yolov5-7.0是yolo官方不久前出的一种实例分割的算法,讲实话yolov5系列的代码都不好阅读,不管是马赛克数据集部分,还是推理部分。今天博主自己根据yolov5-7.0源码进行了精简推理。有pt和torchscript两种,其实大差不差,只是有几个地方需要改动。话不多说,看代码。
首先我们从github中下载官方的yolov5-7.0源码。为了方便,将其copy一份修改。
目录如下:
拿到代码后,先别管其他,python segment/predict.py一下。能运行成功,在扯其他。要不然都是扯淡。yolo系列的代码对环境要求都很友好,只要装了torch基本就能成。
这里假设各位都成功了,我们进行第二步。
copy我的代码去你电脑上运行,改图像路径,模型路径, 名字 就行了。运行成功了再看,否则还是扯淡。注释都写好了,最好结合源码debug去看,很简单就能明白整个逻辑。因为所有这种任务无非就是 加载模型 -> 对数据进行前处理 -> forward -> 后处理
pt版:
'''
自己写的yolov7分割推理代码
只支持图片 视频流和截图等要查看源码
'''
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torchvision
import cv2
import math
from pathlib import Path
import argparse
import numpy as np
FILE = Path(__file__).resolve() # 获取当前文件的绝对路径
ROOT = FILE.parents[0] # 获取当前文件所在这一级的父目录
def load_model(weights, device=None):
ckpt = torch.load(str(weights), map_location='cuda:0')
ckpt = ckpt['model'].to(device).float()
# model.append(ckpt.eval())
return ckpt.eval()
def load_image(path, image_size, stride=32):
'''
args:
path: 图像路径
image_size: 只是一种图像尺寸而已
return:
im: 经过尺寸变换 padding过后的图像 大小为
copy_img: 原图
other: 不用关注
'''
img = cv2.imread(path)
copy_img = img.copy()
shape = img.shape[:2]
ratio = min(image_size[0] / shape[0], image_size[1] / shape[1])
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1]*ratio)), int(round(shape[0]*ratio)) # 缩放后的尺寸
dw, dh = image_size[1] - new_unpad[0], image_size[0] - new_unpad[1] # 计算目标图像与缩放后图像的差值
dw, dh = np.mod(dw, stride), np.mod(dh, stride) # 计算dw/stride dh/stride的余数
dw /= 2 # 确定需要填充的pad
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
im = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR) # 如果原图大小不等于缩放后图像大小的话 就resize到这个大小
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1)) # 为图像添加边框
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=(114, 114, 114)) # add border
cv2.imwrite('./forward.jpg', im)
return im, copy_img, ratio, (dw, dh)
def scale_image(im1_shape, masks, im0_shape, ratio_pad=None):
"""
img1_shape: model input shape, [h, w]
img0_shape: origin pic shape, [h, w, 3]
masks: [h, w, num]
"""
# Rescale coordinates (xyxy) from im1_shape to im0_shape
if ratio_pad is None: # calculate from im0_shape
gain = min(im1_shape[0] / im0_shape[0], im1_shape[1] / im0_shape[1]) # 短边缩放大小
pad = (im1_shape[1] - im0_shape[1] * gain) / 2, (im1_shape[0] - im0_shape[0] * gain) / 2 # w,h需要补齐的pad大小
else:
pad = ratio_pad[1]
top, left = int(pad[1]), int(pad[0]) # y, x 左上
bottom, right = int(im1_shape[0] - pad[1]), int(im1_shape[1] - pad[0]) # 右下
if len(masks.shape) < 2:
raise ValueError(f'"len of masks shape" should be 2 or 3, but got {len(masks.shape)}')
masks = masks[top:bottom, left:right]
masks = cv2.resize(masks, (im0_shape[1], im0_shape[0]))
if len(masks.shape) == 2:
masks = masks[:, :, None]
return masks
def xywh2xyxy(x):
# Convert nx4 boxes from [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2] where xy1=top-left, xy2=bottom-right
y = x.clone() if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) else np.copy(x)
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2 # top left x
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2 # top left y
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2 # bottom right x
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2 # bottom right y
