Towards Real World Human Parsing: Multiple-Human Parsing in the Wild
https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.07206
数据库没给出来啊!
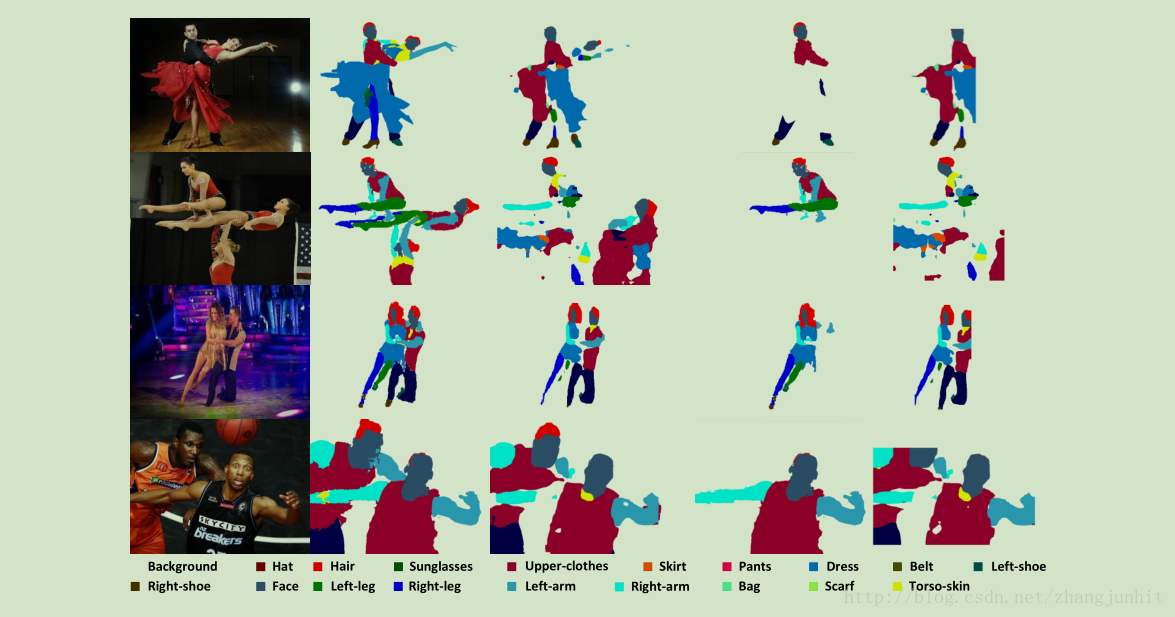
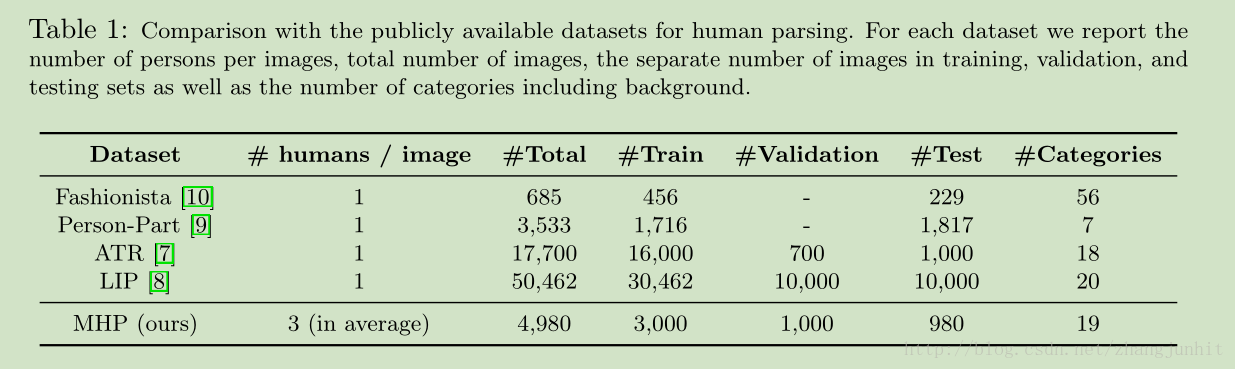
本文针对当前 human parsing 数据库基本都是单人标记,而图像实际情况经常含有多人,这里我们提出了一个 Multiple-Human Parsing (MHP) 数据库,一般2-16人每张图像。接着我们提出了一个 Multiple-Human Parser (MH-Parser) 算法,在单人解析过程中同时考虑 global context and local cues,得到不错的效果。
