凸集

在凸几何中,凸集(convex set)是在凸组合下闭合的仿射空间的子集。更具体地说,在欧氏空间中,凸集是对于集合内的每一对点,连接该对点的直线段上的每个点也在该集合内。例如,立方体是凸集,但是任何中空的或具有凹痕的例如月牙形都不是凸集
如果S是n维空间中的凸集,则对于S中的任何r> 1,n维向量
![]() 的集合,对于任何非负数
的集合,对于任何非负数
![]() , 如果
, 如果![]()
,那么:![]()
这种类型的向量被称为![]() 的凸组合。
的凸组合。
一般的:令![]() 和
和![]() 是凸集,则有以下重要性质:
是凸集,则有以下重要性质:
(1) 交集
![]() 为凸集。
为凸集。
(2) 和集
![]() 为凸集。
为凸集。
(3) 直和
为凸集。
凸集交叉和联合
向量空间的凸子集的集合具有以下属性:
(1)空集和整个向量空间是凸的。
(2)任意凸集集合的凸点是凸的。
(3)凸子集的非递减序列的并集是凸集。 对于凸集的非递减序列的联合的前述属性,对嵌套集的限制很重要:两个凸集的并集不必是凸的。
凸集封闭凸集
闭合凸集是包含其所有极限点的凸集。 它们可以被表征为闭合半空间(位于超平面的一侧上的空间中的点集合)的交集。
从刚才所说的,很明显这样的交叉是凸的,它们也是封闭的。 为了证明相反,即每个凸集可以表示为这样的交集,需要以对于给定的闭凸集C和其外的点P的形式的支持超平面定理,存在封闭的半空间H,其包含 C而不是P.支持超平面定理是功能分析的哈恩 - 巴拿赫定理的特殊情况。
凸包
矢量空间的每个子集A包含在最小的凸集(称为A的凸包)中,即包含A的所有凸集的交集。凸包运算符Conv()具有包集的特征属性:
一般的:S⊆Conv(S);
不减少S⊆T意味着Conv(S)⊆Conv(T)和幂等于Conv(Conv(S))= Conv(S)。
凸集运算是需要的一组凸集合形成一个格子,其中“连接”操作是两个凸集合的凸包的凸包
Conv(S)∨Conv(T)= Conv(S∪T)= Conv(Conv(S)∪Conv(T))
任何一组凸集合的集合本身都是凸的,所以(实数或复合)向量空间的凸子集形成一个完整的网格。
闵可夫斯基加法
在实际向量空间中,将两个(非空)集合S1和S2的闵可夫斯基之和定义为通过向量元集合中的向量集合形成的集合S1 + S2:
更一般地,有限族(非空)集合的闵可夫斯基和是通过元素向量的向量
对于闵可夫斯基加法,仅包含零向量0的零集合{0}具有特殊的重要性:对于向量空间的每个非空子集S
在代数术语中,{0}是闵可夫斯基加法的本体元素(在非空集合的集合上)。
闵可夫斯基加法和凸包
闵可夫斯基加法在获得凸包的操作方面表现良好,如以下命题所示:
令S1,S2为真实矢量空间的子集,其闵可夫斯基和的凸包是其凸包的闵可夫斯基和:
对于非空集合的每个有限集合,此结果更为一般:
在数学术语中,闵可夫斯基求和和形成凸包的操作是相关联的操作。
闵可夫斯基凸集合:
闵可夫斯基的两个紧凑凸集的和是紧凑的。 紧凑凸集和闭合凸集合的总和是闭合的。
凸函数Convex function


In mathematics, a real-valued function defined on an n-dimensional interval is called convex (or convex downward or concave upward) if the line segment between any two points on the graph of the function lies above or on the graph, in a Euclidean space (or more generally a vector space) of at least two dimensions. Equivalently, a function is convex if its epigraph (the set of points on or above the graph of the function) is a convex set. For a twice differentiable function of a single variable, if the second derivative is always greater than or equal to zero for its entire domain then the function is convex.[1] Well-known examples of convex functions include the quadratic function x 2 {\displaystyle x^{2}} 

Convex functions play an important role in many areas of mathematics. They are especially important in the study of optimization problems where they are distinguished by a number of convenient properties. For instance, a (strictly) convex function on an open set has no more than one minimum. Even in infinite-dimensional spaces, under suitable additional hypotheses, convex functions continue to satisfy such properties and as a result, they are the most well-understood functionals in the calculus of variations. In probability theory, a convex function applied to the expected value of a random variable is always less than or equal to the expected value of the convex function of the random variable. This result, known as Jensen's inequality, underlies many important inequalities (including, for instance, the arithmetic–geometric mean inequality and Hölder's inequality).







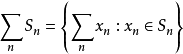














 5236
5236

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








