在使用simulink仿真和其他语言编写的仿真模块合作时,总存在两种语言模块的数据交互的问题,本文考虑使用S-Function构建一个单独的通信模块,将该模块添加到simulink模型中,实现仿真数据的交互。
Matlab的simulink仿真有提供一个用户自定义模块,该模块可以用多种编程语言来实现,本文介绍:使用C++的Socket通信来编写代码,实现和Vc的交互。
1. VC++用户自定义模块的实现方法
a. 在模型中添加S-Function, 编写模块对应的函数代码
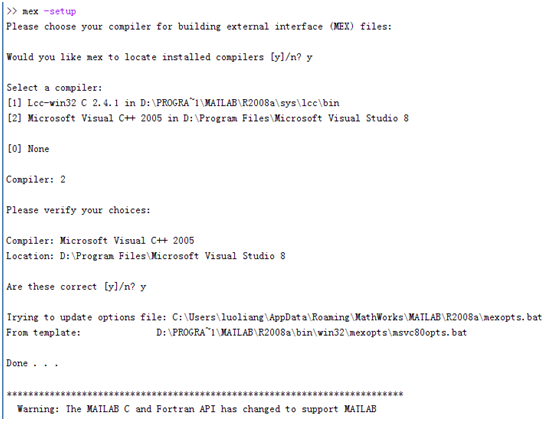
b、编译C++代码,在matlab中编译,需要先通过matlab命令行设置matlab的mex编译器,方法如下:
选择VS2005编译器,然后使用mex 命令来编译代码,命令格式:mex cppfile(模块对应的代码的文件名),编译成功会有相应的提示
c. 编译成功会产生一个后缀为mexw32的mex程序,有了这个程序,用户自定义模块就可以工作了
2. 例子
Demo说明:两个正弦输入信号经过mux模块集束成一个输入数组,经过自定义模块,最后到达Scope模块显示。在自定义模块(UseFunc)中,通过Socket采用UDP将输入数据发送到某个端口。
2.1 Simulink模型
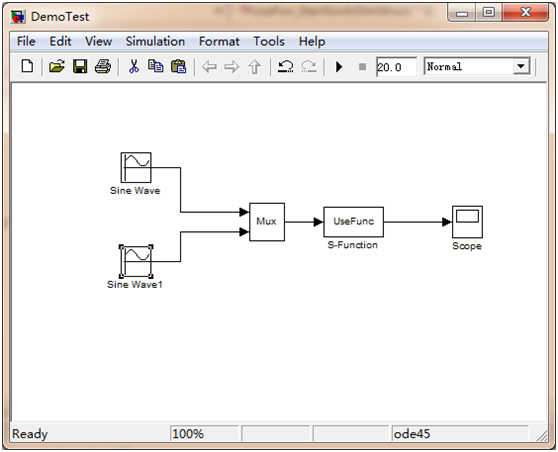
S-Function代码:
UseFunc.h
/* Copyright 2003-2004 The MathWorks, Inc. */
#ifndef _SFUN_CPP_USER_DEFINE_CPP_
#define _SFUN_CPP_USER_DEFINE_CPP_
// Define a generic template that can accumulate
// values of any numeric data type
template <class DataType> class GenericAdder {
private:
DataType Peak;
public:
GenericAdder() {
Peak = 0;
}
DataType AddTo(DataType Val) {
Peak += Val;
return Peak;
}
DataType GetPeak() {
return Peak;
}
};
// Specialize the generic adder to a 'double'
// data type adder
class DoubleAdder : public GenericAdder<double> {};
#endifUseFunc.cpp
/* Copyright 2003-2004 The MathWorks, Inc. */
// *******************************************************************
// **** To build this mex function use: mex sfun_cppcount_cpp.cpp ****
// *******************************************************************
#include "UseFunc.h"
#define S_FUNCTION_LEVEL 2
#define S_FUNCTION_NAME UseFunc
// Need to include simstruc.h for the definition of the SimStruct and
// its associated macro definitions.
#include "simstruc.h"
#include "mex.h"
#ifndef WIN32_LEAN_AND_MEAN
#define WIN32_LEAN_AND_MEAN
#endif
#include <winsock2.h>
#include <Ws2tcpip.h>
#include <stdio.h>
// Link with ws2_32.lib
#pragma comment(lib, "Ws2_32.lib")
void UseFun_StartSock(SimStruct *S);
void UseFun_SentData(SimStruct *S, const real_T *data, int DataNum);
void UseFun_CloseSock(SimStruct *S);
#define IS_PARAM_DOUBLE(pVal) (mxIsNumeric(pVal) && !mxIsLogical(pVal) &&\
!mxIsEmpty(pVal) && !mxIsSparse(pVal) && !mxIsComplex(pVal) && mxIsDouble(pVal))
// Function: mdlInitializeSizes ===============================================
// Abstract:
// The sizes information is used by Simulink to determine the S-function
// block's characteristics (number of inputs, outputs, states, etc.).