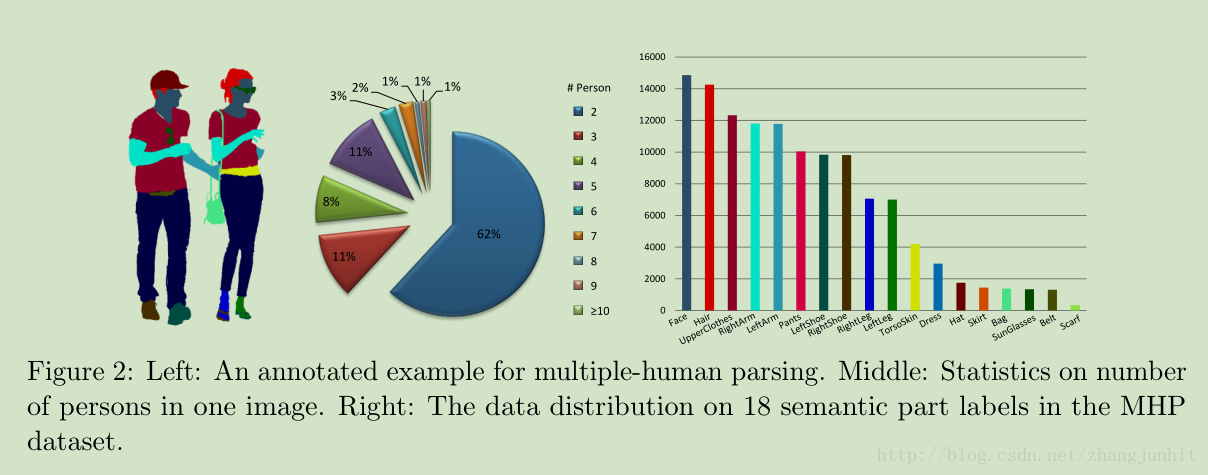
先看数据库:
各个数据库规模:
Dataset statistics
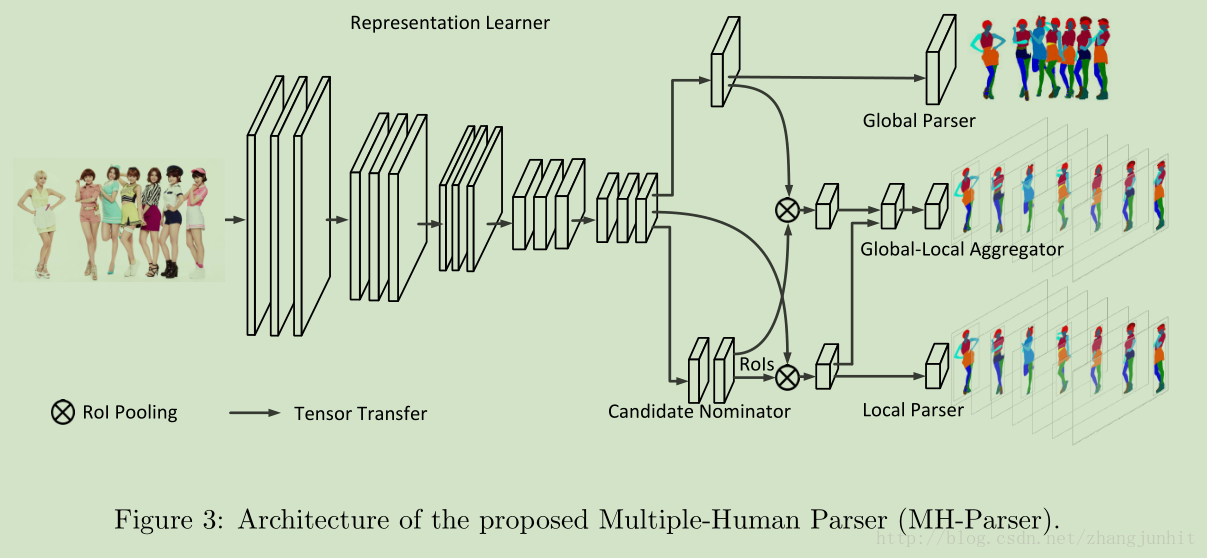
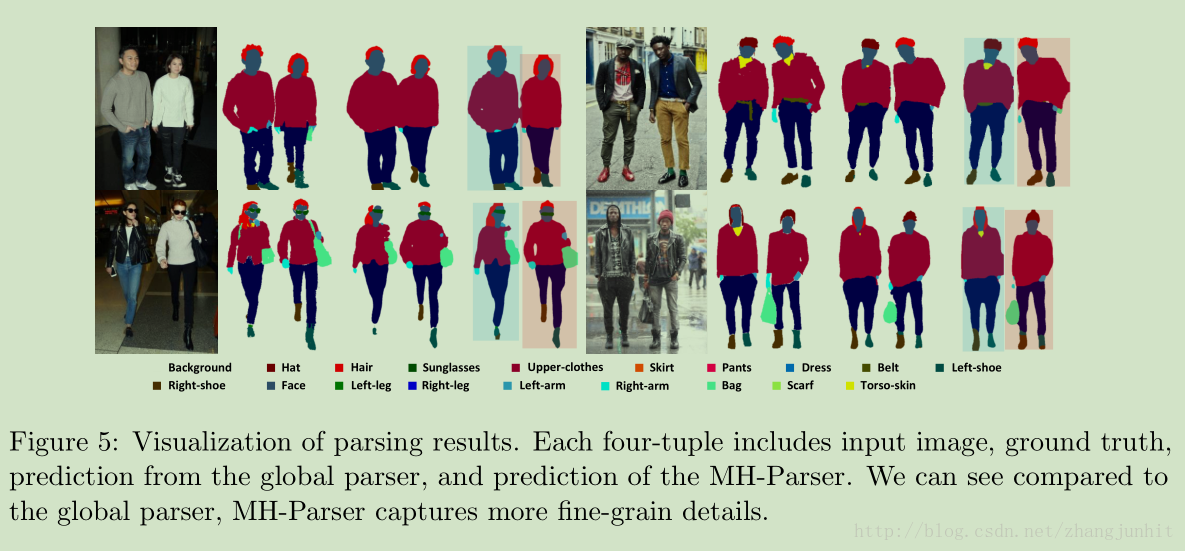
MH-Parser:
MH-Parser 主要包含五个模块:
1)Representation learner: 是一个CNN特征器,它提取的特征由后面几个模块共享,这里使用全卷积网络,以保持 spatial 信息
2)Global parser : 获取整幅图像的全局信息,生成 a semantic parsing map of the whole image
3) Candidate nominator:包括三个子模块 Region Proposal Network (RPN), a bounding box classifier
