koyejo, O., Gregory, B., Hover, A., Chen, M. Y., ... & Mumford, J. A. (2015). Long-term neural and physiological phenotyping of a single human. Nature communications, 6(1), 1-15.
18个月里,Russell A. Poldrack自己当被试做了很多很多次的采样。

③Fisher, A. J., Medaglia, J. D., & Jeronimus, B. F. (2018). Lack of group-to-individual generalizability is a threat to human subjects research. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115(27), E6106-E6115.
We provide evidence that conclusions drawn from aggregated data may be worryingly imprecise. Specifically,the variance in individuals is up to four times larger than in groups.

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








