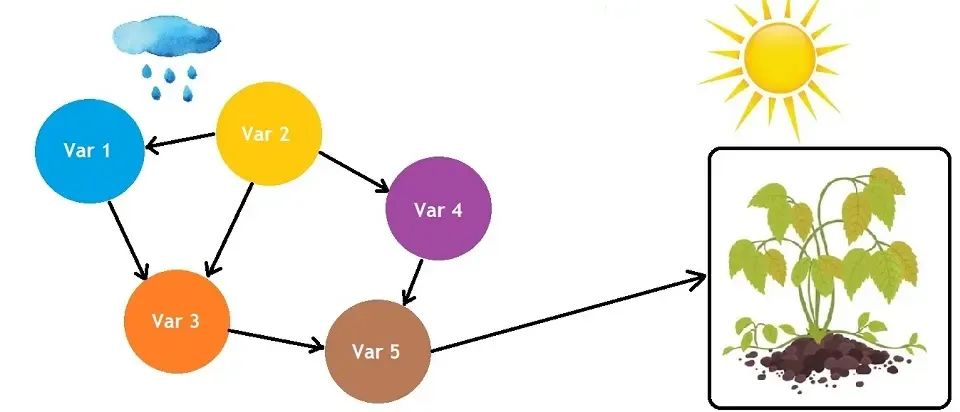
Bayesian Network
贝叶斯网络(Bayesian Network),也被称为贝叶斯有向无环图(Bayesian Directed Acyclic Graph, BDAG)或概率依赖网络(Probabilistic Dependence Network),是一种强大的概率图模型,用于描述随机变量之间的概率依赖关系。
Bayesian Network
__一、贝叶斯统计_(Bayesian Statistics)___
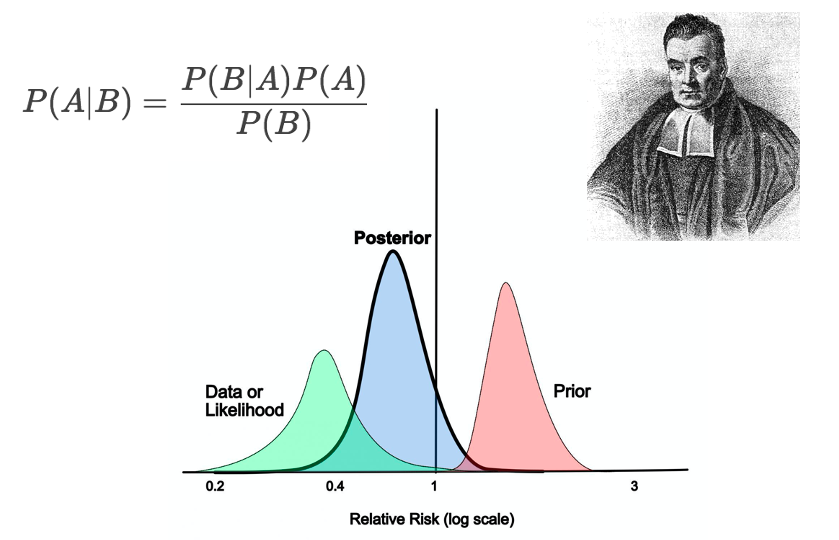
什么是贝叶斯统计(Bayesian Statistics)?贝叶斯统计(Bayesian Statistics)是一种基于贝叶斯定理****的统计推断方法,它利用先验信息和样本数据来更新我们对未知参数或事件概率的信念。
-
先验分布:统计推断前,对未知参数的初步判断,基于历史、专家经验或主观信念,不必客观。
-
后验分布:结合先验和样本信息,通过贝叶斯定理计算得到的未知参数新分布,综合了两者信息,是贝叶斯推断的基础。
