目录
前面两章介绍了线程基础及线程Dump日志分析,Java线程<一> _ 介绍、Java线程<二> _ Thread Dump日志分析。本章详细介绍线程间通信及数据传输及代码实例。
一、构造线程
当我们创建线程的时候,如下代码所示。
Thread createThread = new Thread(new CreateThread(threadLocal), "CreateThread");java.lang.Thread中初始化线程实际调用init()方法,该方法设置了线程所需的属性,如线程组、优先级、是否是Daemon线程等信息。如下代码是摘自init()初始化的部分代码。注意:一个新构造的线程是由其父线程进行空间分配。
// 初始化线程
private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,
long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc,
boolean inheritThreadLocals) {
if (name == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null");
}
// 设置线程名称
this.name = name;
// 获取父线程,即:当前线程
Thread parent = currentThread();
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (g == null) {
/* Determine if it's an applet or not */
/* If there is a security manager, ask the security manager
what to do. */
if (security != null) {
g = security.getThreadGroup();
}
/* If the security doesn't have a strong opinion of the matter
use the parent thread group. */
if (g == null) {
g = parent.getThreadGroup();
}
}
/* checkAccess regardless of whether or not threadgroup is
explicitly passed in. */
g.checkAccess();
/*
* Do we have the required permissions?
*/
if (security != null) {
if (isCCLOverridden(getClass())) {
security.checkPermission(SUBCLASS_IMPLEMENTATION_PERMISSION);
}
}
g.addUnstarted();
// 创建线程的属性设置为父线程对应的属性
this.group = g;
this.daemon = parent.isDaemon();
this.priority = parent.getPriority();
// 获取该线程的类加载器
if (security == null || isCCLOverridden(parent.getClass()))
this.contextClassLoader = parent.getContextClassLoader();
else
this.contextClassLoader = parent.contextClassLoader;
this.inheritedAccessControlContext =
acc != null ? acc : AccessController.getContext();
this.target = target;
setPriority(priority);
// 将父线程的ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap复制给新线程,可继承的ThreadLocal
if (inheritThreadLocals && parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null)
this.inheritableThreadLocals =
ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals);
/* Stash the specified stack size in case the VM cares */
// 设置线程的堆栈大小
this.stackSize = stackSize;
/* Set thread ID */
// 分配一个线程ID
tid = nextThreadID();
}二、启动线程
start()方法的含义:当前线程(父线程)同步通知JVM,只要线程规划器空闲,则立即调用start()来启动线程。
三、等待/通知机制
1. 等待/通知机制
等待/通知机制是指,一个线程A调用了对象O的wait()方法进入等待状态,而另一个线程B调用了对象O的notify()或者notifyAll()方法,线程A收到通知后从对象O的wait()方法返回,进而执行后续操作。上述两个线程通过对象O来完成交互,而对象上的wait()和notify/notifyAll()用来完成等待方和通知方之间的交互工作。
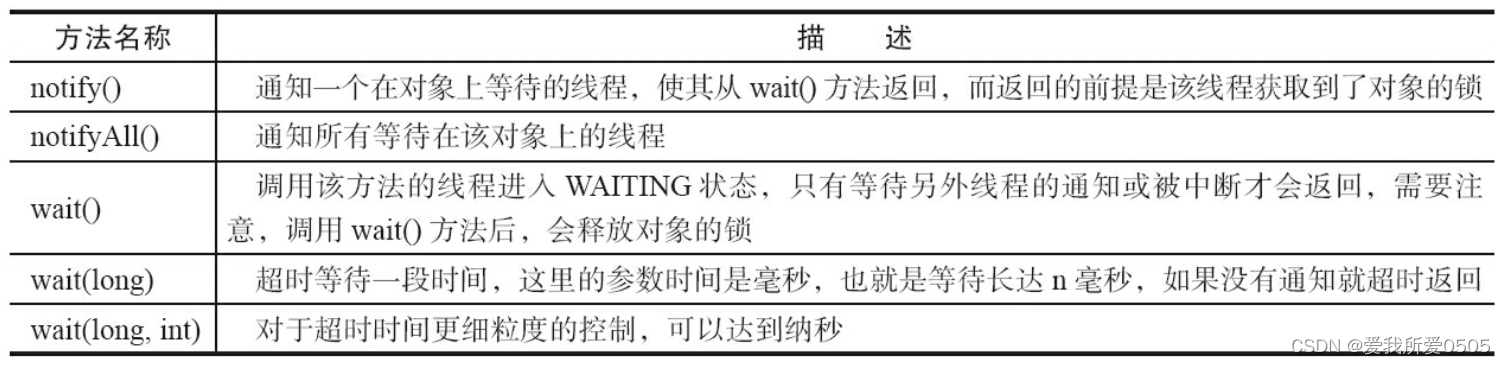
wait()、notify/notifyAll()方法都是java.lang.Object类中的方法,如上表所示的方法。一个对象拥有一个同步队列和一个等待队列。使用注意问题:
- 调用wait()、notify/notifyAll()时,先对调用对象加锁;
- 调用wait()后,当前线程状态由RUNNING变为WAITING,释放锁,该线程放入等待队列中;
- 调用notify/notifyAll()后,等待线程状态由WAITING变为BLOCKED,等待线程从等待队列移到同步队列中,当前线程释放锁后等待线程从wait()返回;
- 从wait()返回必须获取对象的锁。
2. 代码实例
package com.thread;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @description 测试线程wait()、notify()
* @author TCM
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022/4/5 13:42
**/
public class WaitAndNotifyTest {
public static boolean flag = true;
public static Object lock = new Object();
public static SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss");
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread waitThread = new Thread(new WaitThread(), "WaitThread");
