-
结构
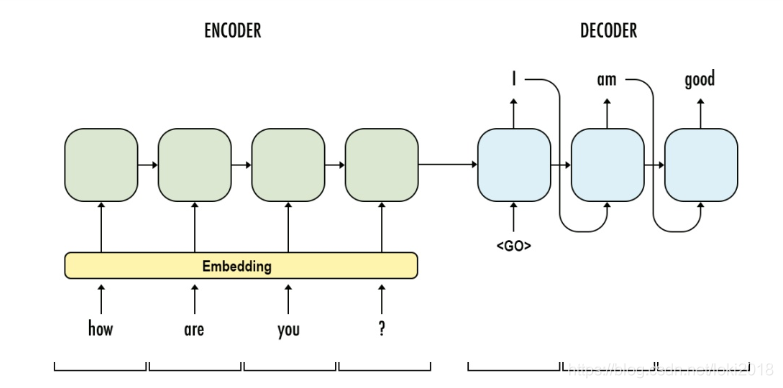
这是一种经典的Seq2Seq结构,由两部分组成,Encoder 和 Decoder(编码器和解码器), 这两个部分的构造几乎一模一样,都是由循环神经网络组成,层数,隐藏层维度都是一样的。
它的原理是一个序列输入到编码器之后,编码器输出最后的隐藏状态(h)到解码器, h包含了序列的前后信息,然后通过解码器对h处理,逐步生成相应的预测序列。
-
Encoder
以下是Encoder的一段基本代码,由最基本的RNN组成:
需要弄清楚它矩阵的变换。
class EncoderRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,input_size, hidden_size, n_layers, emb_size, dropout=0.5, bidirections=False):
"""
:param input_size:源序列的编码总数, 例如英文26个字母,那么这里就是26
:param hidden_size:隐藏层参数
:param n_layers: 网络层数
:param emb_size: embedding维度
:param dropout: dropout参数
:param bidierctions: 双向还是单向
"""
super(EncoderRNN, self).__init__()
self.input_size = input_size
self.n_layers = n_layers
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.emb_size = emb_size
self.dropout = dropout
self.bidirecions = bidirections
self.Embedding = nn.Embedding(self.input_size, self.emb_size) # embedding编码
self.RNN = nn.RNN(self.emb_size, self.hidden_size, self.n_layers, dropout=self.dropout, bidirectional=self.bidirecions)
def forward(self, src):
# src [seq_len, batch]
embedded = self.Embedding(src)
#embedded [seq_len, batch, emb_size]
out, h = self.RNN(embedded)
# out [seq_len, batch, direction*hidden_size]
# h [n_layers*directions, batch, hidden_size]
return out, h
然后我们任意设定一个序列输入到网络中,pytorch中的循环神经网络喂入的数据形式比较特殊,它的batch_size并不是在第一维,而是在第二维,因此我们的数据也要做相应的调整。
if __name__ == "__main__":
INPUT_SIZE = 10
HIDDEN_SIZE = 20
N_LAYERS = 2
EMB_SIZE = 10
model = EncoderRNN(INPUT_SIZE, HIDDEN_SIZE, N_LAYERS, EMB_SIZE)
x = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3, 4, 9], [2, 2, 3, 4, 6]]).T # 做转置就是为了将batch放到第二维
# batch : 2
# seq_len : 5
out, h = model(x)
print(f"out shape is {out.shape}")
print(f"h shape is {h.shape}")
"""
out shape is torch.Size([5, 2, 20])
h shape is torch.Size([2, 2, 20])
"""
由此可见,输出的维度符合我们的预期。学习RNN最重要的就是要弄明白这里面的维度变化。
- Decoder
以下是解码器部分的代码,需要注意解码器的输入和编码器的区别
class DecoderRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, out_dim, hidden_size, n_layers, emb_size, dropout=0.5, bidirections=False):
"""
:param out_dim:目标序列的编码长度,若是中文翻译为英文,那么英文就是目标序列,那这里就是26
:param hidden_size: 隐藏层维度,和编码器一致
:param n_layers: 层数,和编码器一致
:param emb_size: embedding维度,任意,为了方便一般和编码器一致
:param dropout: dropout参数
:param bidirections: 双向或是单向,和编码器一致
"""
super(DecoderRNN, self).__init__()
self.out_dim = out_dim
self.n_layers = n_layers
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.emb_size = emb_size
self.dropout = dropout
self.bidirecions = bidirections
self.Embedding = nn.Embedding(self.out_dim, self.emb_size) # embedding编码
self.RNN = nn.RNN(self.emb_size, self.hidden_size, self.n_layers, dropout=self.dropout,
bidirectional=self.bidirecions)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.softmax = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1) # 由于后面使用的损失函数是NLLLOSS,要做个logsoftmax,如果用的是CrossEntropyLoss可以不用加这一操作
# 定义线性层
if bidirections:
self.fc_out = nn.Linear(hidden_size*2, self.out_dim)
else:
self.fc_out = nn.Linear(hidden_size, self.out_dim)
def forward(self, token_input, hidden):
"""
需要注意的是解码器的输入:每次都是输入一个单步的词或者字,还有来自编码器的h
第一次的输入是开始符
:param token_input:[batch]
:param hidden: [directions*n_layers, batch, hidden_size]
"""
embedded = self.dropout(self.Embedding(token_input)) # 这里可以增加一个dropout,减少过拟合
# embedded [batch, emb_size]
embedded = embedded.unsqueeze(0) # 为了保证输入到RNN中的形状正确,那么要对它升一个维度
# embedded [1, batch, emb_size]
out, hidden = self.RNN(embedded)
# out [1, batch, hidden_size*directions]
# hidden [directions*n_layers, batch, hidden_size]
out = self.fc_out(out)
