目录
sprintf与sscanf
与之前学习过的进行对比:
scanf 是针对标准输入的格式化输入语句
printf 是针对标准输出的格式化输出语句
fscanf 是针对所有输入流的格式化语句
fprintf 是针对所有输出流的格式化语句
sprintf 把一个格式化的数据转化成字符串(序列化)
sscanf 从一个字符串中转化成一个格式化的数据 (反序列化)
sprintf

下面的一个示例就是把结构体内部的数据转换成一个字符串:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
struct S {
int count;
float amount;
};
typedef struct S S;
int main()
{
S s = { 5,20.00 };
char buf[100] = { 0 };
sprintf(buf, "%d %f", s.count, s.amount);
printf("字符串:%s\n", buf);
printf("格式化:%d %f\n", s.count, s.amount);
return 0;
}运行结果为:![]()
sscanf

与sprintf相反,sscanf函数是将字符串转化成格式化的数据
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
struct S {
int count;
float amount;
};
typedef struct S S;
int main()
{
S s = { 0 };
char buf[100] = { "20 50.000" };
sscanf(buf, "%d %f", &(s.count), &(s.amount));
printf("字符串:%s\n", buf);
printf("格式化:%d %f\n", s.count, s.amount);
return 0;
} 运行结果也是类似的:![]()
这两个函数的作用是与序列化与反序列化有关的,目前只做简单了解。
文件的随机读写
fseek
根据文件指针的位置和偏移量来定位文件指针。
 fseek函数的偏移量要根据原始位置来确定的,库函数中给出了三个原始位置的定义:
fseek函数的偏移量要根据原始位置来确定的,库函数中给出了三个原始位置的定义:

用法示例
文件:
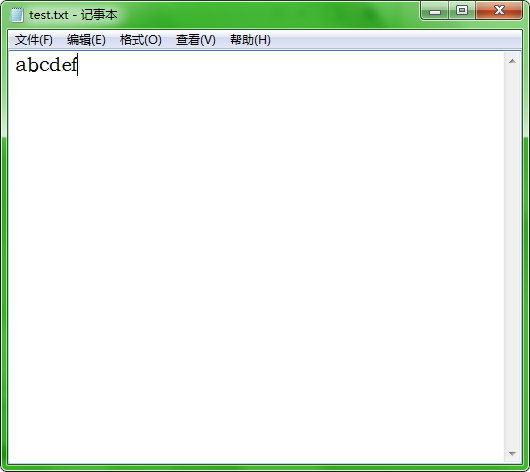
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main()
{
FILE* pf = fopen("test.txt", "r");
if (pf == NULL)
{
perror("fopen");
return 1;
}
fseek(pf, 2, SEEK_SET);//打印c
int ch = fgetc(pf);
printf("%c\n", ch);
fseek(pf, 2, SEEK_CUR);//打印f
ch = fgetc(pf);
printf("%c\n", ch);
fseek(pf, -6, SEEK_END);//打印a
ch = fgetc(pf);
printf("%c\n", ch);
fclose(pf);
pf = NULL;
return 0;
}程序运行结果:

ftell
返回文件指针相对于起始位置的偏移量。

#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main()
{
FILE* pf = fopen("test.txt", "r");
if (pf == NULL)
{
perror("fopen");
return 1;
}
fseek(pf, 2, SEEK_SET);//打印2
int pos = ftell(pf);
printf("%d\n", pos);
fseek(pf, 2, SEEK_CUR);//打印4
pos = ftell(pf);
printf("%d\n", pos);
fseek(pf, -6, SEEK_END);//打印0
pos = ftell(pf);
printf("%d\n", pos);
fclose(pf);
pf = NULL;
return 0;
}程序运行结果:

rewind
让文件指针的位置回到文件的起始位置。
 经过上面的一系列操作之后,如果找不到原来的文件指针的位置到哪里了,就可以使用这个函数重置文件指针。
经过上面的一系列操作之后,如果找不到原来的文件指针的位置到哪里了,就可以使用这个函数重置文件指针。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main()
{
FILE* pf = fopen("test.txt", "r");
if (pf == NULL)
{
perror("fopen");
return 1;
}
fseek(pf, 2, SEEK_SET);//打印2
int pos = ftell(pf);
printf("%d\n", pos);
fseek(pf, 2, SEEK_CUR);//打印4
pos = ftell(pf);
printf("%d\n", pos);
fseek(pf, -6, SEEK_END);//打印0
pos = ftell(pf);
printf("%d\n", pos);
rewind(pf);
pos = fgetc(pf);
printf("%c\n", pos);
fclose(pf);
pf = NULL;
return 0;
}程序运行结果:

end
学习自:比特鹏哥——C语言课程






















 1287
1287











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








