- #include <iostream.h>
- #include <math.h>
- #define Precision 0.000001 //控制精度要求
- #define MaxIterative 60 //最大允许迭代次数
- void function(double &x,double &y0,double &y1)
- {
- y0=x*x*x-3*x-1.0;//原函数
- y1=3.0*x*x-3; //函数导数
- }
- double NewtonIterative (double &x,void f(double &x,double &y0,double &y1))
- {
- int MI;
- double y0,y1,PCS,x0,x1,PCSy;//MI均来计算迭代的次数,PCS表示x0与x1的差,PCSy表示x1对应的y的绝对值
- MI=MaxIterative;
- x0=x;
- f(x0,y0,y1); //先运行一次,计算出y0,y1
- PCS=Precision+1.0;
- while ((PCS>=Precision)&&(MI!=0))//结束迭代过程的条件,x,y
- {
- if (fabs(y1+1.0==1.0))//判断导数是否为0
- {
- cout<<"wrong";
- return -1;
- }
- x1=x0-y0/y1; //迭代计算x1=x0-f(x0)/f'(x0);
- f(x1,y0,y1);
- PCS=fabs(x1-x0);
- PCSy=fabs(y0);
- if(PCSy>PCS)
- PCS=PCSy;
- x0=x1;
- MI=MI-1;
- }
- x=x1; //把最后求出的结果付给x
- return MaxIterative-MI;//迭代的次数
- }
- main()
- {
- int k;
- double x;
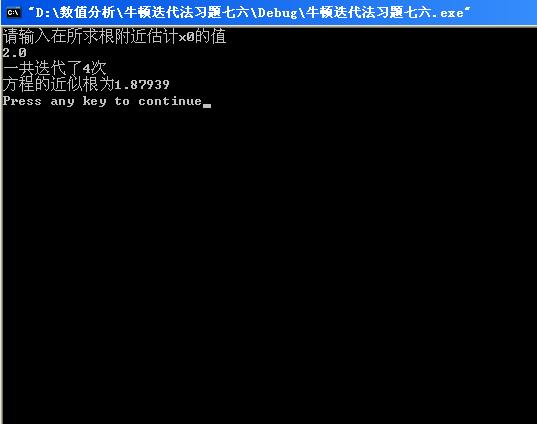
- cout<<"请输入在所求根附近估计x0的值"<<endl;
- cin>>x;
- k=NewtonIterative (x,function);
- if (k>=0)
- {
- cout<<"一共迭代了"<<k<<"次"<<endl;
- cout<<"方程的近似根为"<<x<<endl;
- }
- return 0;
- }
牛顿迭代法






















 4180
4180

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