return y
def scale_boxes(img1_shape, boxes, img0_shape, ratio_pad=None):
# Rescale boxes (xyxy) from img1_shape to img0_shape
if ratio_pad is None: # calculate from img0_shape
gain = min(img1_shape[0] / img0_shape[0], img1_shape[1] / img0_shape[1]) # gain = old / new
pad = (img1_shape[1] - img0_shape[1] * gain) / 2, (img1_shape[0] - img0_shape[0] * gain) / 2 # wh padding
else:
gain = ratio_pad[0][0]
pad = ratio_pad[1]
boxes[:, [0, 2]] -= pad[0] # x padding
boxes[:, [1, 3]] -= pad[1] # y padding
boxes[:, :4] /= gain
clip_boxes(boxes, img0_shape)
return boxes
def clip_boxes(boxes, shape):
# Clip boxes (xyxy) to image shape (height, width)
if isinstance(boxes, torch.Tensor): # faster individually
boxes[:, 0].clamp_(0, shape[1]) # x1
boxes[:, 1].clamp_(0, shape[0]) # y1
boxes[:, 2].clamp_(0, shape[1]) # x2
boxes[:, 3].clamp_(0, shape[0]) # y2
else: # np.array (faster grouped)
boxes[:, [0, 2]] = boxes[:, [0, 2]].clip(0, shape[1]) # x1, x2
boxes[:, [1, 3]] = boxes[:, [1, 3]].clip(0, shape[0]) # y1, y2
def non_max_suppression(
prediction,
conf_thres=0.25,
iou_thres=0.45,
agnostic=False, # 是否忽略类别信息的标记
max_det=300,
nm=0, # number of masks
):
bs = prediction.shape[0] # batch size
nc = prediction.shape[2] - nm - 5 # number of classes
xc = prediction[..., 4] > conf_thres # 取出预测结果是confidence大于阈值的结果 shape(batch, num_boxes)
# Settings
max_wh = 7680 # (像素)框的最大宽度和高度
max_nms = 30000 # torchvision.ops.nms()中的最大框数
mi = 5 + nc # 掩码起始索引
output = [torch.zeros((0, 6 + nm), device=prediction.device)] * bs
for xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # image index, image inference
# Apply constraints
# x[((x[..., 2:4] < min_wh) | (x[..., 2:4] > max_wh)).any(1), 4] = 0 # width-height
x = x[xc[xi]] # confidence xc[xi]表示第xi个样本 选中x中对应位置为True的结果
# Compute conf obj_conf衡量了框内是否存在物体 cls_conf表示这个框中每个物体类别的得分 综合乘积就是综合置信度
x[:, 5:] *= x[:, 4:5] # conf = cls_conf * obj_conf
# Box/Mask
box = xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4]) # center_x, center_y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
mask = x[:, mi:] # 如果没有掩码,则为零列
conf, j = x[:, 5:mi].max(1, keepdim=True) # 得到每一行(即每个预测结果)类别得分最高的 并保持维度不变 得到其索引
x = torch.cat((box, conf, j.float(), mask), 1)[conf.view(-1) > conf_thres] # 进行cat之后得到维度为(55, n)的结果 然后将大于阈值的结果给取出来
# Check shape
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n: # no boxes
continue
elif n > max_nms: # excess boxes
x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)[:max_nms]] # sort by confidence
else:
x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)] # 按置信度降序排序
# Batched NMS
# 这里乘以 max_wh 是为了缩放类别信息,使其具有与边界框尺度相匹配的量级。
# 这样做是为了确保类别信息的重要程度与边界框的位置信息相匹配。
# 通过乘以 max_wh,我们将类别信息映射到与边界框尺度相同的范围内。
# 这样处理后,变量 c 就包含了根据类别信息调整后的值,用于后续的边界框计算和筛选过程。
c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
boxes, scores = x[:, :4] + c, x[:, 4] # boxes (offset by class), scores
i = torchvision.ops.nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres) # NMS
if i.shape[0] > max_det: # limit detections
i = i[:max_det]
output[xi] = x[i]
return output
def process_mask(protos, masks_in, bboxes, shape, upsample=False):
"""
args:
proto_out: [mask_dim, mask_h, mask_w]
out_masks: [n, mask_dim], n is number of masks after nms