static void mdlInitializeSizes(SimStruct *S)
{
// No expected parameters
ssSetNumSFcnParams(S, 0);
// Parameter mismatch will be reported by Simulink
if (ssGetNumSFcnParams(S) != ssGetSFcnParamsCount(S)) {
return;
}
// Specify I/O
if (!ssSetNumInputPorts(S, 1)) return;
ssSetInputPortWidth(S, 0, DYNAMICALLY_SIZED);
ssSetInputPortDirectFeedThrough(S, 0, 1);
if (!ssSetNumOutputPorts(S,1)) return;
ssSetOutputPortWidth(S, 0, DYNAMICALLY_SIZED);
ssSetNumSampleTimes(S, 1);
// Reserve place for C++ object
ssSetNumPWork(S, 3);
ssSetOptions(S,
SS_OPTION_WORKS_WITH_CODE_REUSE |
SS_OPTION_EXCEPTION_FREE_CODE);
}
// Function: mdlInitializeSampleTimes =========================================
// Abstract:
// This function is used to specify the sample time(s) for your
// S-function. You must register the same number of sample times as
// specified in ssSetNumSampleTimes.
static void mdlInitializeSampleTimes(SimStruct *S)
{
ssSetSampleTime(S, 0, INHERITED_SAMPLE_TIME);
ssSetOffsetTime(S, 0, 0.0);
ssSetModelReferenceSampleTimeDefaultInheritance(S);
}
// Function: mdlStart =======================================================
// Abstract:
// This function is called once at start of model execution. If you
// have states that should be initialized once, this is the place
// to do it.
#define MDL_START
static void mdlStart(SimStruct *S)
{
// Store new C++ object in the pointers vector
DoubleAdder *da = new DoubleAdder();
ssGetPWork(S)[0] = da;
UseFun_StartSock(S);
}
// Function: mdlOutputs =======================================================
// Abstract:
// In this function, you compute the outputs of your S-function
// block.
static void mdlOutputs(SimStruct *S, int_T tid)
{
// Retrieve C++ object from the pointers vector
DoubleAdder *da = static_cast<DoubleAdder *>(ssGetPWork(S)[0]);
// Get data addresses of I/O
InputRealPtrsType u = ssGetInputPortRealSignalPtrs(S,0);
real_T *y = ssGetOutputPortRealSignal(S, 0);
int InputNum = ssGetInputPortWidth(S, 0);
for(int i=0;i<InputNum;i++)
{
y[i] = *u[i];
}
UseFun_SentData(S, y, InputNum);
}
// Function: mdlTerminate =====================================================
// Abstract:
// In this function, you should perform any actions that are necessary
// at the termination of a simulation. For example, if memory was
// allocated in mdlStart, this is the place to free it.
static void mdlTerminate(SimStruct *S)
{
// Retrieve and destroy C++ object
DoubleAdder *da = static_cast<DoubleAdder *>(ssGetPWork(S)[0]);
delete da;
UseFun_CloseSock(S);
}
void UseFun_StartSock(SimStruct *S)
{
int iResult;
WSADATA wsaData;
SOCKET *pSendSocket = new SOCKET;
*pSendSocket = INVALID_SOCKET;
sockaddr_in *pRecvAddr = new sockaddr_in;
unsigned short Port = 27015;
printf("Start socket communication, please wait...\n");
//----------------------
// Initialize Winsock
iResult = WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2, 2), &wsaData);
if (iResult != NO_ERROR) {
printf("WSAStartup failed with error: %d\n", iResult);
return ;
}
//---------------------------------------------
// Create a socket for sending data
*pSendSocket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, IPPROTO_UDP);
if (*pSendSocket == INVALID_SOCKET) {
printf("socket failed with error: %ld\n", WSAGetLastError());
WSACleanup();
return ;
}
//---------------------------------------------
// Set up the RecvAddr structure with the IP address of
// the receiver (in this example case "192.168.1.1")
// and the specified port number.
pRecvAddr->sin_family = AF_INET;
pRecvAddr->sin_port = htons(Port);
pRecvAddr->sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("127.0.0.1");
ssGetPWork(S)[1] = pSendSocket;
ssGetPWork(S)[2] = pRecvAddr;
}
void UseFun_SentData(SimStruct *S, const real_T *data, int DataNum)
{
int iResult;
char SendBuf[1024]={'\0'};
int BufLen = 1024;
SOCKET *pSendSocket = static_cast<SOCKET *>(ssGetPWork(S)[1]);
sockaddr_in *pRecvAddr = static_cast<sockaddr_in *>(ssGetPWork(S)[2]);
if (*pSendSocket == SOCKET_ERROR) {
printf("SOCKET_ERROR error: %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
closesocket(*pSendSocket);
WSACleanup();
return ;
}
//---------------------------------------------
// Send a datagram to the receiver
//printf("Sending a datagram to the receiver...\n");
int ValidateBufLen = 0;
for(int i=0;i<DataNum;i++)
{
ValidateBufLen = strlen(SendBuf);
sprintf(SendBuf+ValidateBufLen, "%g;", data[i]);
}
iResult = sendto(*pSendSocket,
SendBuf, BufLen, 0, (SOCKADDR *)pRecvAddr, sizeof(sockaddr_in));
}
void UseFun_CloseSock(SimStruct *S)
{
SOCKET *pSendSocket = static_cast<SOCKET *>(ssGetPWork(S)[1]);
sockaddr_in *pRecvAddr = static_cast<sockaddr_in *>(ssGetPWork(S)[2]);
//---------------------------------------------
// When the application is finished sending, close the socket.
