Georgios K. Apostolidis在2017年提出了一种非稳态信号分解的新方法,即群体分解算法(SWD)。SWD的基石是蜂群过滤(SwF),这是一种由蜂群-猎物狩猎设想的处理方法。在适当的参数化下,SwF的迭代应用的输出结果是输入信号的单个输入信号的一个组成部分。为了控制该方法,"狩猎 "参数与SwF特定响应之间的关系被提取出来。SWD由连续的
在不同的 "猎取 "参数下连续应用迭代SwF,以便将现有的成分提取出来。提取的现有成分通过将SWD应用于非稳态多分量(包括合成和现实生活中的)信号分解,对其进行了评估。用SWD得到的结果与用经验模式分解得到的结果进行了比较。经验模式分解、基于小波的多分辨率分析和基于特征值分解的迭代方法所获得的结果进行比较。基于汉克尔矩阵的特征值分解的方法,在大多数情况下,在正确隔离分析信号的成分方面取得了更高的精度。这些可喜的结果为为信号分解的新方法铺平了道路,具有广泛的应用潜力。SWD 是一种智能的模态分解算法,通过迭代 群滤波器将多分量信号分解为多个本征模态函数 分量( Intrinsic Mode Function,IMF) 之和,SWD 的 过程为:

1、代码实现
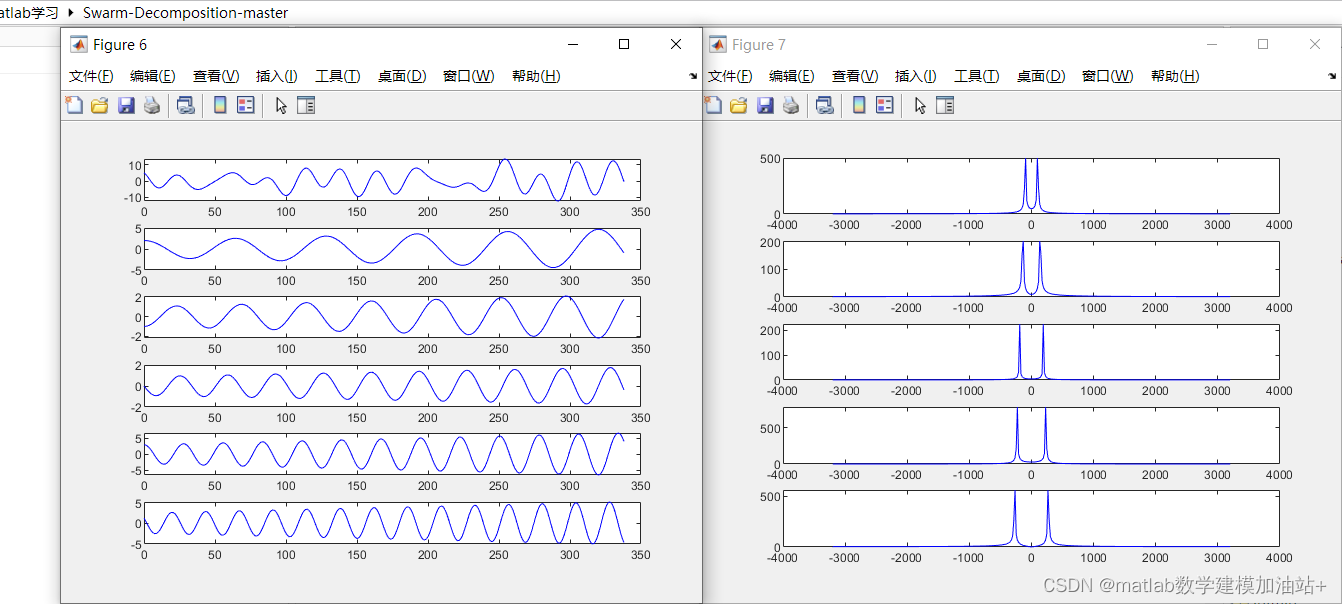
load 'chb01_01_edfm.mat'; signal_idx = 20; x = val(signal_idx, :); x = (x - mean(x)) / max(abs(x)); fs = 256; dt = 1 / fs; L = length(x); t = 0:dt:(L - 1) * dt; nfft = 2 ^ nextpow2(L); X = abs(fft(x, nfft)) / L; f = (fs / 2) * linspace(0, 1, nfft/2); figure; subplot(1, 2, 1); plot(t, x); subplot(1, 2, 2); plot(f, X(1:end/2)); % bandpass filtering [b, a] = butter(5, [7 31.5] / (fs / 2), 'bandpass'); x_filt = filtfilt(b, a, x); nfft = 2 ^ nextpow2(length(x_filt)); X_filt = abs(fft(x_filt, nfft)) / nfft; f = (fs / 2) * linspace(0, 1, nfft/2); figure; subplot(1, 2, 1); plot(t, x_filt); subplot(1, 2, 2); plot(f, X_filt(1:end/2)); % downsamping q = 4; fs2 = fs / q; dt2 = 1 / fs2; x_dec = resample(x_filt, 1, q); L_dec = length(x_dec); nfft = 2 ^ nextpow2(L_dec); X_dec = abs(fft(x_dec, nfft)) / L_dec; t2 = 0:dt2:(length(x_dec) - 1) * dt2; f2 = (fs2 / 2) * linspace(0, 1, nfft/2); figure; subplot(1, 2, 1); plot(t2, x_dec); subplot(1, 2, 2); plot(f2, X_dec(1:end/2)); %% ******************* SWD execution ******************* L1 = length(x_dec); s_SWD = [x_dec, zeros(1,100)]; % zero-padding L2 = length(s_SWD); % parameter setting % ------------------------ % How coarse/fine the decomposition will be depends on the smoothing of the FFT spectrum using Savitsky-Golay filter, according to the paper. % Here a better approach is adopted calculating the Welch spectrum and we configure the smoothness % via the Welch spectrum parameters which are the Welch window length and the overlapping (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Welch's_method). % If the Welch window is equal to the length of the input signal and the overlap is 0% the Welch spectrum is identical to FFT-based power spectrum. % More segments (i.e. "small" windows) means more smoothing so more coarse decomposition, whereas, % less segments (i.e. "big" windows) means less smoothing so finer decomposition. % In short, the smoothing process is replaced from Savitsky-Golay filtering of FFT to calculating Welch spectrum. % ------------------------ welch_window = round(L2 / 16); welch_no_overlap = round(welch_window / 2); welch_nfft = 2^nextpow2(L2); param_struct = struct('P_th', 0.2, ... 'StD_th', 0.2, ... 'Welch_window', welch_window, ... 'Welch_no_overlap', welch_no_overlap, ... 'Welch_nfft', welch_nfft); y_SWD_res = SwD(s_SWD, param_struct); disp('end') y_SWD = y_SWD_res.'; %% ******************* Plot results ******************* no_comp_SWD = size(y_SWD, 1); figure; for i = 1:1:no_comp_SWD subplot(no_comp_SWD, 1, i); plot(t2, y_SWD(i, 1:L1)); end figure; for i = 1:1:no_comp_SWD nfft = 2 ^ nextpow2(length(y_SWD(i, :))); Y = abs(fft(y_SWD(i,:), nfft)) / nfft; ff = (fs2 / 2) * linspace(0,1, nfft / 2); subplot(no_comp_SWD, 1, i); plot(ff, Y(1:end/2)); end结果展示
关注公众号“matlab之家”输入群体分解算法获取



























 562
562

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