Bayesian Statistics
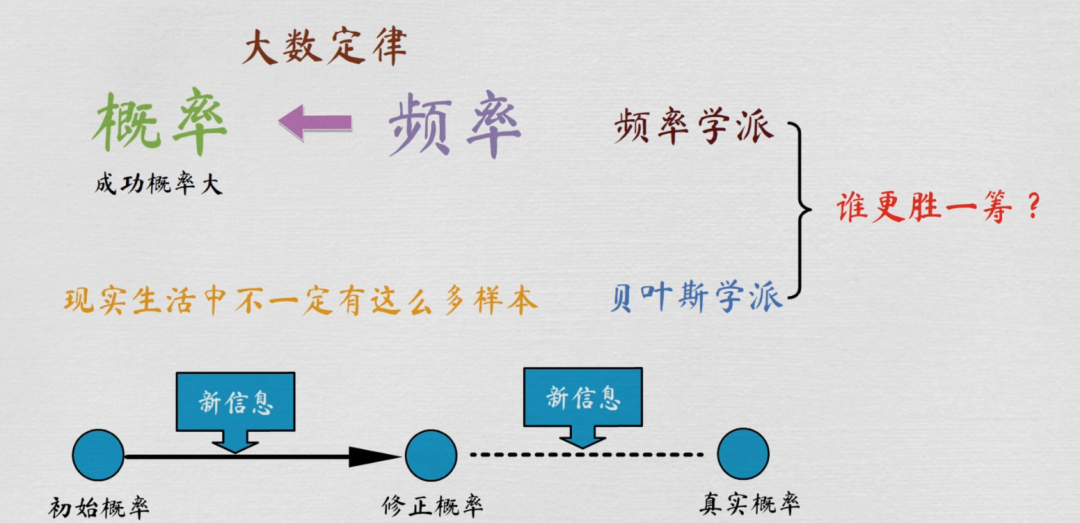
频率学派(Frequentist School)与贝叶斯学派(Bayesian School):频率学派强调通过大量数据揭示客观规律,而贝叶斯学派则注重结合先验知识与新数据来更新信念。
Frequentist School vs Bayesian School
一、频率学派(Frequentist School)
-
基本观点:世界是客观的,概率是事件在长时间内发生的频率。必须通过大量独立采样来获得统计均值。不主张先给出一个主观的先验概率或假设。
-
应用场景:适用于可以通过大量重复实验来获得统计规律的场景,**如抛硬币、掷骰子等。
-
优势:在简单、可重复的实验场景下非常有效。
-
局限:对于无法进行大量重复实验或实验成本高昂的现实场景,频率学派的方法可能不适用。
二、贝叶斯学派(Bayesian School)
-
基本观点:概率是一种信念度,可以有主观的先验概率。通过观察新的数据来不断更新先验概率,使之逼近客观事实。
-
