MNIST 手写体识别通常是神经网络入门的一个例子,每个deep框架 都无例外。
一. MNIST数据
MNISt 为 0-9的手写阿拉伯数字,提供了6万的 训练集数据(mnist.train) 和 1万的 测试集数据(mnist.test)。
下载地址:http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/index.html
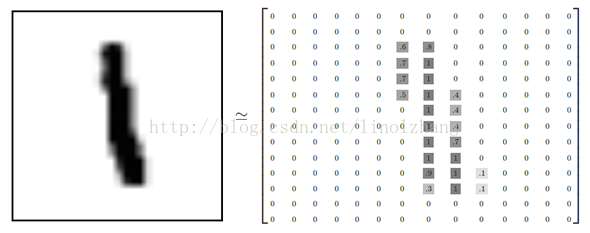
如上图所示,数据格式为 28*28的灰度图,图片表示为矩阵形式(有填充的地方为正值,无填充为0):
每个数据均包含对应标签 Label(Ground Truth),标签结果是一个10维的float数组,对应每个数字的概率:
0 -> [1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0 ]
5 -> [ 0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0 ]
即对应位的概率为 1,其他位为 0。
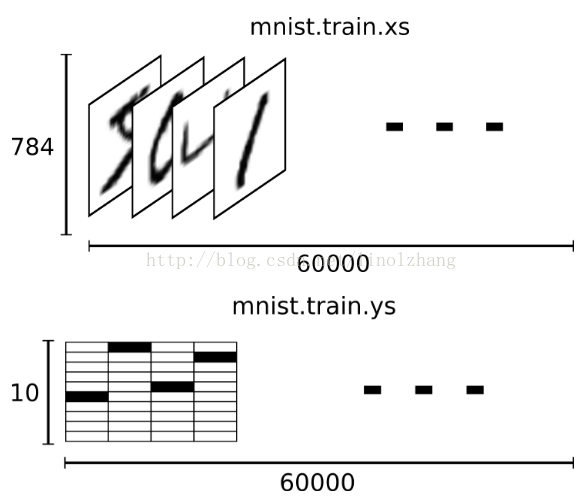
这样我们就得到了一组对应的 输入-输出,即 输入为 28*28=784维向量,输出为10维向量:
二. MNIST网络结构
MNIST 采用LeNet-5,因Lecun而命名,该网络拓扑图结构(caffe结构图,看着比Tensor的清晰一些):
数据层 Data -> 隐层 Layer1 -> 隐层 Layer2 -> 全连接层 FC1 -> 全连接层 FC2 -> Loss | Accuracy
conv1 conv2 innerProduct innerProduct Softmax
pool1 pool2
激活层根据需要添加,一般放在 Pooling层后面,这个就根据需要了。
三. TensorFlow运行
TensorFlow提供了MNIST 的例子,我们直接上Python代码,可以自己测试运行:
#coding=utf-8
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
# define W & b
def weight_variable(para):
# 采用截断的正态分布,标准差stddev=0.1
initial = tf.truncated_normal(para,stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def bias_variable(para):
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=para)
return tf.Variable(initial)
# define conv & pooling
def conv2d(x,W):
return tf.nn.conv2d( x,W,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME' )
def max_pool_2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME')
# define using data
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None,784]) # 28*28=784 dim
x_input = tf.reshape(x, [-1,28,28,1]) # reshape for conv, -1表示不固定数量,1为通道数
y_label = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10]) # label - 10 dim
# define layer1
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5,5,1,32]) # Weight in:1 out:32
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32]) # bias
h_relu1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_input,W_conv1) + b_conv1) # relu
h_pool1 = max_pool_2(h_relu1) # pool after relu1
# define layer2
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5,5,32,64]) # Weight in:32 out:64
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64]) # bias for 64 kernel
h_relu2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1,W_conv2) + b_conv2) # relu
h_pool2 = max_pool_2(h_relu2) # pool after relu2
# define full connection layer1
W_fc1 = weight_variable([7*7*64,1024]) # Weight in:7*7res*64 out:1024
b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024]) # bias for 1024
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1,7*7*64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1)
# 添加Drop Out层,预防过拟合,通过keep_prob传入需要保持(不Drop)的样本比率
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
drop_fc1 = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1,keep_prob)
# 第二个全连接层,采用softmax执行回归
W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024,10]) # Weight in:1024 out:10
b_fc2 = bias_variable([10]) # bias for 10, 10类划分
y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(drop_fc1,W_fc2) + b_fc2) # 计算结果
# 定义loss
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y_label*tf.log(y),reduction_indices=[1]))
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.001).minimize(cross_entropy) # Adam 替代SGD
# 定义准确率
correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1), tf.argmax(y_label,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred,tf.float32))
# 执行训练
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
for i in range(20000):
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(50) # 每50个一个batch
if i%100 == 0:
# eval执行过程-训练精度
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x:batch[0], y_label:batch[1], keep_prob:1.0})
print("step %d, training accuracy %g"%(i,train_accuracy))
train_step.run(feed_dict={x:batch[0], y_label:batch[1], keep_prob:0.5})
# 测试数据精度
print("test accuracy %g"%accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images, y_label:mnist.test.labels, keep_prob:1.0}))
























 901
901

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