bboxes: [n, 4], n is number of bboxes after nms
shape: 输入模型的维度, (h, w)
return: h, w, n
"""
c, mh, mw = protos.shape # 原始预测结果的维度
ih, iw = shape
masks = (masks_in @ protos.float().view(c, -1)).sigmoid().view(-1, mh, mw) # CHW
downsampled_bboxes = bboxes.clone()
downsampled_bboxes[:, 0] *= mw / iw # 将bboxes的坐标调整到mask的大小范围内
downsampled_bboxes[:, 2] *= mw / iw
downsampled_bboxes[:, 3] *= mh / ih
downsampled_bboxes[:, 1] *= mh / ih
masks = crop_mask(masks, downsampled_bboxes) # 将裁切masks 将masks在框之外的全部归0
if upsample:
masks = F.interpolate(masks[None], shape, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)[0] # 将masks插值到shape大小
return masks.gt_(0.5) # inplace操作 将masks中的值与0.5做比较 大于为1 小于为0
def crop_mask(masks, boxes):
"""用于裁剪预测的masks 使得仅保留bboxes内的部分 不在booxes中部分就归零
Args:
- masks should be a size [h, w, n] tensor of masks
- boxes should be a size [n, 4] tensor of bbox coords in relative point form
"""
n, h, w = masks.shape
x1, y1, x2, y2 = torch.chunk(boxes[:, :, None], 4, 1) # 提取的边界框坐标 shape(n,1,1)
r = torch.arange(w, device=masks.device, dtype=x1.dtype)[None, None, :] # rows shape(1,1,w)
c = torch.arange(h, device=masks.device, dtype=x1.dtype)[None, :, None] # cols shape(1,h,1)
return masks * ((r >= x1) * (r < x2) * (c >= y1) * (c < y2))
def run(
weights=ROOT /'yolov5-7.0-copy/yolov5s-seg.pt', # 模型的路径
source=ROOT / 'data/images/bus.jpg', # 图像的路径
imgsz=[640, 640], # 推理图像大小(h, w)
conf_thres=0.25, # confidence threshold
iou_thres=0.45, # NMS IOU threshold
max_det=1000, # maximum detections per image
device='', # cuda device
agnostic_nms=False, # class-agnostic NMS
fp16=False,
):
image_path = str(source)
device = 'cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
model = load_model(weights, device)
names = model.names # 获取类别名称
model.half() if fp16 else model.float()
im, copy_img = load_image(image_path, imgsz)[:2]
im_copy = im.copy()
im = im.transpose((2, 0, 1))[::-1]
im = np.ascontiguousarray(im)
im = torch.from_numpy(im).to(device)
im = im.half() if fp16 else im.float() # uint8 to fp16/32
im /= 255 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
if len(im.shape) == 3:
im = im[None] # expand for batch dim
b, c, h, w = im.shape
if fp16 and im.dtype != torch.float16:
im = im.half()
# inference
print(im.shape)
pred, proto = model(im)[:2] # yolo源码中取了前2个
# NMS
pred = non_max_suppression(pred, conf_thres, iou_thres, agnostic_nms, max_det=max_det, nm=32)
for i, det in enumerate(pred):
if len(det):
masks = process_mask(proto[i], det[:, 6:], det[:, :4], im.shape[2:], upsample=True) # HWC
masks_ = masks.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous()
im_mask = (masks_ * 255).byte().cpu().numpy() # 转为numpy 可以直接显示二值化图片
print(im_copy.shape, copy_img.shape) # 进入模型的图像大小 原图大小
new_mask = scale_image(im_copy.shape, im_mask, copy_img.shape) # 将masks对应回原图大小
new_mask = new_mask.transpose(2, 0, 1)
for i in range(len(new_mask)):
# np_mask = cv2.convertScaleAbs(new_mask[i]) # float32 to uint8
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(new_mask[i], cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
for contour in contours:
area = cv2.contourArea(contour)
if area > 100:
cv2.drawContours(copy_img, contour, -1, (0, 255, 255), 2)