应用场景:适用于需要估算概率但无法进行大量重复实验的现实场景,**如赶飞机时间的估算、《狼来了》故事中村民对小孩诚实度的判断等。
-
优势:能够结合先验知识和新数据进行概率推断,更加灵活和实用。
-
局限:先验概率的选择可能带有主观性,需要谨慎选择。
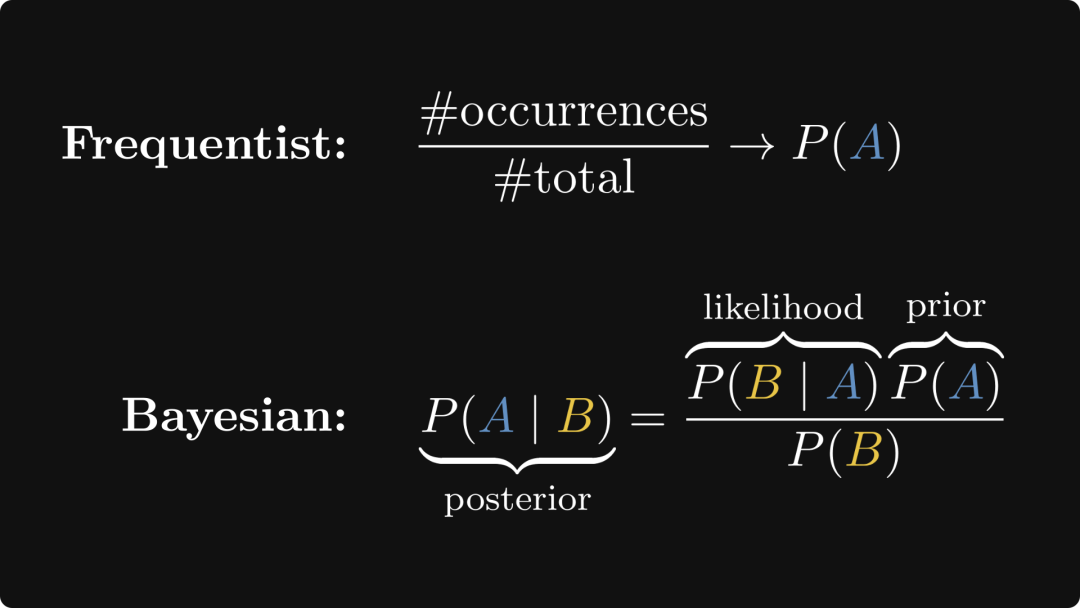
Frequentist School vs Bayesian School
__二、贝叶斯定理_(Bayes’ Theorem)___
什么是贝叶斯定理(Bayes’ Theorem)**?**贝叶斯定理(Bayes’ Theorem) 是一种描述两个条件概率之间关系的定理,它允许我们根据新的证据或数据来更新我们对某一事件或参数的信念。

Bayes’ Theorem
贝叶斯定理公式是一种计算条件概率的方法,它根据新的证据和先前的概率来更新某个假设的可信度。
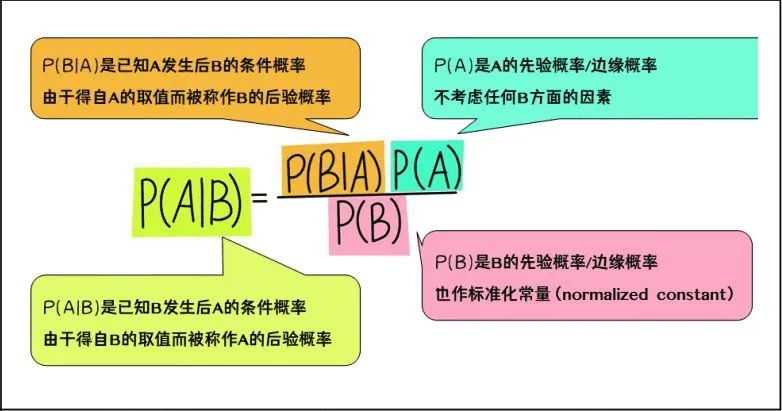
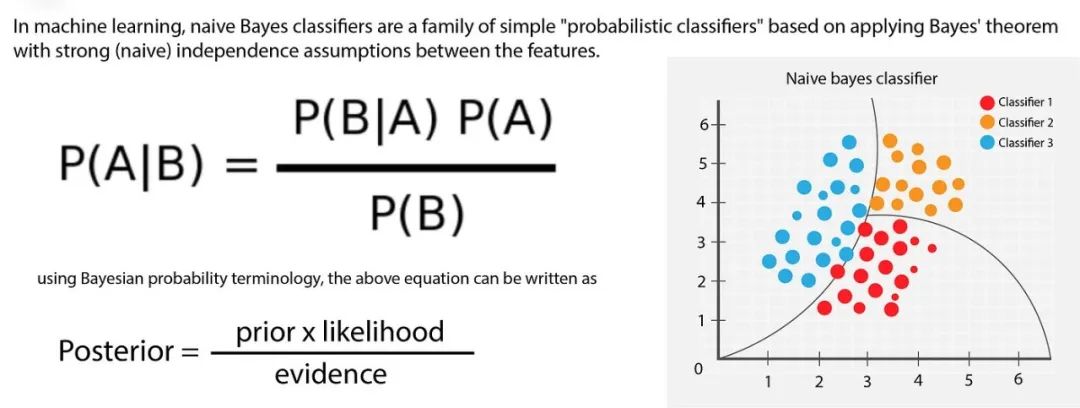
P(A|B) = [P(B|A) * P(A)] / P(B)

