一、单变量线性回归
1 导入数据
(1)导入库
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt(2)导入数据集
data = pd.read_csv('ex1data1.txt',names = ['population','profit'])
data.head()(3)数据可视化
data.head() #查看前五个
data.tail() #查看后五个
data.describe() #描述性统计
--------------------------------------------------------------
#绘制散点图
data.plot.scatter('population','profit',label = 'population')
plt.show()2 数据集构建
(1)模型选择
根据散点图,选择一元线性回归方程。
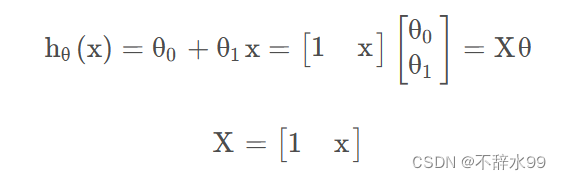
(2) X列增加
data.insert(0,'x',1)
data.head()(3)数据集切割
X = data.iloc[:,0:-1]
X.head()y = data.iloc[:,-1]
y.head()(4)数据类型转化与形状查看
X = X.values
X.shape
y = y.values
y.shape
(5)y形状转为二维
y = y.reshape(97,1)
y.shape3 损失函数
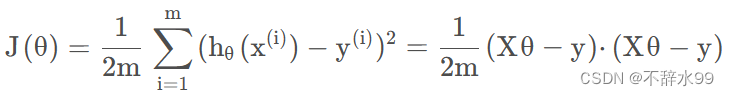
(1)函数定义
def costFunction(X,y,theta):
inner = np.power(X@theta-y,2)
return np.sum(inner)/(2*len(X))(2)实例化
theta = np.zeros((2,1))
theta.shape
cost_init = costFunction(X,y,theta)
print(cost_init)4 梯度下降函数
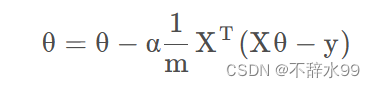
(1)函数定义
def gradientDescent(X,y,theta,alpha,iters):
costs = []
for i in range(iters):
theta = theta - (X.T@(X@theta-y))*alpha/len(X)
cost = costFunction(X,y,theta)
costs.append(cost)
if i%100 ==0:
print(cost)
return theta,costs(2)指定学习率与迭代次数,并实例化
alpha=0.02
iters=2000
theta,costs=gradientDescent(X,y,theta,alpha,iters)5 可视化
fig,ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(np.arange(iters),costs)
ax.set(xlabel='iters',
ylabel='cost',
title='cost vs iters')
plt.show()二、多变量线性回归
1 导入数据
(1)导入库
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt(2)导入数据
data = pd.read_csv('ex1data2.txt',names=['size','bedrooms','price'])
data.head()(3)特征归一化
def normalize_feature(data):
return (data-data.mean())/data.std()
data = normalize_feature(data)(4)可视化
data.plot.scatter('size','price',label='size')
plt.show()
data.plot.scatter('bedrooms','price',label='bedrooms')
plt.show()2 构造数据集
(1)X列增加
data.insert(0,'x',1)
data.head()(2)数据集分割
X = data.iloc[:,0:-1]
y = data.iloc[:,-1](3)数据类型转化与形状查看
X = X.values
X.shape
y = y.values
y = y.reshape(47,1)3 损失函数
def costFunction(X,y,theta):
inner = np.power(X@theta-y,2)
return np.sum(inner)/(2*len(X))
theta = np.zeros((3,1))4 梯度下降函数
def gradientDescent(X,y,theta,alpha,iters,isprint=False):
costs = []
for i in range(iters):
theta = theta - (X.T @ (X@theta - y) ) * alpha / len(X)
cost = costFunction(X,y,theta)
costs.append(cost)
if i%100==0:
if isprint:
print(cost)
return theta,costs5 学习率选择
candinate_alpha = [0.0003,0.003,0.03,0.0001,0.001,0.01]
iters = 2000
fig,ax = plt.subplots()
for alpha in candinate_alpha:
_,costs=gradientDescent(X,y,theta,alpha,iters)
ax.plot(np.arange(iters),costs,label = alpha)
ax.legend()
ax.set(xlabel='iters',
ylabel='cost',
title='cost vs iters')
plt.show()




















 838
838











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