# print(im.shape[2:])
det[:, :4] = scale_boxes(im.shape[2:], det[:, :4], copy_img.shape).round() # rescale boxes to im0 size
# print(det[0,:4])
# cv2.imwrite("./result.jpg", masks[0].cpu().numpy()*255)
# plt.imshow(masks[0].cpu().numpy(), cmap='gray')
# plt.show()
# for c in det[:, 5].unique(): # 获取类别信息
# n = (det[:, 5] == c).sum()
# print(n)
for _, (*xyxy, conf, cls) in enumerate(reversed(det[:, :6])):
c = int(cls)
label = f'{names[c]} {conf:.2f}'
print(xyxy)
p1, p2 = (int(xyxy[0]), int(xyxy[1])), (int(xyxy[2]), int(xyxy[3]))
cv2.rectangle(copy_img, p1, p2, (255, 255, 0), thickness=2, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
w, h = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=1, thickness=2)[0]
outside = p1[1] - h >= 3
p2 = p1[0] + w, p1[1] - h - 3 if outside else p1[1] + h + 3
cv2.putText(copy_img,
label, (p1[0], p1[1] - 2 if outside else p1[1] + h + 2),
0,
1,
(0, 255, 255),
thickness=2,
lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.imwrite("./result.jpg", copy_img)
def main(opt):
run(**vars(opt)) # vars获取当前字符串对应的方法 ** 将字典展开
def check_img_size(img_size, stride=32, floor=0.):
'''
检查图像大小 使得图像大小一定是stride的倍数 方便后面计算
'''
return [max(math.ceil(size / stride)*stride, floor) for size in img_size]
def parse_opt():
'''
参数的值与类型的初始化定义
'''
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--weights', nargs='+', type=str, default=ROOT /'yolov5s-seg.pt', help='model path(s)')
parser.add_argument('--source', type=str, default=ROOT / 'data/images/bus.jpg', help='file/dir/URL/glob/screen/0(webcam)')
parser.add_argument('--imgsz', '--img', '--img-size', nargs='+', type=int, default=[640], help='inference size h,w')
parser.add_argument('--conf-thres', type=float, default=0.25, help='confidence threshold')
parser.add_argument('--iou-thres', type=float, default=0.45, help='NMS IoU threshold')
parser.add_argument('--max-det', type=int, default=1000, help='maximum detections per image')
parser.add_argument('--device', default='', help='cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu')
parser.add_argument('--fp16', type=bool, default=False)
opt = parser.parse_args()
opt.imgsz *= 2 if len(opt.imgsz) == 1 else 1 # expand
return opt
if __name__ == "__main__":
opt = parse_opt()
main(opt)
jit版:
import os
import cv2
import json
import math
import glob
import torch
import torchvision
import numpy as np
import torch.nn.functional as F
def warmup(model, imgsz=(1, 3, 640, 640)):
"""
预热模块 yolov5-7.0源码中是预热两次
所以这里和源码一样
"""
im = torch.empty(*imgsz, dtype=torch.float, device="cuda:0")
for _ in range(2):
model(im)
def load_image(path, image_size):
'''
jit和pt模型的图片处理在这里有差别
args:
path: 图像路径
image_size: 只是一种图像尺寸而已
return:
im: 经过尺寸变换 padding过后的图像 大小为
copy_img: 原图
other: 不用关注
'''
img = cv2.imread(path)
copy_img = img.copy()
shape = img.shape[:2]
ratio = min(image_size[0] / shape[0], image_size[1] / shape[1])
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1]*ratio)), int(round(shape[0]*ratio)) # 缩放后的尺寸
dw, dh = image_size[1] - new_unpad[0], image_size[0] - new_unpad[1] # 计算目标图像与缩放后图像的差值
dw /= 2 # 确定需要填充的pad
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
im = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR) # 如果原图大小不等于缩放后图像大小的话 就resize到这个大小