Bayes’ Theorem
-
P(A|B) 是后验概率,即在事件B发生的条件下,事件A发生的概率。
-
P(B|A) 是似然函数,表示在事件A发生的条件下,事件B发生的概率。
-
P(A) 是先验概率,即在没有事件B发生的条件下,我们对事件A的信念或概率估计。
-
P(B) 是事件B的边缘概率,它是所有可能情况下事件B发生的概率总和,通常作为归一化常数,确保后验概率的总和为1。
Bayes’ Theorem
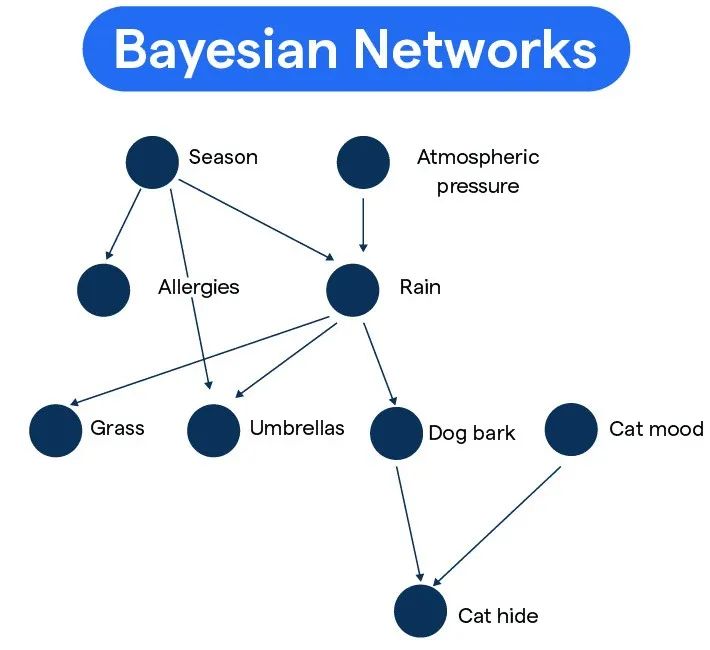
_三、**贝叶斯网络(Bayesian Network)**_
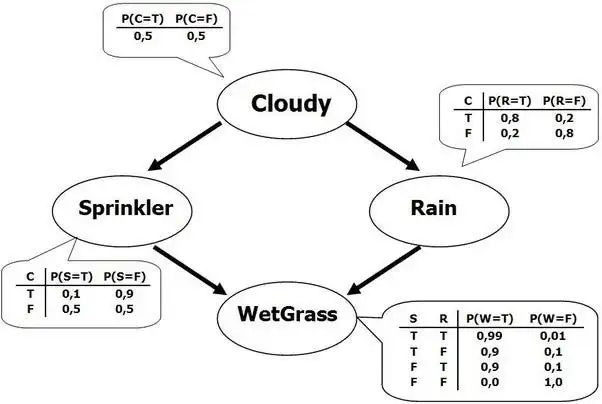
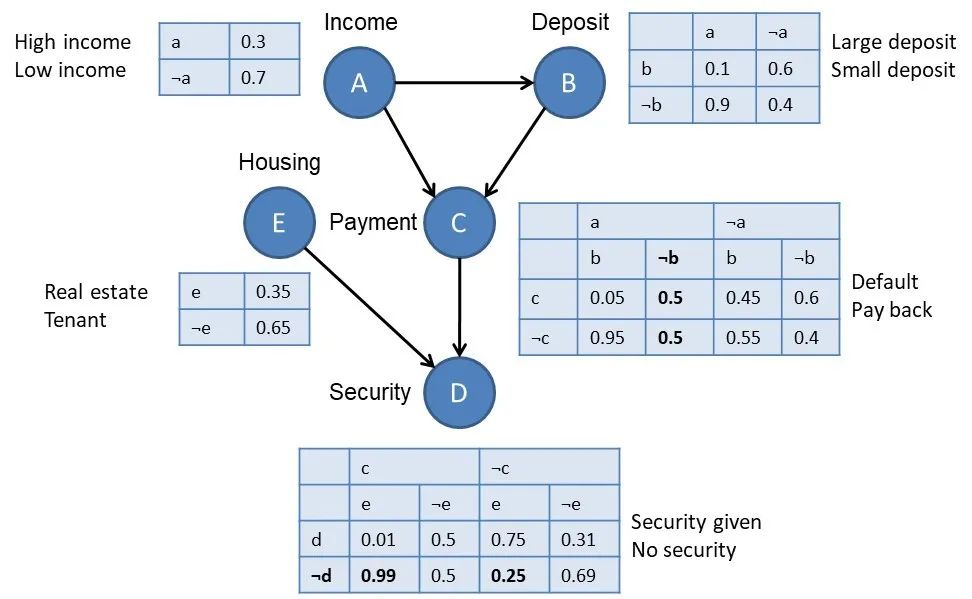
什么是贝叶斯网络(Bayesian Network)?贝叶斯网络(Bayesian Network,简称BN)是一种基于概率推理的图形模型****,用于表示变量之间的依赖关系。它由一个有向无环图(Directed Acyclic Graph,DAG)和条件概率表(Conditional Probability Table,CPT)组成。
