需要说明的是,用户主动调用 request,只会出发 measure 和 layout 过程,而不会执行 draw 过程
2. 概念
measure 和 layout
从整体上来看 Measure 和 Layout 两个步骤的执行:

树的遍历是有序的,由父视图到子视图,每一个 ViewGroup 负责测绘它所有的子视图,而最底层的 View 会负责测绘自身。
具体分析
measure 过程由measure(int, int)方法发起,从上到下有序的测量 View,在 measure 过程的最后,每个视图存储了自己的尺寸大小和测量规格。 layout 过程由layout(int, int, int, int)方法发起,也是自上而下进行遍历。在该过程中,每个父视图会根据 measure 过程得到的尺寸来摆放自己的子视图。
measure 过程会为一个 View 及所有子节点的 mMeasuredWidth 和 mMeasuredHeight 变量赋值,该值可以通过getMeasuredWidth()和getMeasuredHeight()方法获得。而且这两个值必须在父视图约束范围之内,这样才可以保证所有的父视图都接收所有子视图的测量。如果子视图对于 Measure 得到的大小不满意的时候,父视图会介入并设置测量规则进行第二次 measure。比如,父视图可以先根据未给定的 dimension 去测量每一个子视图,如果最终子视图的未约束尺寸太大或者太小的时候,父视图就会使用一个确切的大小再次对子视图进行 measure。
measure 过程传递尺寸的两个类
1.ViewGroup.LayoutParams (View 自身的布局参数)
2.MeasureSpecs 类(父视图对子视图的测量要求)
ViewGroup.LayoutParams
这个类我们很常见,就是用来指定视图的高度和宽度等参数。对于每个视图的 height 和 width,你有以下选择:
1.具体值
2.MATCH_PARENT 表示子视图希望和父视图一样大(不包含 padding 值)
3.WRAP_CONTENT 表示视图为正好能包裹其内容大小(包含 padding 值)
ViewGroup 的子类有其对应的 ViewGroup.LayoutParams 的子类。比如 RelativeLayout 拥有的 ViewGroup.LayoutParams 的子类 RelativeLayoutParams。
有时我们需要使用 view.getLayoutParams() 方法获取一个视图 LayoutParams,然后进行强转,但由于不知道其具体类型,可能会导致强转错误。其实该方法得到的就是其所在父视图类型的 LayoutParams,比如 View 的父控件为 RelativeLayout,那么得到的 LayoutParams 类型就为 RelativeLayoutParams。
MeasureSpecs
测量规格,包含测量要求和尺寸的信息,有三种模式:
1.UNSPECIFIED
父视图不对子视图有任何约束,它可以达到所期望的任意尺寸。比如 ListView、ScrollView,一般自定义 View 中用不到,
2.EXACTLY
父视图为子视图指定一个确切的尺寸,而且无论子视图期望多大,它都必须在该指定大小的边界内,对应的属性为 match_parent 或具体值,比如 100dp,父控件可以通过MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec)直接得到子控件的尺寸。
3.AT_MOST
父视图为子视图指定一个最大尺寸。子视图必须确保它自己所有子视图可以适应在该尺寸范围内,对应的属性为 wrap_content,这种模式下,父控件无法确定子 View 的尺寸,只能由子控件自己根据需求去计算自己的尺寸,这种模式就是我们自定义视图需要实现测量逻辑的情况。
3. measure 核心方法
measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
该方法定义在View.java类中,为 final 类型,不可被复写,但 measure 调用链最终会回调 View/ViewGroup 对象的 onMeasure()方法,因此自定义视图时,只需要复写 onMeasure() 方法即可。
onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
该方法就是我们自定义视图中实现测量逻辑的方法,该方法的参数是父视图对子视图的 width 和 height 的测量要求。在我们自身的自定义视图中,要做的就是根据该 widthMeasureSpec 和 heightMeasureSpec 计算视图的 width 和 height,不同的模式处理方式不同。
setMeasuredDimension()
测量阶段终极方法,在 onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) 方法中调用,将计算得到的尺寸,传递给该方法,测量阶段即结束。该方法也是必须要调用的方法,否则会报异常。在我们在自定义视图的时候,不需要关心系统复杂的 Measure 过程的,只需调用setMeasuredDimension()设置根据 MeasureSpec 计算得到的尺寸即可,你可以参考 ViewPagerIndicator 的 onMeasure 方法。
下面我们取 ViewGroup 的 measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) 方法对复合 View 的 Measure 流程做一个分析: MeasureChild 的方法调用流程图:
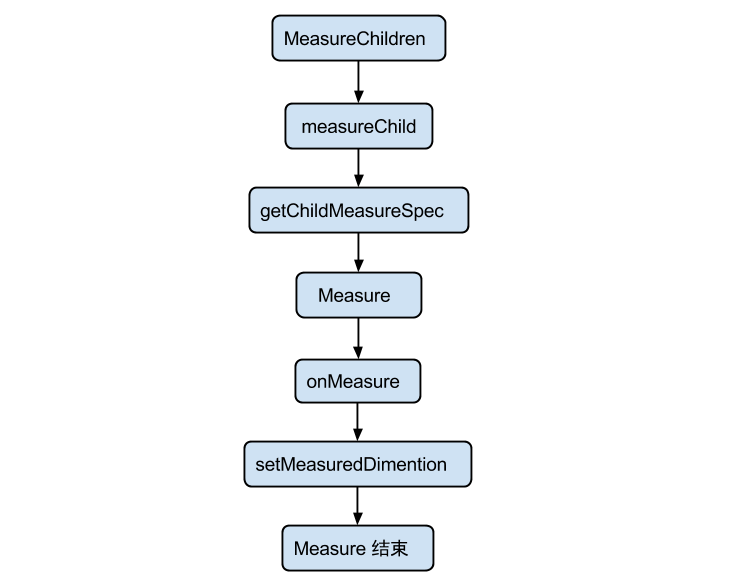
源码分析
/**
- 请求所有子 View 去 measure 自己,要考虑的部分有对子 View 的测绘要求 MeasureSpec 以及其自身的 padding
- 这里跳过所有为 GONE 状态的子 View,最繁重的工作是在 getChildMeasureSpec 方法中处理的
- @param widthMeasureSpec 对该 View 的 width 测绘要求
- @param heightMeasureSpec 对该 View 的 height 测绘要求
*/
protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
final int size = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
final View child = children[i];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != GONE) {
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();//获取 Child 的 LayoutParams