printf("Finished socket communication, Closing socket.\n");
if (closesocket(*pSendSocket) == SOCKET_ERROR)
{
printf("closesocket failed with error: %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
}
//---------------------------------------------
// Clean up and quit.
WSACleanup();
delete pSendSocket;
pSendSocket = NULL;
delete pRecvAddr;
pRecvAddr = NULL;
}
// Required S-function trailer
#ifdef MATLAB_MEX_FILE /* Is this file being compiled as a MEX-file? */
#include "simulink.c" /* MEX-file interface mechanism */
#else
#include "cg_sfun.h" /* Code generation registration function */
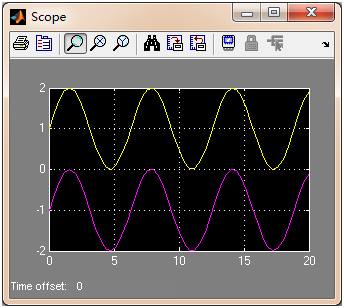
#endif运行效果图:
2.2 数据接收
通过辅助程序,收到上面自定义模型发出来的数据如下
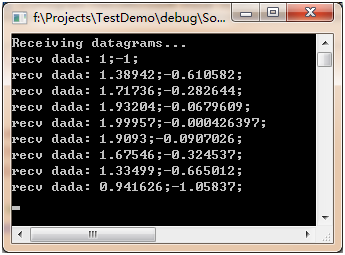
说明:分号前为第一个正弦输入信号的数据,分号后为第二个正弦输入信号的数据。
VC2005 控制台程序代码如下:
SocketServer.cpp
// SocketServer.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#ifndef UNICODE
#define UNICODE
#endif
#define WIN32_LEAN_AND_MEAN
#include <winsock2.h>
#include <stdio.h>
// Link with ws2_32.lib
#pragma comment(lib, "Ws2_32.lib")
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int iResult = 0;
WSADATA wsaData;
SOCKET RecvSocket;
sockaddr_in RecvAddr;
unsigned short Port = 27015;
char RecvBuf[1024];
int BufLen = 1024;
sockaddr_in SenderAddr;
int SenderAddrSize = sizeof (SenderAddr);
//-----------------------------------------------
// Initialize Winsock
iResult = WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2, 2), &wsaData);
if (iResult != NO_ERROR) {
wprintf(L"WSAStartup failed with error %d\n", iResult);
return 1;
}
//-----------------------------------------------
// Create a receiver socket to receive datagrams
RecvSocket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, IPPROTO_UDP);
if (RecvSocket == INVALID_SOCKET) {
wprintf(L"socket failed with error %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
return 1;
}
//-----------------------------------------------
// Bind the socket to any address and the specified port.
RecvAddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
RecvAddr.sin_port = htons(Port);
RecvAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
iResult = bind(RecvSocket, (SOCKADDR *) & RecvAddr, sizeof (RecvAddr));
if (iResult != 0) {
wprintf(L"bind failed with error %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
return 1;
}
//-----------------------------------------------
// Call the recvfrom function to receive datagrams
// on the bound socket.
wprintf(L"Receiving datagrams...\n");
iResult = 0;
int RecvNum = 0;
while(RecvNum < 100)
{
memset(RecvBuf,0,BufLen);
iResult = recvfrom(RecvSocket,
RecvBuf, BufLen, 0, (SOCKADDR *) & SenderAddr, &SenderAddrSize);
if (iResult == SOCKET_ERROR)
{
wprintf(L"recvfrom failed with error %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
break;
}
printf("recv dada: %s \n", RecvBuf);
RecvNum++;
}
//-----------------------------------------------
// Close the socket when finished receiving datagrams
wprintf(L"Finished receiving. Closing socket.\n");
iResult = closesocket(RecvSocket);
if (iResult == SOCKET_ERROR) {
wprintf(L"closesocket failed with error %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
return 1;
}
//-----------------------------------------------
// Clean up and exit.
wprintf(L"Exiting.\n");
WSACleanup();
return 0;
}http://www.cnblogs.com/xpvincent/archive/2013/02/05/2892978.html






















 328
328

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