Bayesian Network
-
有向无环图(DAG):用于表示变量之间的依赖关系。图中的节点代表变量,有向边(或称为弧)则表示变量之间的依赖关系。如果两个节点之间存在有向边,则意味着一个节点的状态会影响另一个节点的状态。
-
条件概率表(CPT):与DAG中的每个节点相关联,用于描述节点与其父节点之间的概率关系。条件概率表详细列出了在给定父节点状态下,当前节点取各个可能值的概率。
Bayesian Network
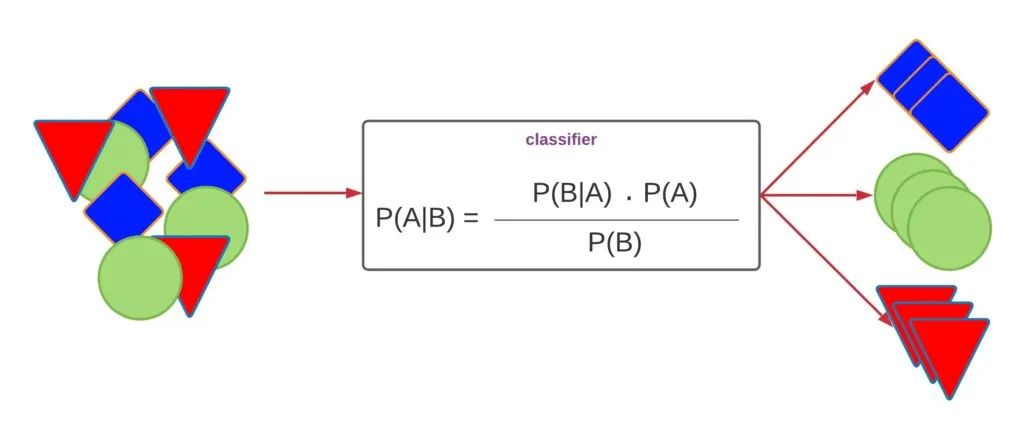
什么是朴素贝叶斯**(Naive Bayes)?朴素贝叶斯(Naive Bayes,简称NB)是一种基于概率理论的分类算法**,其理论基础是贝叶斯定理与特征条件独立假设。****
Naive Bayes
朴素贝叶斯****假设给定目标值时,属性之间相互条件独立,通过已给定的训练集学习从输入到输出的联合概率分布。基于学习到的模型,输入新的样本数据,求出使得后验概率最大的输出,即该样本所属的类别。****