waitThread.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
Thread notifyThread = new Thread(new NotifyThread(), "NotifyThread");
notifyThread.start();
}
public static class WaitThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
// lock加锁
synchronized (lock) {
while (flag) {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " flag is true. wait @" + dateFormat.format(new Date()));
/*
* 调用lock的wait():
* a. 当前线程释放lock对象的锁对象;
* b. 当前线程由RUNNING变为WAITING状态;
* c. 当前线程进入等待队列中。
*/
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 业务处理
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " flag is false. running @" + dateFormat.format(new Date()));
}
}
}
public static class NotifyThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
// lock加锁
synchronized (lock) {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " flag is true. notify @" + dateFormat.format(new Date()));
/*
* 调用lock的notify():
* a. 等待线程状态由WAITING变为BLOCKED;
* b. 等待线程从等待队列移到同步队列中;
* c. 当前线程释放锁后等待线程从wait()返回。
*/
lock.notifyAll();
flag = false;
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 业务处理,再次获取lock对象的锁
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " hold lock again. sleep @" + dateFormat.format(new Date()));
}
}
}
}
以上代码执行结果,如下所示。第三、四行可能执行结果互换。
Thread[WaitThread,5,main] flag is true. wait @19:09:12
Thread[NotifyThread,5,main] flag is true. notify @19:09:13
Thread[NotifyThread,5,main] hold lock again. sleep @19:09:18
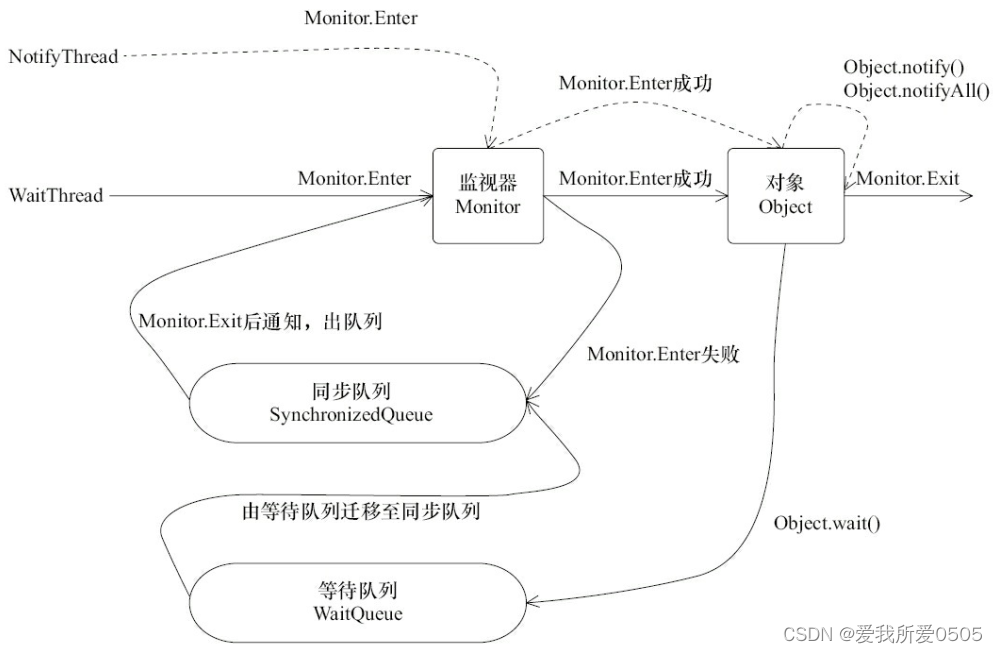
Thread[WaitThread,5,main] flag is false. running @19:09:18如下图所示,是代码实例执行的过程。
- 1):WaitThread首先获取了对象的锁;
- 2):调用对象的wait()方法,从而放弃了锁并进入了对象的等待队列WaitQueue中,进入等待状态;
- 3):NotifyThread随后获取了对象的锁,并调用对象的notify()方法,将WaitThread从WaitQueue移到SynchronizedQueue中,此时WaitThread的状态变为阻塞状态;
- 4):NotifyThread释放了锁之后,WaitThread与NotifyThread进行锁竞争;
- 5):NotifyThread再次获取到锁执行业务处理。
四、管道输入/输出流
管道输入/输出流的作用是线程之间的数据传输,内存为传输媒介。其分类为:
- 字节:PipedOutputStream、PipedInputStream
- 字符:PipedReader、PipedWriter
package com.thread;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PipedReader;
import java.io.PipedWriter;
/**
* @description 线程间数据传输 - 管道测试
* @author TCM
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022/4/5 13:51
**/
public class PipedTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
PipedWriter out = new PipedWriter();
PipedReader in = new PipedReader();
// 输出流连接输入流,否则报异常
out.connect(in);
Thread printThread = new Thread(new PrintThread(in), "PrintThread");
printThread.start();
int receive = 0;
try {
while ((receive = System.in.read()) != -1) {
out.write(receive);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static class PrintThread implements Runnable {
private PipedReader in;
public PrintThread(PipedReader in){
this.in = in;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int receive = 0;
try {
while ((receive = in.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) receive);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
运行该实例,输入字符串,如下所示:
test thread piped
test thread piped
注意:Piped类型的流,则必须要提前绑定,即:out.connect(in),否则会抛出异常。
五、参考资料
Java线程<一> _ 介绍_爱我所爱0505的博客-CSDN博客
Java线程<二> _ Thread Dump日志分析_爱我所爱0505的博客-CSDN博客_java 线程日志分析
InheritableThreadLocal——父线程传递本地变量到子线程的解决方式及分析_代码小司机的博客-CSDN博客_threadlocal传递到子线程





















 1955
1955











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