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1)) # 为图像添加边框
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=(114, 114, 114)) # add border
return im, copy_img, ratio, (dw, dh)
def xywh2xyxy(x):
# Convert nx4 boxes from [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2] where xy1=top-left, xy2=bottom-right
y = x.clone() if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) else np.copy(x)
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2 # top left x
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2 # top left y
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2 # bottom right x
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2 # bottom right y
return y
def non_max_suppression(
prediction,
conf_thres=0.25,
iou_thres=0.45,
agnostic=False, # 是否忽略类别信息的标记
max_det=300,
nm=0, # number of masks
):
if isinstance(prediction , (list, tuple)):
prediction = prediction[0]
print(type(prediction))
bs = prediction.shape[0] # batch size
nc = prediction.shape[2] - nm - 5 # number of classes
xc = prediction[..., 4] > conf_thres # 取出预测结果是confidence大于阈值的结果 shape(batch, num_boxes)
# Settings
max_wh = 7680 # (像素)框的最大宽度和高度
max_nms = 30000 # torchvision.ops.nms()中的最大框数
mi = 5 + nc # 掩码起始索引
output = [torch.zeros((0, 6 + nm), device=prediction.device)] * bs
for xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # image index, image inference
# Apply constraints
# x[((x[..., 2:4] < min_wh) | (x[..., 2:4] > max_wh)).any(1), 4] = 0 # width-height
x = x[xc[xi]] # confidence xc[xi]表示第xi个样本 选中x中对应位置为True的结果
# Compute conf obj_conf衡量了框内是否存在物体 cls_conf表示这个框中每个物体类别的得分 综合乘积就是综合置信度
x[:, 5:] *= x[:, 4:5] # conf = cls_conf * obj_conf
# Box/Mask
box = xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4]) # center_x, center_y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
mask = x[:, mi:] # 如果没有掩码,则为零列
conf, j = x[:, 5:mi].max(1, keepdim=True) # 得到每一行(即每个预测结果)类别得分最高的 并保持维度不变 得到其索引
x = torch.cat((box, conf, j.float(), mask), 1)[conf.view(-1) > conf_thres] # 进行cat之后得到维度为(55, n)的结果 然后将大于阈值的结果给取出来
# Check shape
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n: # no boxes
continue
elif n > max_nms: # excess boxes
x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)[:max_nms]] # sort by confidence
else:
x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)] # 按置信度降序排序
# Batched NMS
# 这里乘以 max_wh 是为了缩放类别信息,使其具有与边界框尺度相匹配的量级。
# 这样做是为了确保类别信息的重要程度与边界框的位置信息相匹配。
# 通过乘以 max_wh,我们将类别信息映射到与边界框尺度相同的范围内。
# 这样处理后,变量 c 就包含了根据类别信息调整后的值,用于后续的边界框计算和筛选过程。
c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
boxes, scores = x[:, :4] + c, x[:, 4] # boxes (offset by class), scores
i = torchvision.ops.nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres) # NMS
if i.shape[0] > max_det: # limit detections
i = i[:max_det]
output[xi] = x[i]
return output
def scale_boxes(img1_shape, boxes, img0_shape, ratio_pad=None):
# Rescale boxes (xyxy) from img1_shape to img0_shape
if ratio_pad is None: # calculate from img0_shape
gain = min(img1_shape[0] / img0_shape[0], img1_shape[1] / img0_shape[1]) # gain = old / new
pad = (img1_shape[1] - img0_shape[1] * gain) / 2, (img1_shape[0] - img0_shape[0] * gain) / 2 # wh padding
else:
gain = ratio_pad[0][0]
pad = ratio_pad[1]
