Class 1:神经网络和深度学习
Week 4:深层神经网络——编程练习
目录
1深层网络用到的函数
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import h5py
# 1 下载数据集
def load_data():
train_dataset = h5py.File('datasets/train_catvnoncat.h5', "r")
train_set_x_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_x"][:]) # your train set features
train_set_y_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_y"][:]) # your train set labels
test_dataset = h5py.File('datasets/test_catvnoncat.h5', "r")
test_set_x_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_x"][:]) # your test set features
test_set_y_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_y"][:]) # your test set labels
classes = np.array(test_dataset["list_classes"][:]) # the list of classes
train_set_y_orig = train_set_y_orig.reshape((1, train_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
test_set_y_orig = test_set_y_orig.reshape((1, test_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
return train_set_x_orig, train_set_y_orig, test_set_x_orig, test_set_y_orig, classes
# 2-1 初始化参数:2层
def initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y):
"""
Argument:
n_x -- size of the input layer
n_h -- size of the hidden layer
n_y -- size of the output layer
Returns:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters:
W1 -- weight matrix of shape (n_h, n_x)
b1 -- bias vector of shape (n_h, 1)
W2 -- weight matrix of shape (n_y, n_h)
b2 -- bias vector of shape (n_y, 1)
"""
np.random.seed(1)
W1 = np.random.randn(n_h, n_x)*0.01
b1 = np.zeros((n_h, 1))
W2 = np.random.randn(n_y, n_h)*0.01
b2 = np.zeros((n_y, 1))
assert(W1.shape == (n_h, n_x))
assert(b1.shape == (n_h, 1))
assert(W2.shape == (n_y, n_h))
assert(b2.shape == (n_y, 1))
parameters = {"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2}
return parameters
# 2-2 初始化参数:L层
def initialize_parameters_deep(layer_dims):
"""
Arguments:
layer_dims -- python array (list) containing the dimensions of each layer in our network
Returns:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters "W1", "b1", ..., "WL", "bL":
Wl -- weight matrix of shape (layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1])
bl -- bias vector of shape (layer_dims[l], 1)
"""
np.random.seed(1)
parameters = {}
L = len(layer_dims) # number of layers in the network
for l in range(1, L):
parameters['W' + str(l)] = np.random.randn(layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1])*0.01
parameters['b' + str(l)] = np.zeros((layer_dims[l], 1))
assert(parameters['W' + str(l)].shape == (layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1]))
assert(parameters['b' + str(l)].shape == (layer_dims[l], 1))
return parameters
# 3-1 激活函数:sigmoid
def sigmoid(Z):
"""
Implements the sigmoid activation in numpy
Arguments:
Z -- numpy array of any shape
Returns:
A -- output of sigmoid(z), same shape as Z
cache -- returns Z as well, useful during backpropagation
"""
A = 1/(1+np.exp(-Z))
cache = Z
return A, cache
# 3-2 激活函数:ReLU
def relu(Z):
"""
Implement the ReLU function.
Arguments:
Z -- Output of the linear layer, of any shape
Returns:
A -- Post activation parameter, of the same shape as Z
cache -- a python dictionary containing "A" ; stored for computing backward efficiently
"""
A = np.maximum(0,Z)
assert(A.shape == Z.shape)
cache = Z
return A, cache
# 4-1 relu backward, 对激活函数计算后向传播
def relu_backward(dA, cache):
"""
Implement the backward propagation for a single RELU unit.
Arguments:
dA -- post-activation gradient, of any shape
cache -- 'Z' where we store for computing backward propagation efficiently
Returns:
dZ -- Gradient of the cost with respect to Z
"""
Z = cache
dZ = np.array(dA, copy=True) # just converting dz to a correct object.
# When z <= 0, you should set dz to 0 as well.
dZ[Z <= 0] = 0
assert (dZ.shape == Z.shape)
return dZ
# 4-2 sigmoid backward 对激活函数计算后向传播
def sigmoid_backward(dA, cache):
"""
Implement the backward propagation for a single SIGMOID unit.
