之前激活函数几乎就只用sigmoid,然而实际上有很多激活函数可以用,本文介绍ReLU函数的使用
ReLU全拼Rectified Linear Unit,直译矫正过的线性单元,不过意思相当于保留数据的正数部分,负数部分全部变为0
1.导入
注意layers和activations的导入
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.gridspec import GridSpec
plt.style.use('./deeplearning.mplstyle')
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, LeakyReLU
from tensorflow.keras.activations import linear, relu, sigmoid
%matplotlib inline
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider
from lab_utils_common import dlc
from autils import plt_act_trio
from lab_utils_relu import *
import warnings
warnings.simplefilter(action='ignore', category=UserWarning)
2.ReLU介绍
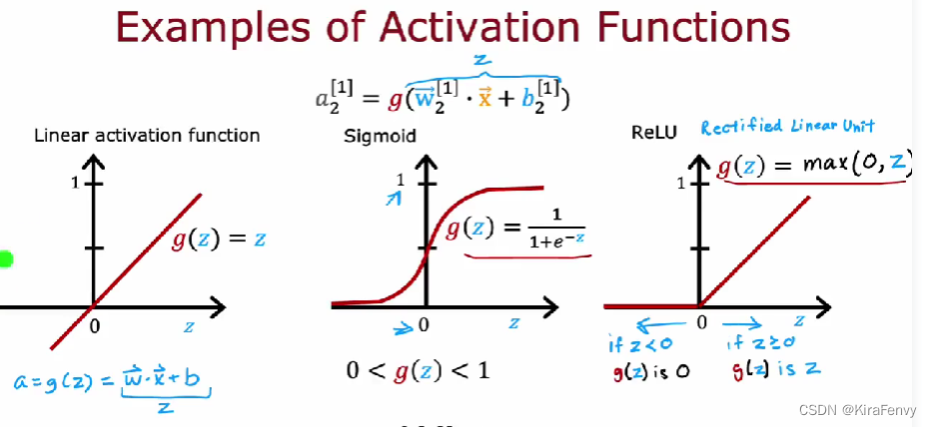
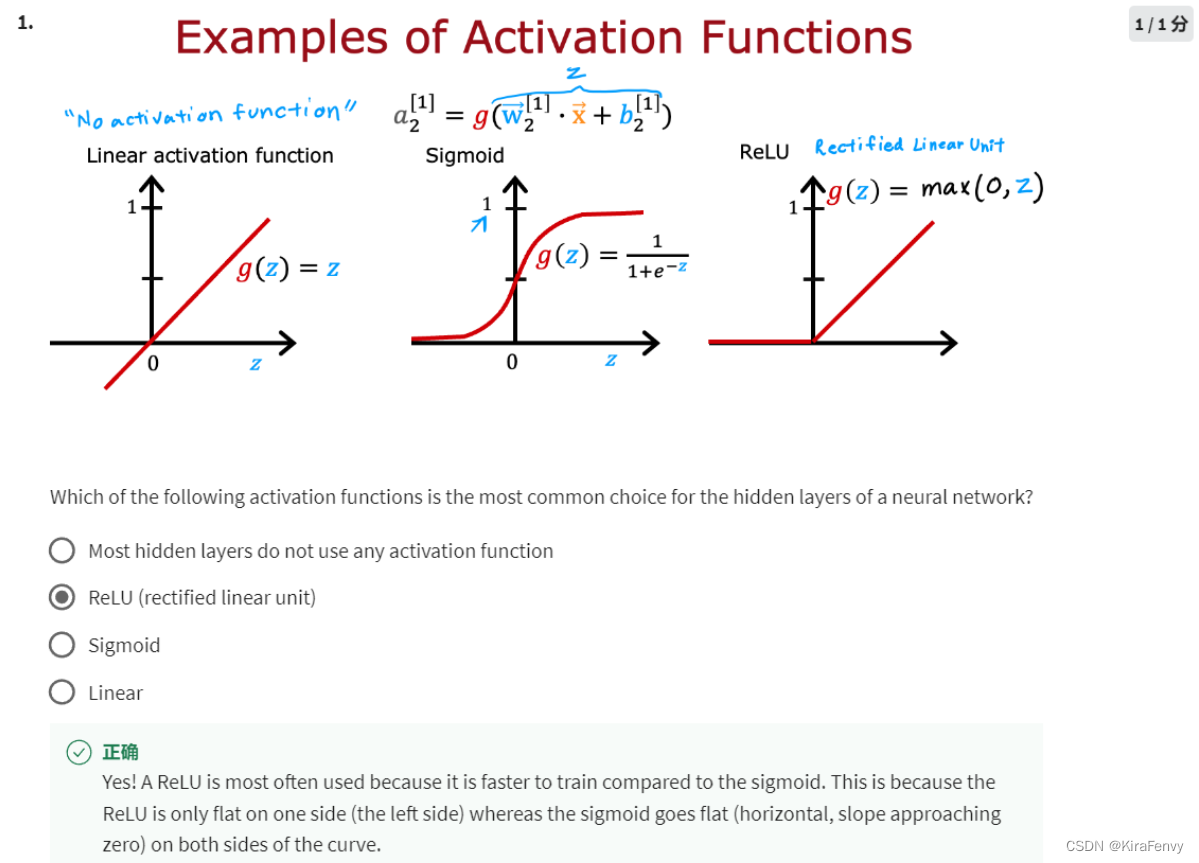
激活函数
这里有三种不同的激活函数
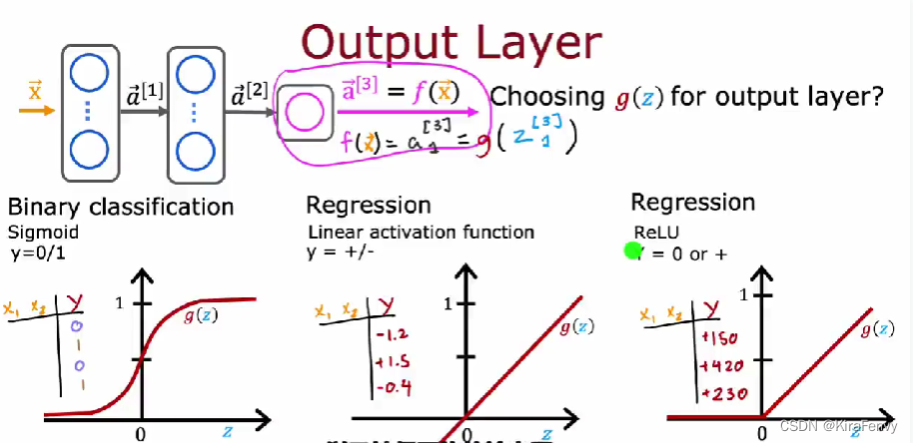
如何选择激活函数?
这是输出层的选择, 如果输出必须为0-1(二分类问题),则sigmoid,如果必须非负则ReLU(比如房价),其他回归问题一般就linear
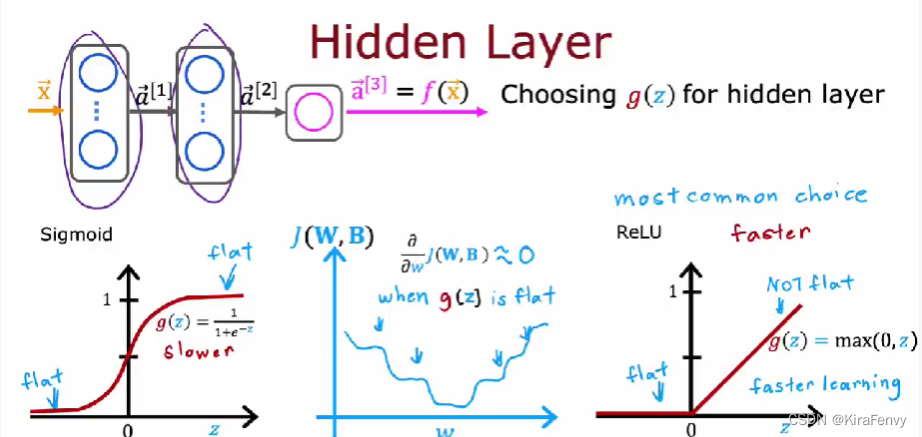
隐藏层的选择:选ReLU比较多(一般都是relu),因为运算速度快,梯度下降速度快,尽量别用linear激活函数,这样跟线性回归没区别
为什么需要激活函数:激活函数决定了,一个神经元是否应该通过加权求和并添加偏差而被激活。激活函数的目的是为神经元添加非线形的输入。一个没有激活函数的神经网络就只是一个线性回归模型,非线形的激活函数能够增加非线性的变换到输入中,使得它能够学习和表现更复杂的任务。
3.使用
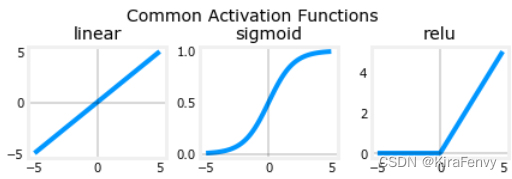
3.1 可视化
