491.递增子序列
思路:
1.确定回溯函数参数:定义全局遍历存放res集合和单个path,还需要
- nums数组
- startindex(int)为下一层for循环搜索的起始位置。
2.终止条件:当startindex >len(nums),return;如果len(path) >= 2,则将当前递增子序列添加到 res 数组中(注意:不用返回,因为还要继续向下查找)
3.遍历过程:去重,for循环层(树层)不能使用相同元素
- 判断nums[i]在本层是否出现过,出现过跳出
- 判断是否递增,非递增跳出
- 若不跳出:记录nums[i],加入path,继续遍历,回溯
class Solution:
def findSubsequences(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
path = []
def backtrack(nums,startindex):
if startindex>len(nums):
return
if len(path)<=len(nums) and len(path) >= 2:
res.append(path[:])
nums_dict = set()
for i in range(startindex,len(nums)):
if path and path[-1]>nums[i] or nums[i] in nums_dict:
continue
nums_dict.add(nums[i])
path.append(nums[i])
backtrack(nums,i+1)
path.pop()
backtrack(nums,0)
return res
46.全排列
思路:
首先排列是有序的,也就是说 [1,2] 和 [2,1] 是两个集合,这和之前分析的子集以及组合所不同的地方。
1.确定回溯函数参数:定义全局遍历存放res集合和单个path,还需要
- nums数组
2.终止条件:当len(path)==len(nums)时,将当前结果放入res
3.遍历过程:去重,for循环层(树层)不能使用相同元素
- 判断nums[i]在本层是否出现过,出现过跳出
- 判断是否递增,非递增跳出
- 若不跳出:记录nums[i],加入path,继续遍历,回溯
class Solution:
def permute(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
path = []
def backtrack(nums):
if len(path)==len(nums):
res.append(path[:])
return
for i in range(len(nums)): #枚举可选择元素
if nums[i] in path: #选取不在当前路劲元素
continue
path.append(nums[i]) #选择元素
backtrack(nums) #递归搜索
path.pop() #撤销选择
backtrack(nums)
return res
47.全排列 II
思路:
重复数字数组,去重一定要对元素进行排序,这样我们才方便通过相邻的节点来判断是否重复使用了
1.确定回溯函数参数:定义全局遍历存放res集合和单个path,还需要
- nums数组
- check数组,记录此时path里都有哪些元素使用了,一个排列里一个元素只能使用一次
2.终止条件:当len(path)==len(nums)时,将当前结果放入res
3.遍历过程:去重,for循环层(树层)不能使用相同元素
- 判断nums[i]是否使用过,if check[i] ==1
- 判断前一个相同元素 是否使用过,if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1] and check[i-1] == 0:
- 若不跳出:check[i]=1,选择元素,递归,回溯,check[i]=0
1. if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1] and check[i-1] == 0
灰色为剪枝部分,蓝色为答案部分: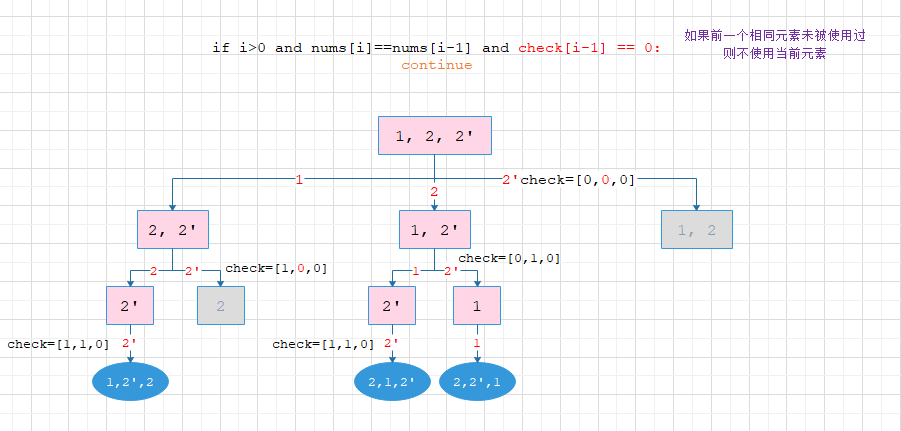
2. if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1] and check[i-1] == 1
灰色为剪枝部分,蓝色为答案部分: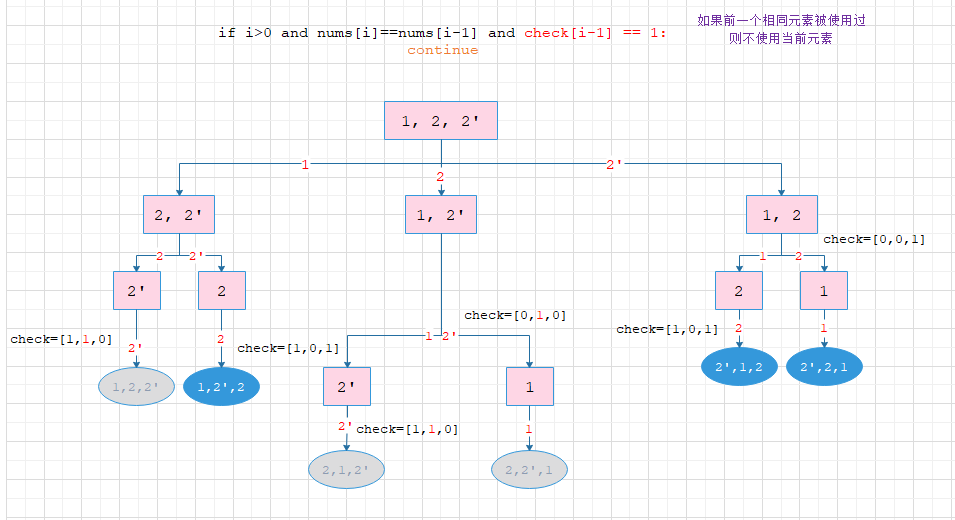
能够明显发现第一种能够提前剪枝,减少计算步骤和搜索次数,并且第一种选择了重复元素的第一个,而第二种选择了重复元素的最后一个
参考链接 :47. 全排列 II - 力扣(Leetcode)题解
class Solution:
def permuteUnique(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
path = []
nums.sort()
check = [0 for i in range(len(nums))]
def backtrack(nums,check):
if len(path)==len(nums):
res.append(path[:])
return
for i in range(len(nums)):
if check[i] == 1:
continue
if i > 0 and nums[i]==nums[i-1] and check[i-1] == 0:
continue
check[i] = 1
path.append(nums[i]) #选择元素
backtrack(nums,check) #递归搜索
path.pop() #撤销选择
check[i] = 0
backtrack(nums,check)
return res






















 367
367











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