Arguments:
dA -- post-activation gradient, of any shape
cache -- 'Z' where we store for computing backward propagation efficiently
Returns:
dZ -- Gradient of the cost with respect to Z
"""
Z = cache
s = 1/(1+np.exp(-Z))
dZ = dA * s * (1-s) # 感觉 dA = dZ * s * (1-s)
assert (dZ.shape == Z.shape)
return dZ
# 5-1 前向传播的线性部分
def linear_forward(A, W, b):
"""
Implement the linear part of a layer's forward propagation.
Arguments:
A -- activations from previous layer (or input data): (size of previous layer, number of examples)
W -- weights matrix: numpy array of shape (size of current layer, size of previous layer)
b -- bias vector, numpy array of shape (size of the current layer, 1)
Returns:
Z -- the input of the activation function, also called pre-activation parameter
cache -- a python dictionary containing "A", "W","b" ; stored for computing the backward efficiently
"""
Z = np.dot(W,A) + b
assert(Z.shape == (W.shape[0], A.shape[1]))
cache = (A, W, b)
return Z, cache
# 5-2 前向传播线性激活
def linear_activation_forward(A_prev, W, b, activation):
"""
Implement the forward propagation for the LINEAR->ACTIVATION layer
Arguments:
A_prev -- activations from previous layer (or input data): (size of previous layer, number of examples)
W -- weights matrix: numpy array of shape (size of current layer, size of previous layer)
b -- bias vector, numpy array of shape (size of the current layer, 1)
activation -- the activation to be used in this layer, stored as a text string: "sigmoid" or "relu"
Returns:
A -- the output of the activation function, also called the post-activation value
cache -- a python dictionary containing "linear_cache" and "activation_cache";
stored for computing the backward pass efficiently
"""
if activation == "sigmoid":
# Inputs: "A_prev, W, b". Outputs: "A, activation_cache".
Z, linear_cache = linear_forward(A_prev, W, b)
A, activation_cache = sigmoid(Z)
elif activation == "relu":
# Inputs: "A_prev, W, b". Outputs: "A, activation_cache".
Z, linear_cache = linear_forward(A_prev, W, b)
A, activation_cache = relu(Z)
assert (A.shape == (W.shape[0], A_prev.shape[1]))
cache = (linear_cache, activation_cache) # linear_cache 包含: A_prev,W,b
# activation_cache 包含:Z
return A, cache # cache 包含 A_prev, W, b, Z
# 5-3 L模型 前向传播
def L_model_forward(X, parameters):
"""
Implement forward propagation for the [LINEAR->RELU]*(L-1)->LINEAR->SIGMOID computation
Arguments:
X -- data, numpy array of shape (input size, number of examples)
parameters -- output of initialize_parameters_deep()
Returns:
AL -- last post-activation value
caches -- list of caches containing:
every cache of linear_relu_forward() (there are L-1 of them, indexed from 0 to L-2)
the cache of linear_sigmoid_forward() (there is one, indexed L-1)
"""
caches = []
A = X
L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network
# Implement [LINEAR -> RELU]*(L-1). Add "cache" to the "caches" list.
for l in range(1, L):
A_prev = A
A, cache = linear_activation_forward(A_prev, parameters['W' + str(l)], parameters['b' + str(l)], activation = "relu")
caches.append(cache)