boxes[:, [0, 2]] -= pad[0] # x padding
boxes[:, [1, 3]] -= pad[1] # y padding
boxes[:, :4] /= gain
clip_boxes(boxes, img0_shape)
return boxes
def clip_boxes(boxes, shape):
# Clip boxes (xyxy) to image shape (height, width)
if isinstance(boxes, torch.Tensor): # faster individually
boxes[:, 0].clamp_(0, shape[1]) # x1
boxes[:, 1].clamp_(0, shape[0]) # y1
boxes[:, 2].clamp_(0, shape[1]) # x2
boxes[:, 3].clamp_(0, shape[0]) # y2
else: # np.array (faster grouped)
boxes[:, [0, 2]] = boxes[:, [0, 2]].clip(0, shape[1]) # x1, x2
boxes[:, [1, 3]] = boxes[:, [1, 3]].clip(0, shape[0]) # y1, y2
def scale_image(im1_shape, masks, im0_shape, ratio_pad=None):
"""
img1_shape: model input shape, [h, w]
img0_shape: origin pic shape, [h, w, 3]
masks: [h, w, num]
"""
# Rescale coordinates (xyxy) from im1_shape to im0_shape
if ratio_pad is None: # calculate from im0_shape
gain = min(im1_shape[0] / im0_shape[0], im1_shape[1] / im0_shape[1]) # 短边缩放大小
pad = (im1_shape[1] - im0_shape[1] * gain) / 2, (im1_shape[0] - im0_shape[0] * gain) / 2 # w,h需要补齐的pad大小
else:
pad = ratio_pad[1]
top, left = int(pad[1]), int(pad[0]) # y, x 左上
bottom, right = int(im1_shape[0] - pad[1]), int(im1_shape[1] - pad[0]) # 右下
if len(masks.shape) < 2:
raise ValueError(f'"len of masks shape" should be 2 or 3, but got {len(masks.shape)}')
masks = masks[top:bottom, left:right]
masks = cv2.resize(masks, (im0_shape[1], im0_shape[0]))
if len(masks.shape) == 2:
masks = masks[:, :, None]
return masks
def process_mask(protos, masks_in, bboxes, shape, upsample=False):
"""
args:
proto_out: [mask_dim, mask_h, mask_w]
out_masks: [n, mask_dim], n is number of masks after nms
bboxes: [n, 4], n is number of bboxes after nms
shape: 输入模型的维度, (h, w)
return: h, w, n
"""
c, mh, mw = protos.shape # 原始预测结果的维度
ih, iw = shape
masks = (masks_in @ protos.float().view(c, -1)).sigmoid().view(-1, mh, mw) # CHW
downsampled_bboxes = bboxes.clone()
downsampled_bboxes[:, 0] *= mw / iw # 将bboxes的坐标调整到mask的大小范围内
downsampled_bboxes[:, 2] *= mw / iw
downsampled_bboxes[:, 3] *= mh / ih
downsampled_bboxes[:, 1] *= mh / ih
masks = crop_mask(masks, downsampled_bboxes) # 将裁切masks 将masks在框之外的全部归0
if upsample:
masks = F.interpolate(masks[None], shape, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)[0] # 将masks插值到shape大小
return masks.gt_(0.5) # inplace操作 将masks中的值与0.5做比较 大于为1 小于为0
def crop_mask(masks, boxes):
"""用于裁剪预测的masks 使得仅保留bboxes内的部分 不在booxes中部分就归零
Args:
- masks should be a size [h, w, n] tensor of masks
- boxes should be a size [n, 4] tensor of bbox coords in relative point form
"""
n, h, w = masks.shape
x1, y1, x2, y2 = torch.chunk(boxes[:, :, None], 4, 1) # 提取的边界框坐标 shape(n,1,1)
r = torch.arange(w, device=masks.device, dtype=x1.dtype)[None, None, :] # rows shape(1,1,w)
c = torch.arange(h, device=masks.device, dtype=x1.dtype)[None, :, None] # cols shape(1,h,1)
return masks * ((r >= x1) * (r < x2) * (c >= y1) * (c < y2))
img_size = [640, 640]
conf_thres=0.25 # confidence threshold
iou_thres=0.45 # NMS IOU threshold
agnostic_nms=False
max_det=1000 # maximum detections per image
fp16 = False
device = 'cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
extra_files = {'config.txt': ''}