and a bounding box regression,类似于 Faster RCNN,将每个人检测出来,得到矩形框
4)Local parser: 针对每个含有人的矩形框,进行 semantic labels 语义标记
5)Global-local aggregator :同时将 local parser and the global parser 网络中隐含的信息输入,用于单人矩形框的 semantic parsing predictions
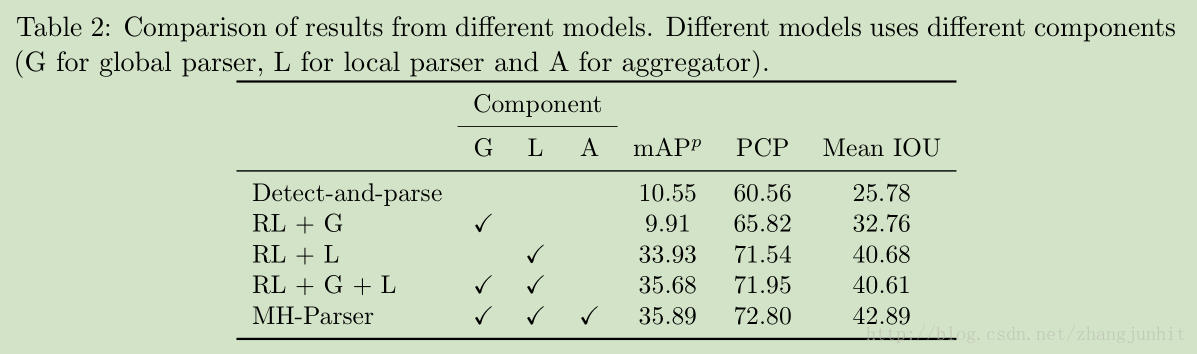
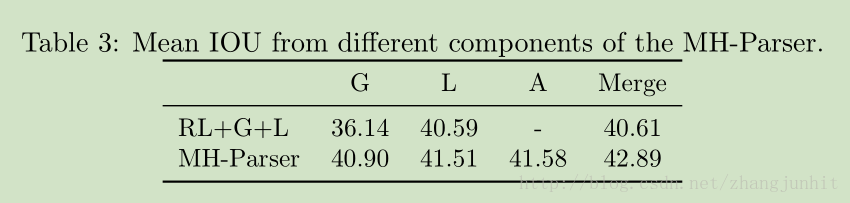
4.2 Detect-and-parse baseline
检测阶段和解析阶段是分离的:
In the detection stage, we use the representation learner and the candidate nominator as the detection
model.