# Implement LINEAR -> SIGMOID. Add "cache" to the "caches" list.
AL, cache = linear_activation_forward(A, parameters['W' + str(L)], parameters['b' + str(L)], activation = "sigmoid")
caches.append(cache)
assert(AL.shape == (1,X.shape[1]))
return AL, caches # caches 包含每一层的 A_prev, W, b, Z
# 6 计算损失函数
def compute_cost(AL, Y):
"""
Implement the cost function
Arguments:
AL -- probability vector corresponding to your label predictions, shape (1, number of examples)
Y -- true "label" vector (for example: containing 0 if non-cat, 1 if cat), shape (1, number of examples)
Returns:
cost -- cross entropy cost
"""
m = Y.shape[1]
# Compute loss from AL and y.
cost = (1./m) * (-np.dot(Y,np.log(AL).T) - np.dot(1-Y, np.log(1-AL).T))
cost = np.squeeze(cost) # To make sure your cost's shape is what we expect
return cost
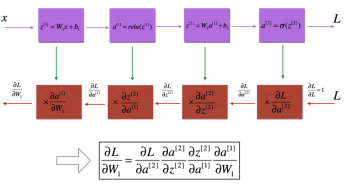
# 7-1 反向传播 线性部分
def linear_backward(dZ, cache):
"""
Implement the linear portion of backward propagation for a single layer (layer l)
Arguments:
dZ -- Gradient of the cost with respect to the linear output (of current layer l)
cache -- tuple of values (A_prev, W, b) coming from the forward propagation in the current layer
Returns:
dA_prev -- Gradient of the cost with respect to the activation (of the previous layer l-1), same shape as A_prev
dW -- Gradient of the cost with respect to W (current layer l), same shape as W
db -- Gradient of the cost with respect to b (current layer l), same shape as b
"""
A_prev, W, b = cache
m = A_prev.shape[1]
dW = 1./m * np.dot(dZ,A_prev.T)
db = 1./m * np.sum(dZ, axis = 1, keepdims = True)
dA_prev = np.dot(W.T,dZ)
assert (dA_prev.shape == A_prev.shape)
assert (dW.shape == W.shape)
assert (db.shape == b.shape)
return dA_prev, dW, db
# 7-2 反向传播: 线性激活
def linear_activation_backward(dA, cache, activation):
"""
Implement the backward propagation for the LINEAR->ACTIVATION layer.
Arguments:
dA -- post-activation gradient for current layer l
cache -- tuple of values (linear_cache, activation_cache) we store for computing backward propagation efficiently
activation -- the activation to be used in this layer, stored as a text string: "sigmoid" or "relu"
Returns:
dA_prev -- Gradient of the cost with respect to the activation (of the previous layer l-1), same shape as A_prev
dW -- Gradient of the cost with respect to W (current layer l), same shape as W
db -- Gradient of the cost with respect to b (current layer l), same shape as b
"""
linear_cache, activation_cache = cache
if activation == "relu":
dZ = relu_backward(dA, activation_cache)
dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache)
elif activation == "sigmoid":
dZ = sigmoid_backward(dA, activation_cache)
dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache)
return dA_prev, dW, db
# 7-3 反向传播 L模型
def L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches):
"""
Implement the backward propagation for the [LINEAR->RELU] * (L-1) -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID group
Arguments:
AL -- probability vector, output of the forward propagation (L_model_forward())
Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if non-cat, 1 if cat)
caches -- list of caches containing:
every cache of linear_activation_forward() with "relu" (there are (L-1) or them, indexes from 0 to L-2)
the cache of linear_activation_forward() with "sigmoid" (there is one, index L-1)
Returns:
grads -- A dictionary with the gradients
grads["dA" + str(l)] = ...
grads["dW" + str(l)] = ...
grads["db" + str(l)] = ...
"""
grads = {}
L = len(caches) # the number of layers
m = AL.shape[1]
Y = Y.reshape(AL.shape) # after this line, Y is the same shape as AL
# Initializing the backpropagation
dAL = - (np.divide(Y, AL) - np.divide(1 - Y, 1 - AL))
# Lth layer (SIGMOID -> LINEAR) gradients. Inputs: "AL, Y, caches". Outputs: "grads["dAL"], grads["dWL"], grads["dbL"]
current_cache = caches[L-1]
grads["dA" + str(L)], grads["dW" + str(L)], grads["db" + str(L)] = linear_activation_backward(dAL, current_cache, activation = "sigmoid")
for l in reversed(range(L-1)):
# lth layer: (RELU -> LINEAR) gradients.
current_cache = caches[l]
dA_prev_temp, dW_temp, db_temp = linear_activation_backward(grads["dA" + str(l + 2)], current_cache, activation = "relu")
grads["dA" + str(l + 1)] = dA_prev_temp
grads["dW" + str(l + 1)] = dW_temp
grads["db" + str(l + 1)] = db_temp
return grads
# 8、更新参数
def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate):
"""
Update parameters using gradient descent
Arguments:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters
grads -- python dictionary containing your gradients, output of L_model_backward
Returns:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your updated parameters
parameters["W" + str(l)] = ...
parameters["b" + str(l)] = ...