# out [1, batch, out_dim]
out = out.squeeze(0) # 降一次维
# out [batch, out_dim]
out = self.softmax(out)
# 这里的out就是我们预测的值了
# hidden在传给下一个时间步使用
return out, hidden
任意取一个初始开始字符数组输入到解码器中
if __name__ == "__main__":
INPUT_DIM = 10
OUT_DIM = 8
HIDDEN_SIZE = 20
N_LAYERS = 2
EMB_SIZE = 10
encoder = EncoderRNN(INPUT_DIM, HIDDEN_SIZE, N_LAYERS, EMB_SIZE)
decoder = DecoderRNN(OUT_DIM, HIDDEN_SIZE, N_LAYERS, EMB_SIZE)
x = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3, 4, 9], [2, 2, 3, 4, 6]]).T
# batch : 2
# seq_len : 5
out, h = encoder(x)
token = torch.tensor([0, 0])
print(f"encoder out shape is {out.shape}")
print(f"encoder h shape is {h.shape}")
out, h = decoder(token, h)
print(f"decoder out shape is {out.shape}")
print(f"decoder h shape is {h.shape}")
"""
encoder out shape is torch.Size([5, 2, 20])
encoder h shape is torch.Size([2, 2, 20])
decoder out shape is torch.Size([2, 8])
decoder h shape is torch.Size([2, 2, 20])
"""
- Seq2Seq
最后只需要将编码器和解码器组合到一起就是一个完整的Seq2Seq模型了
class Seq2Seq(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, encoder, decoder, device, max_len=5):
"""
:param encoder: 编码器模块
:param decoder: 解码器模块
:param device: 训练设备类型
:param max_len: 预测序列的最大长度
"""
super(Seq2Seq, self).__init__()
self.encoder = encoder
self.decoder = decoder
self.max_len = max_len
self.device = device
en_layers = self.encoder.n_layers
de_layers = self.decoder.n_layers
en_hid = self.encoder.hidden_size
de_hid = self.decoder.hidden_size
en_direction = self.encoder.bidirections
de_direction = self.decoder.bidirections
# 编码器和解码器需要保证以下参数都是一致的
assert en_layers == de_layers, \
"Hidden dimensions of encoder and decoder must be equal!"
assert en_hid == de_hid, \
"Encoder and decoder must have equal number of layers!"
assert en_direction == de_direction, \
"If decoder is bidirectional, encoder must be bidirectional either!"
def forward(self, src):
self.encoder.to(self.device)
self.decoder.to(self.device)
# src [seq_len, batch]
en_out, hidden = self.encoder(src)
# en_out [seq_len, batch, direction*hidden_size]
# hidden [n_layers*directions, batch, hidden_size]
batch_size = en_out.shape[1]
#设置一个张量来存储所有的解码器输出
all_decoder_outputs = torch.zeros((self.max_len, batch_size, self.decoder.out_dim), device=self.device)
token = torch.tensor([0, 0], device=device) # decoder的初始输入
for i in range(self.max_len):
de_out, hidden = decoder(token, hidden)
all_decoder_outputs[i] = de_out
# de_out [batch, out_dim]
topv, topi = de_out.topk(1) # 获取每个batch预测的最大概率值以及索引,索引对应的目标序列就是预测的值
token = topi.flatten() # 解码器下一次的输入
# 最后返回输出的所有概率矩阵来计算交叉熵损失
return all_decoder_outputs
设置一组标签和特征,送入网络中,得到的结果计算交叉熵损失。
if __name__ == "__main__":
INPUT_DIM = 10
OUT_DIM = 8
HIDDEN_SIZE = 20
N_LAYERS = 2
EMB_SIZE = 10
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
encoder = EncoderRNN(INPUT_DIM, HIDDEN_SIZE, N_LAYERS, EMB_SIZE)
decoder = DecoderRNN(OUT_DIM, HIDDEN_SIZE, N_LAYERS, EMB_SIZE)
x = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3, 4, 9], [2, 2, 3, 4, 6]], device=device).T
y = torch.tensor([[3, 1, 3, 4, 6], [4, 1, 3, 4, 4]], device=device).reshape(-1)
# batch : 2
# seq_len : 5
seq2seq = Seq2Seq(encoder, decoder, device)
o = seq2seq(x)
print(o.shape)
criterion = nn.NLLLoss()
loss = criterion(o.reshape(-1, OUT_DIM), y)
print(loss)
"""
torch.Size([5, 2, 8])
tensor(2.0671, device='cuda:0', grad_fn=<NllLossBackward>)
"""





















 833
833











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








