【数据结构与算法】十六 二叉树遍历 Breadth-First-Search 广度优先
Breadth-First-Search 广度优先 ,
广度优先遍历是连通图的一种遍历策略。因为它的思想是从一个顶点V0开始,辐射状地优先遍历其周围较广的区域,故得名。
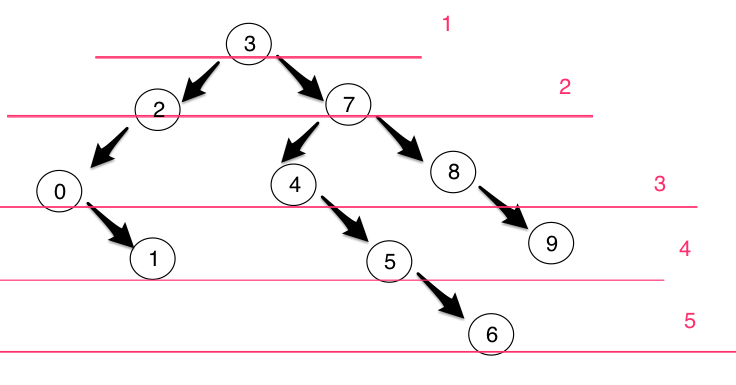
以层为单位进行遍历.如图
-
广度优先遍历与深度优先遍历的区别在于:广度优先遍历是以层为顺序,将某一层上的所有节点都搜索到了之后才向下一层搜索;而深度优先遍历是将某一条枝桠上的所有节点都搜索到了之后,才转向搜索另一条枝桠上的所有节点。 - 深度优先遍历从某个顶点出发,首先访问这个顶点,然后找出刚访问这个结点的第一个未被访问的邻结点,然后再以此邻结点为顶点,继续找它的下一个新的顶点进行访问,重复此步骤,直到所有结点都被访问完为止。
- 广度优先遍历从某个顶点出发,首先访问这个顶点,然后找出这个结点的所有未被访问的邻接点,访问完后再访问这些结点中第一个邻接点的所有结点,重复此方法,直到所有结点都被访问完为止。
- 可以看到两种方法最大的区别在于前者从顶点的第一个邻接点一直访问下去再访问顶点的第二个邻接点;后者从顶点开始访问该顶点的所有邻接点再依次向下,一层一层的访问。
package com.cn.mark.algorithm.binarytree;
/**
* Created by mark on 6/19/16.
*/
public class BSTBreadth {
Node root = null;
class Node {
int value;
int position;
Node left = null, right = null;
Node(int value, int position){
this.value = value;
this.position = position;
}
}
public void add(int value, int position){
if(root == null){
root = new Node(value, position);
} else {
add(value, position, root);
}
}
private void add(int value, int position, Node node){
if(node == null)
throw new RuntimeException("treenode cannot be null");
if(node.value == value)
return; //ignore the duplicated value
if(value < node.value){
if(node.left == null){
node.left = new Node(value, position);
}else{
add(value, position, node.left);
}
}else{
if(node.right == null){
node.right = new Node(value, position);
}else{
add(value, position, node.right);
}
}
}
public int depth(){
return depth(root);
}
private int depth(Node node){
if(node == null)
return 0;
int leftDepth = depth(node.left);
int rightDepth = depth(node.right);
return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
public void levelOrder(){
int depth = depth();
for(int level = 0; level < depth; level ++){
printLevel(root, level);
System.out.println("\n-------------------");
}
}
private void printLevel(Node node, int level){
if(node == null)
return;
if(level == 0){
System.out.print(" " + node.value);
}else{
printLevel(node.left, level - 1);
printLevel(node.right, level - 1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BSTBreadth bst = new BSTBreadth();
int a[] = {3,7,8,4,2,5,9,0,6,1};
for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++){
bst.add(a[i], i);
}
System.out.println("Tree Depth:" + bst.depth());
bst.levelOrder();
}
}






 本文介绍了二叉树遍历中的BFS(广度优先搜索)策略。BFS是一种从根节点开始,逐层遍历所有节点的算法。与DFS(深度优先搜索)不同,BFS先访问当前层的所有节点,再进入下一层。通过BFS,可以有效地探索树的广度,适合解决最短路径等问题。
本文介绍了二叉树遍历中的BFS(广度优先搜索)策略。BFS是一种从根节点开始,逐层遍历所有节点的算法。与DFS(深度优先搜索)不同,BFS先访问当前层的所有节点,再进入下一层。通过BFS,可以有效地探索树的广度,适合解决最短路径等问题。
















 6521
6521

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