"""
L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network
# Update rule for each parameter. Use a for loop.
for l in range(L):
parameters["W" + str(l+1)] = parameters["W" + str(l+1)] - learning_rate * grads["dW" + str(l+1)]
parameters["b" + str(l+1)] = parameters["b" + str(l+1)] - learning_rate * grads["db" + str(l+1)]
return parameters
# 9、预测新样本
def predict(X, y, parameters):
"""
This function is used to predict the results of a L-layer neural network.
Arguments:
X -- data set of examples you would like to label
parameters -- parameters of the trained model
Returns:
p -- predictions for the given dataset X
"""
m = X.shape[1]
n = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network
p = np.zeros((1,m))
# Forward propagation
probas, caches = L_model_forward(X, parameters)
# convert probas to 0/1 predictions
for i in range(0, probas.shape[1]):
if probas[0,i] > 0.5:
p[0,i] = 1
else:
p[0,i] = 0
print("Accuracy: " + str(np.sum((p == y)/m)))
return p
# 10、打印错误标签的图像
def print_mislabeled_images(classes, X, y, p):
"""
Plots images where predictions and truth were different.
X -- dataset
y -- true labels
p -- predictions
"""
a = p + y
mislabeled_indices = np.asarray(np.where(a == 1)) # 返回错误的索引
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (40.0, 40.0) # set default size of plots
num_images = len(mislabeled_indices[0]) # 识别错误的数量
for i in range(num_images):