In the parsing stage, we use the representation learner and the local prediction as the
the parsing model.
图像分割"LIP: Self-supervised Structure-sensitive Learning and A New Benchmark for Human Parsing"
数据集:http://hcp.sysu.edu.cn/lip
code: https://github.com/Engineering-Course/LIP_SSL.
做人体部件分割,构建了一个新的数据库“LIP”,包含19个语义标记。在训练中融入结构信息,提升分割效果。
人体分割具体应用:行人再认证,行为分析等。
目前三个人体部件数据库ATR,Pascal-Person-Part和LIP复杂度比较:
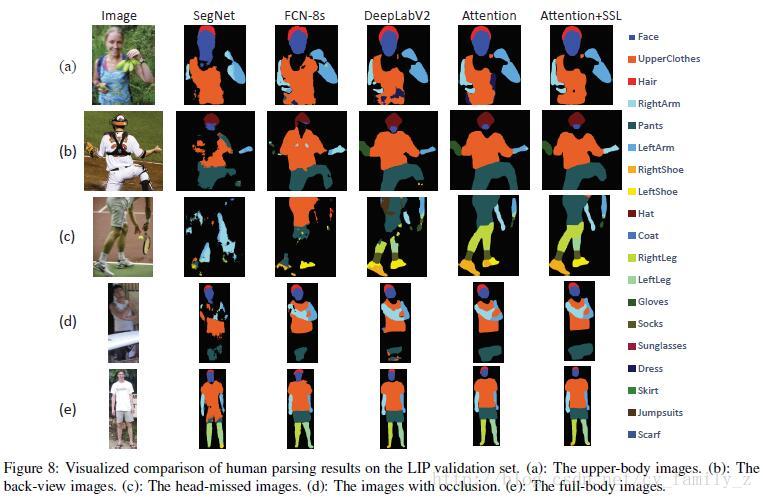
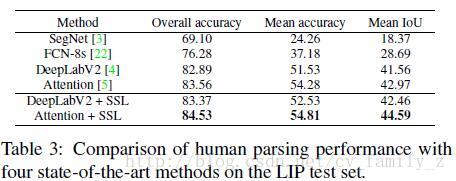
使用目前主流分割方法FCN-8S,SegNet,DeepLabV2和Attention机制在LIP数据库上的结果如下:
目前方法主要的问题:
1.背部图像左右胳膊容易混淆
2.头部在图像中不存在时,效果最差,说明头部是人体分割的重要线索。
3.对小物体检测不好,如鞋子
Self-supervised Structure-sensitive Learning