def plt_act_trio():
X = np.linspace(-5,5,100)
fig,ax = plt.subplots(1,3, figsize=(6,2))
widgvis(fig)
ax[0].plot(X,tf.keras.activations.linear(X))
ax[0].axvline(0, lw=0.3, c="black")
ax[0].axhline(0, lw=0.3, c="black")
ax[0].set_title("linear")
ax[1].plot(X,tf.keras.activations.sigmoid(X))
ax[1].axvline(0, lw=0.3, c="black")
ax[1].axhline(0, lw=0.3, c="black")
ax[1].set_title("sigmoid")
ax[2].plot(X,tf.keras.activations.relu(X))
ax[2].axhline(0, lw=0.3, c="black")
ax[2].axvline(0, lw=0.3, c="black")
ax[2].set_title("relu")
fig.suptitle("Common Activation Functions", fontsize=14)
fig.tight_layout(pad=0.2)
plt.show()
plt_act_trio()
3.2 载入数据
X = np.random.rand(300, 2)
y = np.sqrt( X[:,0]**2 + X[:,1]**2 ) < 0.6
#y = np.logical_and( X[:,0] < 0.5, X[:,1] < 0.5 ).astype(int)
3.3 模型构建
model = Sequential(
[
Dense(2,activation="relu", name = 'l1'),
Dense(1,activation="sigmoid", name = 'l2')
]
)
model.compile(
loss=tf.keras.losses.MeanSquaredError(),
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.01),
)
model.fit(
X,y,
epochs=150
)
绘图函数的代码
def plt_mc_data(ax, X, y, classes, class_labels=None, map=plt.cm.Paired,
legend=False, size=50, m='o', equal_xy = False):