index = mislabeled_indices[1][i]
plt.subplot(2, num_images, i + 1)
plt.imshow(X[:,index].reshape(64,64,3), interpolation='nearest')
plt.axis('off')
plt.title("Prediction: " + classes[int(p[0,index])].decode("utf-8") + " \n Class: " + classes[y[0,index]].decode("utf-8"))
plt.show()
2、初始化模型参数及反向传播
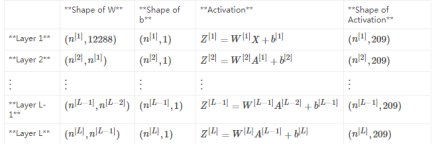
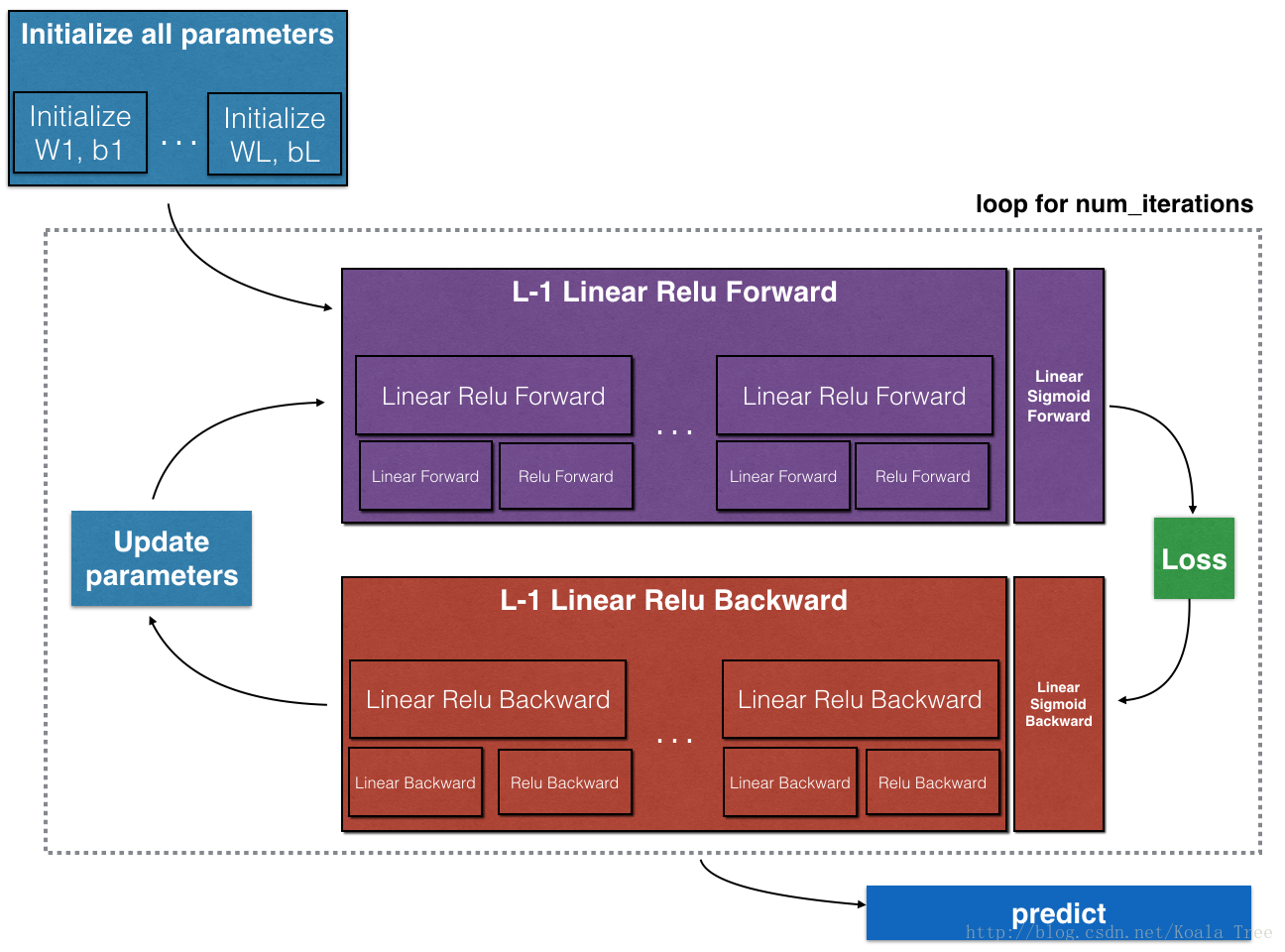
3、两层、L层神经网络模型
import time
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import h5py
import scipy
from PIL import Image
from scipy import ndimage
from testCases_v2 import *
from dnn_app_utils_v2 import *
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (5.0,4.0) #设置 plots 的默认大小
plt.rcParams['image.interpolation'] = 'nearest'
plt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'gray'
np.random.seed(1)
# 1、数据集
train_x_orig, train_y, test_x_orig, test_y, classes = load_data()
num_px = train_x_orig.shape[1]
print(train_x_orig.shape, test_x_orig.shape)
'''
# 显示其中一张图片
index = 10
plt.imshow(train_x_orig[index])
plt.show()
print ("y = " + str(train_y[0,index]) +\
". It's a " + classes[train_y[0,index]].decode("utf-8") + " picture.")
'''
# 重铺数据,并标准化
train_x_flatten = train_x_orig.reshape(train_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T
test_x_flatten = test_x_orig.reshape(test_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T
train_x = train_x_flatten/255.
test_x = test_x_flatten/255.