model = torch.jit.load("yolov5s-seg.torchscript", _extra_files=extra_files, map_location='cuda:0')
model.half() if fp16 else model.float()
if extra_files['config.txt']: # 加载模型的源数据 方面后面使用
d = json.loads(extra_files['config.txt'],
object_hook=lambda d: {int(k) if k.isdigit() else k: v
for k, v in d.items()})
stride, names = int(d['stride']), d['names']
new_imgsize = [max(math.ceil(i/stride)*stride, 0) for i in img_size]
path = glob.glob("images/*")
img_path = [i.replace("/", os.sep).replace("\\", os.sep) for i in path]
warmup(model)
for path in img_path:
im, copy_img = load_image(path, new_imgsize)[:2]
im_copy = im.copy()
im = im.transpose((2, 0, 1))[::-1]
im = np.ascontiguousarray(im)
im = torch.from_numpy(im).to(device)
im = im.half() if fp16 else im.float() # uint8 to fp16/32
im /= 255 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
if len(im.shape) == 3:
im = im[None] # expand for batch dim
b, c, h, w = im.shape
if fp16 and im.dtype != torch.float16:
im = im.half()
pred, proto = model(im)[:2]
pred = non_max_suppression(pred, conf_thres, iou_thres, agnostic_nms, max_det=max_det, nm=32)
for i, det in enumerate(pred):
if len(det):
masks = process_mask(proto[i], det[:, 6:], det[:, :4], im.shape[2:], upsample=True) # HWC
masks_ = masks.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous()
im_mask = (masks_ * 255).byte().cpu().numpy() # 转为numpy 可以直接显示二值化图片
print(im_copy.shape, copy_img.shape) # 进入模型的图像大小 原图大小
new_mask = scale_image(im_copy.shape, im_mask, copy_img.shape) # 将masks对应回原图大小
new_mask = new_mask.transpose(2, 0, 1)
for i in range(len(new_mask)):
# np_mask = cv2.convertScaleAbs(new_mask[i]) # float32 to uint8
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(new_mask[i], cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
for contour in contours:
area = cv2.contourArea(contour)
if area > 100:
cv2.drawContours(copy_img, contour, -1, (0, 255, 255), 2)
det[:, :4] = scale_boxes(im.shape[2:], det[:, :4], copy_img.shape).round() # rescale boxes to im0 size
for _, (*xyxy, conf, cls) in enumerate(reversed(det[:, :6])):
c = int(cls)
label = f'{names[c]} {conf:.2f}'
print(xyxy)
p1, p2 = (int(xyxy[0]), int(xyxy[1])), (int(xyxy[2]), int(xyxy[3]))
cv2.rectangle(copy_img, p1, p2, (255, 255, 0), thickness=2, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
w, h = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=1, thickness=2)[0]
outside = p1[1] - h >= 3
p2 = p1[0] + w, p1[1] - h - 3 if outside else p1[1] + h + 3
cv2.putText(copy_img,
label, (p1[0], p1[1] - 2 if outside else p1[1] + h + 2),
0,
1,
(0, 255, 255),
thickness=2,
lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join("predict_result/", path.split("\\")[1]), copy_img)
**下面说一下这两者的差别。
1. pt版本模型的文件结构:**
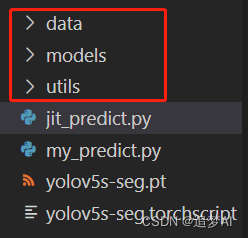
红框圈起来的,是必须要有结构,这和作者保存模型的方式有关。这些都是依赖。所以必须的有。如果你是自己训练且改动它train文件,自己保存的话,就当我没说过。
jit版本模型的结构:
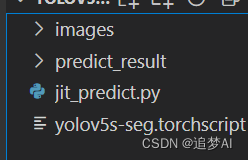
啥都不需要,只要有模型就行,这是因为jitscript模型在转换时,已经跟踪了模型结构,所以可以不需要模型结构这些依赖,但是需要注意的是你转换时输入的数据格式与导出之后输入的数据格式需要相同。
2. 在load_image函数中
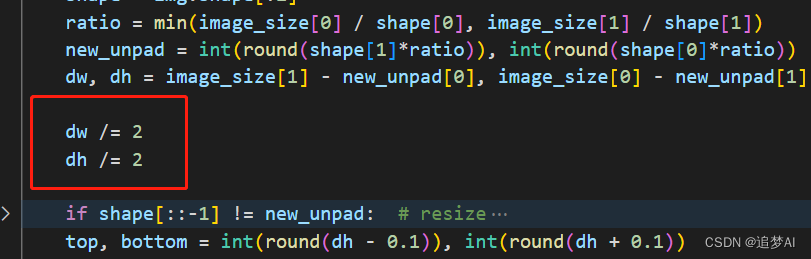
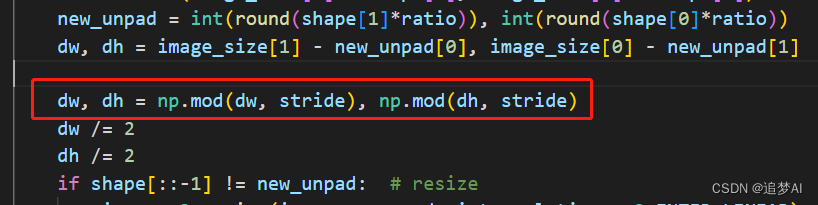
这里是和转换时有关系,因为关系到输入的维度大小。当然也可以修改它的export.py代码。这些都不重要。




















 1808
1808











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








