代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
typedef struct DoubleLinkedNode {
char data;
struct DoubleLinkedNode *previous;//previous是用于指向当前节点的前一节点的指针
struct DoubleLinkedNode *next;
}DLNode,*DLNodePtr;
DLNodePtr initLinkList() {
DLNodePtr tempHeader = (DLNodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct DoubleLinkedNode));
tempHeader->data = '\0';
tempHeader->previous = NULL;
tempHeader->next = NULL;
return tempHeader;
}
void printList(DLNodePtr paraHeader) {
DLNodePtr p = paraHeader->next;
while (p != NULL) {
printf("%c", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\r\n");
}
void insertElement(DLNodePtr paraHeader, char paraChar, int paraPosition) {
DLNodePtr p, q, r;
p = paraHeader;
for (int i = 0; i < paraPosition; i++) {
p = p->next;
if (p == NULL) {
printf("The position % d is beyond the scope of the list.", paraPosition);
return;
}
}
q = (DLNodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct DoubleLinkedNode));
q->data = paraChar;
r = p->next;
q->next = p->next;
q->previous = p;
p->next = q;
if (r != NULL) {
r->previous = q;
}
}
void deleteElement(DLNodePtr paraHeader, char paraChar) {
DLNodePtr p, q, r;
p = paraHeader;
while ((p->next != NULL) && (p->next->data != paraChar)) {
p = p->next;
}
if (p->next == NULL) {
printf("The char '%c' does not exist.\r\n", paraChar);
return;
}
q = p->next;
r = q->next;
p->next = r;
if (r != NULL) {
r->previous = p;
}
free(q);
}
void insertDeleteTest() {
DLNodePtr tempList = initLinkList();
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'H', 0);
insertElement(tempList, 'e', 1);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 2);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 3);
insertElement(tempList, 'o', 4);
insertElement(tempList, '!', 5);
printList(tempList);
deleteElement(tempList, 'e');
deleteElement(tempList, 'a');
deleteElement(tempList, 'o');
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'o', 1);
printList(tempList);
}
void basicAddressTest() {
DLNode tempNode1, tempNode2;
tempNode1.data = 4;
tempNode1.next = NULL;
tempNode2.data = 6;
tempNode2.next = NULL;
printf("The first node: %d, %d, %d\r\n",&tempNode1, &tempNode1.data, &tempNode1.next);
printf("The second node: %d, %d, %d\r\n",&tempNode2, &tempNode2.data, &tempNode2.next);
tempNode1.next = &tempNode2;
}
void main(){
insertDeleteTest();
basicAddressTest();
}运行结果
Hello!
The char 'a' does not exist.
Hll!
Holl!
The first node: 1880291032, 1880291032, 1880291048
The second node: 1880291080, 1880291080, 1880291096代码说明
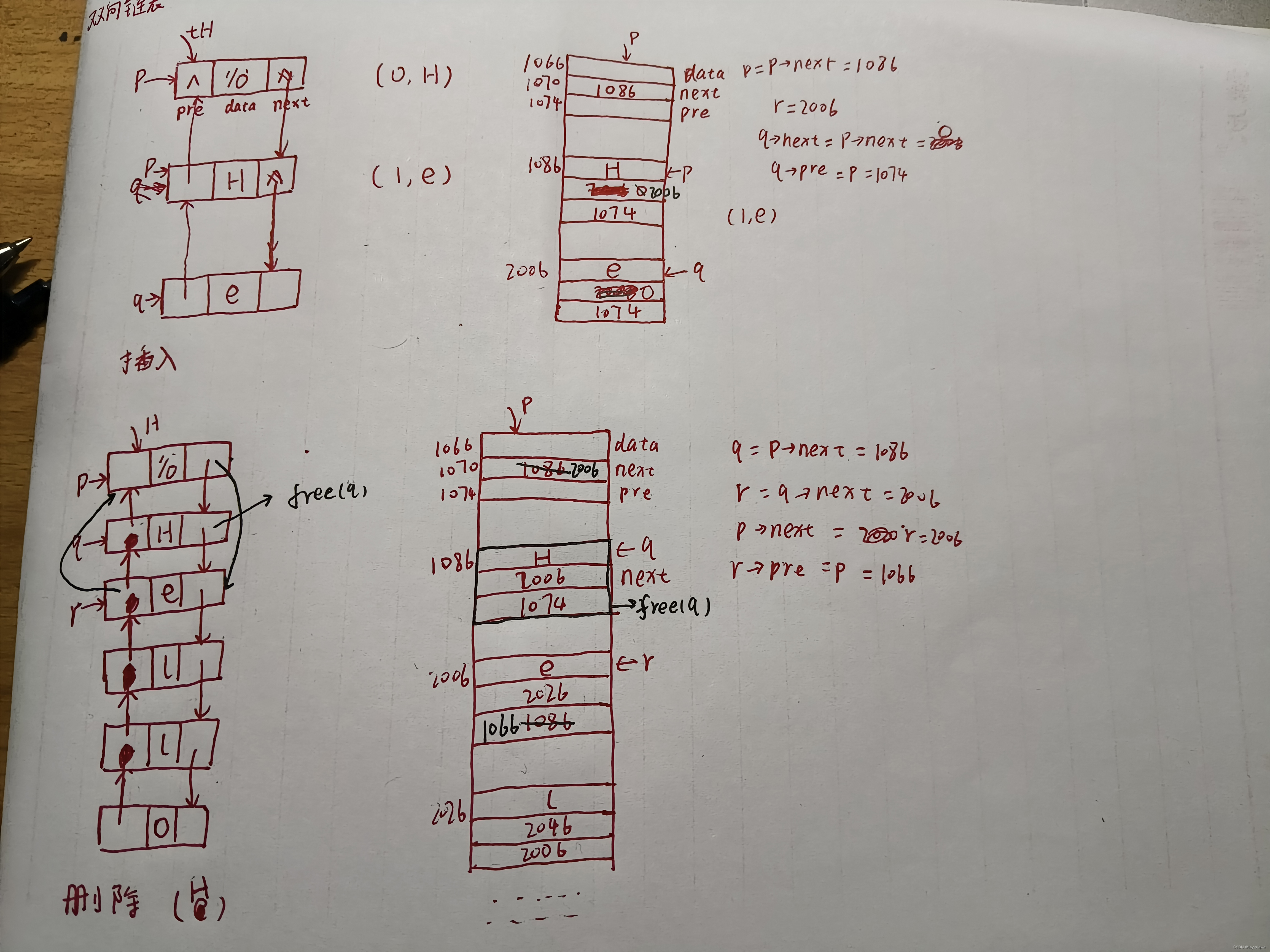
双向链表是一种常见的数据结构,它允许我们在任何方向上遍历链表。每个节点都包含两个链接:一个指向前一个节点,另一个指向下一个节点。双向链表提供了从前往后和从后往前遍历数据的能力。这种双向遍历的能力在某些应用中非常有用,比如当需要反向查找或修改数据时
1.在执行insertElement函数和deleteElement函数时,双向链表不需要遍历整个链表,只需要知道所需修改的节点的前驱和后继指针来插入或删除节点
图示解说





















 3923
3923

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