论文提出的方法,使用人体结构指导训练,定义9个连接点建立姿态结构,分别是head, upper body, lower body, left arm,right arm, left leg, right leg, left shoe and right shoe区域的中心点,网络结构如下图所示。 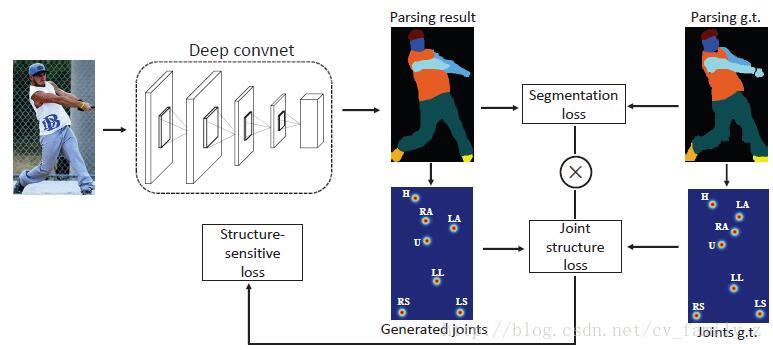
对于每个分解的结果和对应的真值,获取连接点作为热度图,使用Euclidean距离评价生成的结构。之后使用连接点结构损失加权像素级分割损失,即structure-sensitive损失。
即, 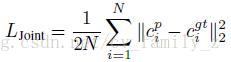
LStructure=LJointLParsing
实验结果
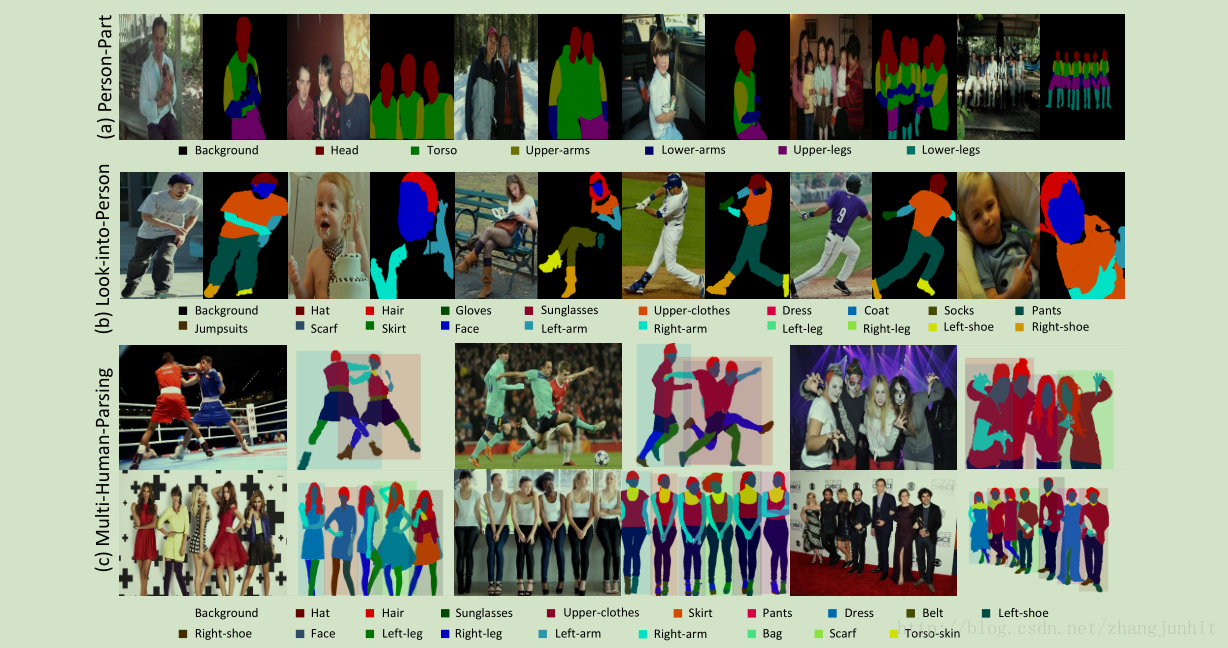
与其他方法对比的结果图,可以分割出较小的物体,如鞋子,也可以解决左右胳膊混淆的问题。










 介绍了MHP数据库和MH-Parser算法,用于解决实际图像中多人人体解析问题,并通过自监督结构敏感学习方法提高分割精度。
介绍了MHP数据库和MH-Parser算法,用于解决实际图像中多人人体解析问题,并通过自监督结构敏感学习方法提高分割精度。





















 2003
2003

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