""" Plot multiclass data. Note, if equal_xy is True, setting ylim on the plot may not work """
for i in range(classes):
idx = np.where(y == i)
col = len(idx[0])*[i]
label = class_labels[i] if class_labels else "c{}".format(i)
ax.scatter(X[idx, 0], X[idx, 1], marker=m,
c=col, vmin=0, vmax=map.N, cmap=map,
s=size, label=label)
if legend: ax.legend()
if equal_xy: ax.axis("equal")
def plt_mc(X_train,y_train,classes):
css = np.unique(y_train)
fig,ax = plt.subplots(1,1,figsize=(3,3))
fig.canvas.toolbar_visible = False
fig.canvas.header_visible = False
fig.canvas.footer_visible = False
plt_mc_data(ax, X_train,y_train,classes, map=dkcolors_map, legend=True, size=10, equal_xy = False)
ax.set_title("Multiclass Data")
ax.set_xlabel("x0")
ax.set_ylabel("x1")
return(ax)
def plot_cat_decision_boundary_mc(ax, X, predict , class_labels=None, legend=False, vector=True):
# create a mesh to points to plot
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min(), X[:, 0].max()
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min(), X[:, 1].max()
h = max(x_max-x_min, y_max-y_min)/200
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
points = np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]
#print("points", points.shape)
#print("xx.shape", xx.shape)
#make predictions for each point in mesh
if vector:
Z = predict(points)
else:
Z = np.zeros((len(points),))
for i in range(len(points)):
Z[i] = predict(points[i].reshape(1,2))
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
#contour plot highlights boundaries between values - classes in this case
ax.contour(xx, yy, Z, linewidths=1)
#ax.axis('tight')
调用并输出结果
ax = plt_mc(X,y,2,)
predict = lambda x: (model.predict(x) > 0.5).astype(int)
plot_cat_decision_boundary_mc(ax, X, predict, legend = True, vector=True)
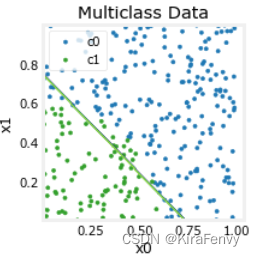
下面显示的是在不同层的参数变化
l1 = model.get_layer("l1")
W1,b1 = l1.get_weights()
l2 = model.get_layer("l2")
W2,b2 = l2.get_weights()
print(W1,b1)
print(W2,b2)
[[ 2.74 -1. ]
[ 2.7 0.24]] [-1.49 -0.21]
[[-4.95]
[ 0.88]] [2.61]
4.课后题
- sigmoid函数适合用在二分类问题
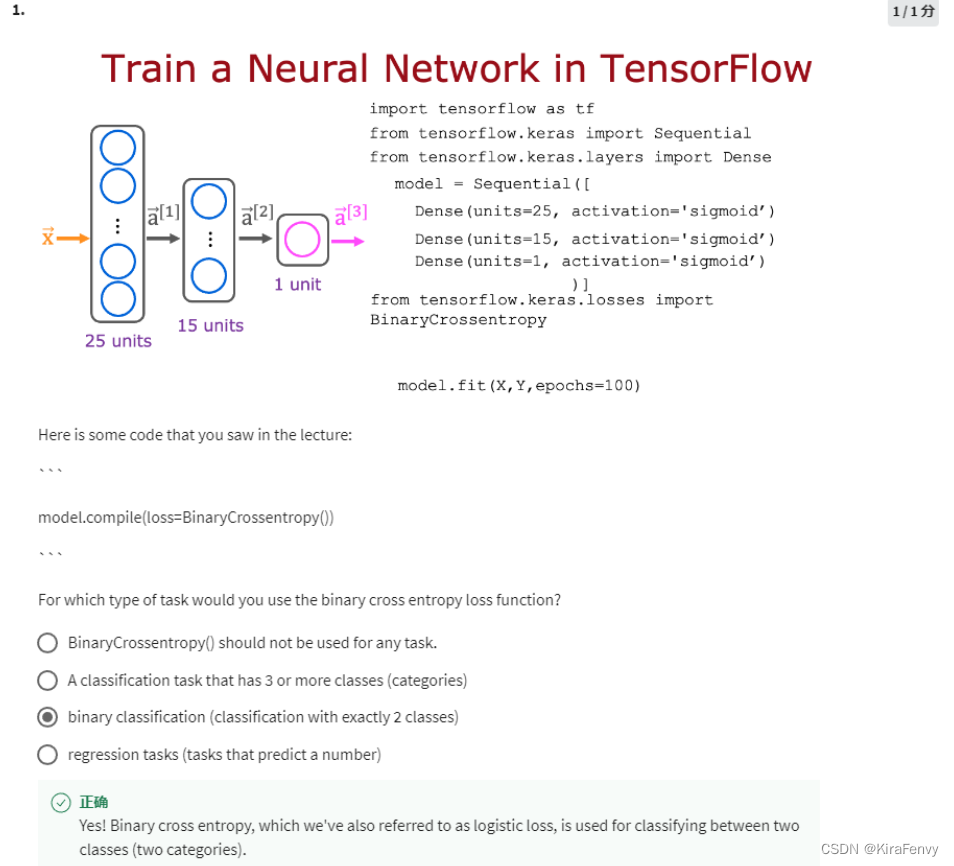
- 最常用的激活函数就是ReLU函数
- 房价预测是回归问题,不适合使用sigmoid函数
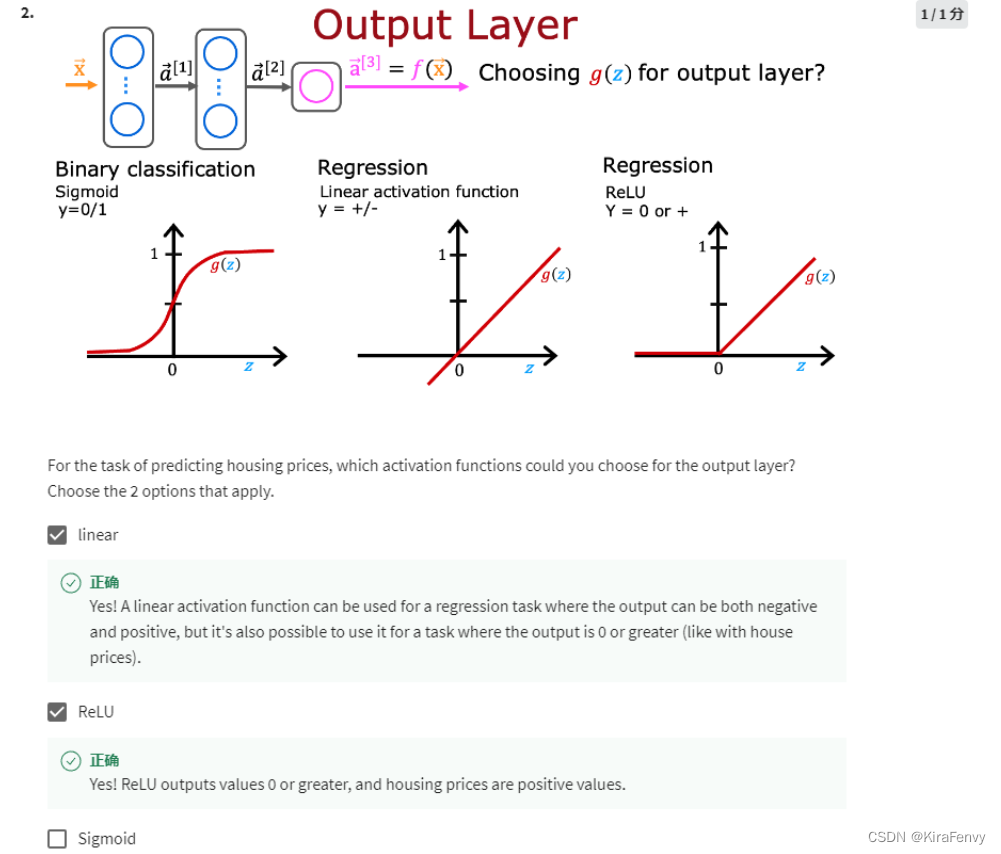
4. 一个神经网络有再多层,没有激活函数是没用的,比如“linear function”实际上就是不做处理






















 1510
1510











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