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,// 获取 ChildView 的 widthMeasureSpec
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,// 获取 ChildView 的 heightMeasureSpec
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
/**
- 该方法是 measureChildren 中最繁重的部分,为每一个 ChildView 计算出自己的 MeasureSpec。
- 目标是将 ChildView 的 MeasureSpec 和 LayoutParams 结合起来去得到一个最合适的结果。
- @param spec 对该 View 的测绘要求
- @param padding 当前 View 在当前唯独上的 paddingand,也有可能含有 margins
- @param childDimension 在当前维度上(height 或 width)的具体指
- @return 子视图的 MeasureSpec
*/
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
…
// 根据获取到的子视图的测量要求和大小创建子视图的 MeasureSpec
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
/**
*
- 用于获取 View 最终的大小,父视图提供了宽、高的约束信息
- 一个 View 的真正的测量工作是在 onMeasure(int, int) 中,由该方法调用。
- 因此,只有 onMeasure(int, int) 可以而且必须被子类复写
- @param widthMeasureSpec 在水平方向上,父视图指定的的 Measure 要求
- @param heightMeasureSpec 在竖直方向上,控件上父视图指定的 Measure 要求
*/
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
…
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
…
}
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
4. layout 相关概念及核心方法
首先要明确的是,子视图的具体位置都是相对于父视图而言的。View 的 onLayout 方法为空实现,而 ViewGroup 的 onLayout 为 abstract 的,因此,如果自定义的 View 要继承 ViewGroup 时,必须实现 onLayout 函数。
在 layout 过程中,子视图会调用getMeasuredWidth()和getMeasuredHeight()方法获取到 measure 过程得到的 mMeasuredWidth 和 mMeasuredHeight,作为自己的 width 和 height。然后调用每一个子视图的layout(l, t, r, b)函数,来确定每个子视图在父视图中的位置。
LinearLayout 的 onLayout 源码分析
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
layoutVertical(l, t, r, b);
} else {
layoutHorizontal(l, t, r, b);
}
}
/**
- 遍历所有的子 View,为其设置相对父视图的坐标
*/
void layoutVertical(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
if (child == null) {
childTop += measureNullChild(i);
} else if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {//不需要立即展示的 View 设置为 GONE 可加快绘制
final int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();//measure 过程确定的 Width
final int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();//measure 过程确定的 height
…确定 childLeft、childTop 的值
setChildFrame(child, childLeft, childTop + getLocationOffset(child),
childWidth, childHeight);
}
}
}
private void setChildFrame(View child, int left, int top, int width, int height) {
child.layout(left, top, left + width, top + height);
}
View.java
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
…
setFrame(l, t, r, b)
}
/**
- 为该子 View 设置相对其父视图上的坐标
*/
protected boolean setFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
…
}
5. 绘制流程相关概念及核心方法
先来看下与 draw 过程相关的函数:
这里我就分享一份资料,希望可以帮助到大家提升进阶。
内容包含:Android学习PDF+架构视频+面试文档+源码笔记,高级架构技术进阶脑图、Android开发面试专题资料,高级进阶架构资料 这几块的内容。分享给大家,非常适合近期有面试和想在技术道路上继续精进的朋友。
如果你有需要的话,可以点击Android学习PDF+架构视频+面试文档+源码笔记获取免费领取方式
喜欢本文的话,不妨给我点个小赞、评论区留言或者转发支持一下呗~
master/Android%E5%BC%80%E5%8F%91%E4%B8%8D%E4%BC%9A%E8%BF%99%E4%BA%9B%EF%BC%9F%E5%A6%82%E4%BD%95%E9%9D%A2%E8%AF%95%E6%8B%BF%E9%AB%98%E8%96%AA%EF%BC%81.md)
喜欢本文的话,不妨给我点个小赞、评论区留言或者转发支持一下呗~






















 1700
1700











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