Naive Bayes
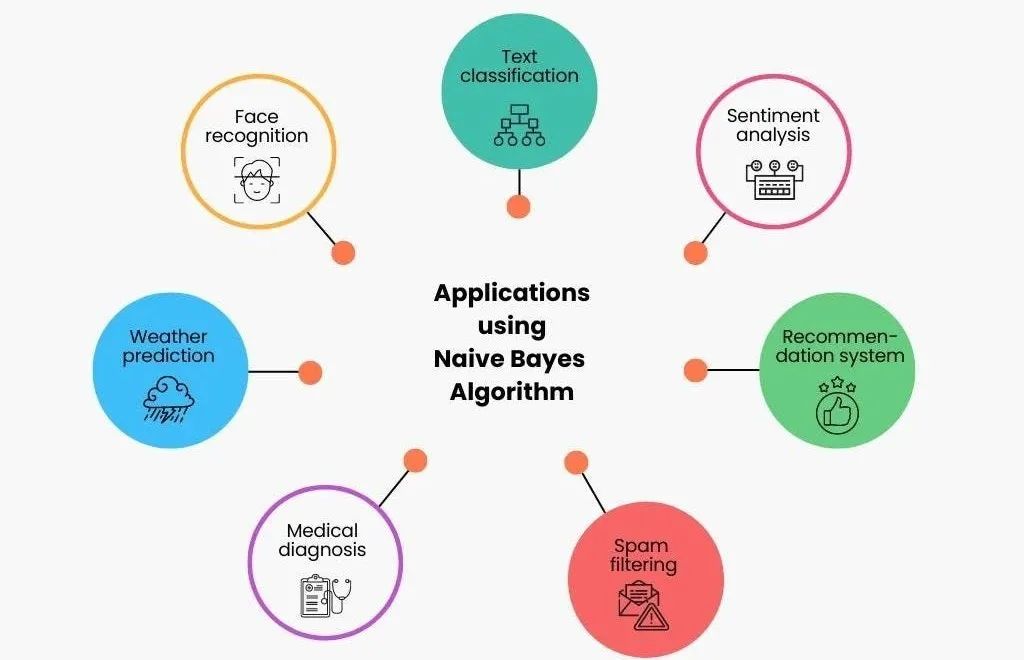
朴素贝叶斯算法在多个领域都有广泛的应用,如文本分类、垃圾邮件的分类、信用评估、钓鱼网站检测等。
 ## 如何学习大模型 AI ?
## 如何学习大模型 AI ?
由于新岗位的生产效率,要优于被取代岗位的生产效率,所以实际上整个社会的生产效率是提升的。
但是具体到个人,只能说是:
“最先掌握AI的人,将会比较晚掌握AI的人有竞争优势”。
这句话,放在计算机、互联网、移动互联网的开局时期,都是一样的道理。
我在一线互联网企业工作十余年里,指导过不少同行后辈。帮助很多人得到了学习和成长。
我意识到有很多经验和知识值得分享给大家,也可以通过我们的能力和经验解答大家在人工智能学习中的很多困惑,所以在工作繁忙的情况下还是坚持各种整理和分享。但苦于知识传播途径有限,很多互联网行业朋友无法获得正确的资料得到学习提升,故此将并将重要的AI大模型资料包括AI大模型入门学习思维导图、精品AI大模型学习书籍手册、视频教程、实战学习等录播视频免费分享出来。

第一阶段(10天):初阶应用
该阶段让大家对大模型 AI有一个最前沿的认识,对大模型 AI 的理解超过 95% 的人,可以在相关讨论时发表高级、不跟风、又接地气的见解,别人只会和 AI 聊天,而你能调教 AI,并能用代码将大模型和业务衔接。
- 大模型 AI 能干什么?
- 大模型是怎样获得「智能」的?
- 用好 AI 的核心心法
- 大模型应用业务架构
- 大模型应用技术架构
- 代码示例:向 GPT-3.5 灌入新知识
- 提示工程的意义和核心思想
- Prompt 典型构成
- 指令调优方法论
- 思维链和思维树
- Prompt 攻击和防范
- …
第二阶段(30天):高阶应用
该阶段我们正式进入大模型 AI 进阶实战学习,学会构造私有知识库,扩展 AI 的能力。快速开发一个完整的基于 agent 对话机器人。掌握功能最强的大模型开发框架,抓住最新的技术进展,适合 Python 和 JavaScript 程序员。
- 为什么要做 RAG
- 搭建一个简单的 ChatPDF
- 检索的基础概念
- 什么是向量表示(Embeddings)
- 向量数据库与向量检索
- 基于向量检索的 RAG
- 搭建 RAG 系统的扩展知识
- 混合检索与 RAG-Fusion 简介
- 向量模型本地部署
- …
第三阶段(30天):模型训练
恭喜你,如果学到这里,你基本可以找到一份大模型 AI相关的工作,自己也能训练 GPT 了!通过微调,训练自己的垂直大模型,能独立训练开源多模态大模型,掌握更多技术方案。
到此为止,大概2个月的时间。你已经成为了一名“AI小子”。那么你还想往下探索吗?
- 为什么要做 RAG
- 什么是模型
- 什么是模型训练
- 求解器 & 损失函数简介
- 小实验2:手写一个简单的神经网络并训练它
- 什么是训练/预训练/微调/轻量化微调
- Transformer结构简介
- 轻量化微调
- 实验数据集的构建
- …
第四阶段(20天):商业闭环
对全球大模型从性能、吞吐量、成本等方面有一定的认知,可以在云端和本地等多种环境下部署大模型,找到适合自己的项目/创业方向,做一名被 AI 武装的产品经理。
- 硬件选型
- 带你了解全球大模型
- 使用国产大模型服务
- 搭建 OpenAI 代理
- 热身:基于阿里云 PAI 部署 Stable Diffusion
- 在本地计算机运行大模型
- 大模型的私有化部署
- 基于 vLLM 部署大模型
- 案例:如何优雅地在阿里云私有部署开源大模型
- 部署一套开源 LLM 项目
- 内容安全
- 互联网信息服务算法备案
- …
学习是一个过程,只要学习就会有挑战。天道酬勤,你越努力,就会成为越优秀的自己。
如果你能在15天内完成所有的任务,那你堪称天才。然而,如果你能完成 60-70% 的内容,你就已经开始具备成为一名大模型 AI 的正确特征了。
这份完整版的大模型 AI 学习资料已经上传CSDN,朋友们如果需要可以微信扫描下方CSDN官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】
























 8206
8206

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