print(train_x.shape, test_x.shape)
# 2、两层神经网络
# 输出 w1 w2 b1 b2
def two_layer_model(X, Y, layers_dims, learning_rate=0.0075, num_iterations=3000, print_cost=False):
np.random.seed(1)
m = X.shape[1]
(n_x, n_h, n_y) = layers_dims
grads = {}
costs = []
parameters = initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y)
W1 = parameters["W1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
for i in range(0, num_iterations):
A1, cache1 = linear_activation_forward(X, W1, b1, activation="relu")
A2, cache2 = linear_activation_forward(A1, W2, b2, activation="sigmoid")
cost = compute_cost(A2, Y)
# 初始化反向传播
dA2 = - (np.divide(Y, A2) - np.divide(1-Y, 1-A2))
#dA2 = np.power(Y-A2,2) #代价函数升高
dA1, dW2, db2 = linear_activation_backward(dA2, cache2, activation="sigmoid")
dA0, dW1, db1 = linear_activation_backward(dA1, cache1, activation="relu")
grads["dW1"] = dW1
grads["dW2"] = dW2
grads["db1"] = db1
grads["db2"] = db2
parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate)
W1 = parameters["W1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
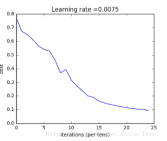
if print_cost and i%100==0:
costs.append(cost)
print("cost after iteration {}:{}".format(i, np.squeeze(cost)))
plt.plot(np.squeeze(costs))
plt.xlabel('iterations (per 100)')
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.title("learning rate = " + str(learning_rate))
plt.show()
return parameters
# 3、L层神经网络
def L_layer_model(X, Y, layers_dims, learning_rate=0.0075, num_iterations=3000, print_cost=False):
np.random.seed(1)
costs = []
parameters = initialize_parameters_deep(layers_dims)
for i in range(0, num_iterations):
AL, caches = L_model_forward(X, parameters)
cost = compute_cost(AL, Y)
grads = L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches)
parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate)
if print_cost and i%100==0:
costs.append(cost)
print("cost after iteration %i: %f" % (i,cost))
plt.plot(np.squeeze(costs))
plt.xlabel('iterations (per 100)')
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.title("learning rate = " + str(learning_rate))
plt.show()
return parameters
# 4、运行两层模型
'''
n_x = train_x.shape[0]
n_h = 7
n_y = 1
layers_dims = [n_x, n_h, n_y]
parameters = two_layer_model(train_x, train_y, layers_dims,
learning_rate=0.01, num_iterations=2500, print_cost=True)
predictions_train = predict(train_x, train_y, parameters)
predictions_test = predict(test_x, test_y, parameters)
'''
# 5、运行L层模型
layers_dims = [train_x.shape[0], 20, 7, 5, 1]
print(layers_dims)
parameters = L_layer_model(train_x, train_y, layers_dims,
learning_rate=0.01, num_iterations = 1000, print_cost = True)
predictions_train = predict(train_x, train_y, parameters)
predictions_test = predict(test_x, test_y, parameters)
'''
# 6、显示一些标记不正确的图像
print_mislabeled_images(classes, test_x, test_y, predictions_test)
# 7、用自己的图像测试
my_image = "my_image.jpg" # change this to the name of your image file
my_label_y = [1] # the true class of your image (1 -> cat, 0 -> non-cat)
fname = "images/" + my_image
image = np.array(ndimage.imread(fname, flatten=False))
my_image = scipy.misc.imresize(image, size=(num_px,num_px)).reshape((num_px*num_px*3,1))
my_predicted_image = predict(my_image, my_label_y, parameters)
plt.imshow(image)
plt.show()
print ("y = " + str(np.squeeze(my_predicted_image)) +", your L-layer model predicts a \"" \
+ classes[int(np.squeeze(my_predicted_image)),].decode("utf-8") + "\" picture.")
'''(1)2层模型:输入-linear-ReLu-linear-sigmoid-输出
循环2500次,1分钟,训练集正确率1.0,测试集正确率0.72
循环1500次,可以提高测试集正确率,叫做“早停”,提前停止防止过拟合
(2)L层模型:输入-(L-1)(linear-ReLU)-linear-sigmoid-输出
测试集正确率 80%,有所提高






















 261
261

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








