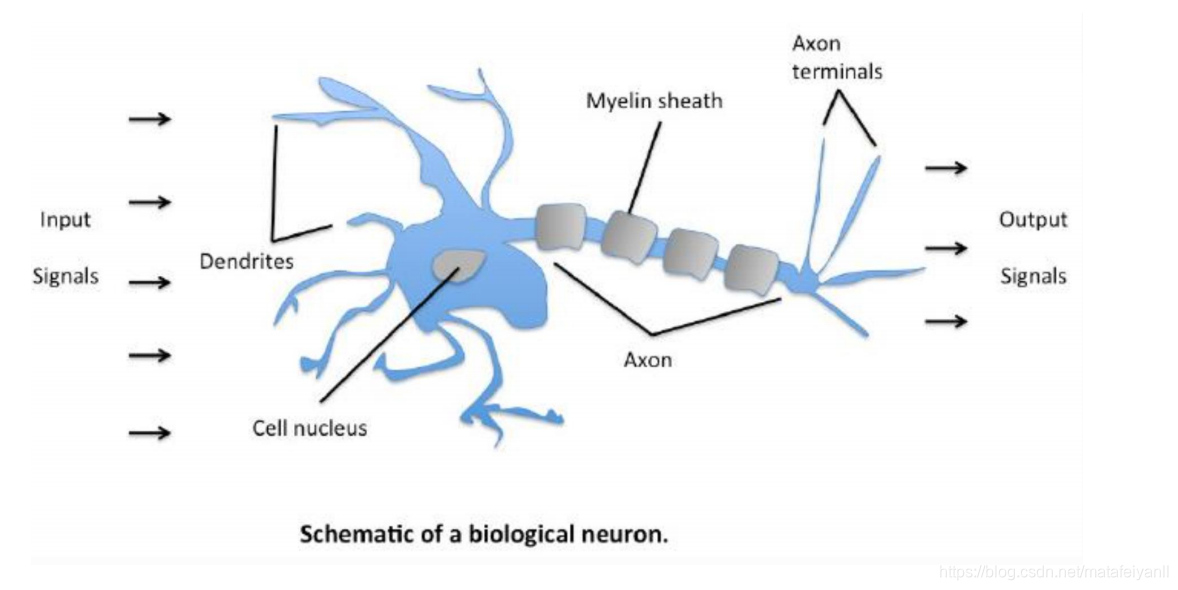
机器学习6:单层感知器
单层感知器
原理
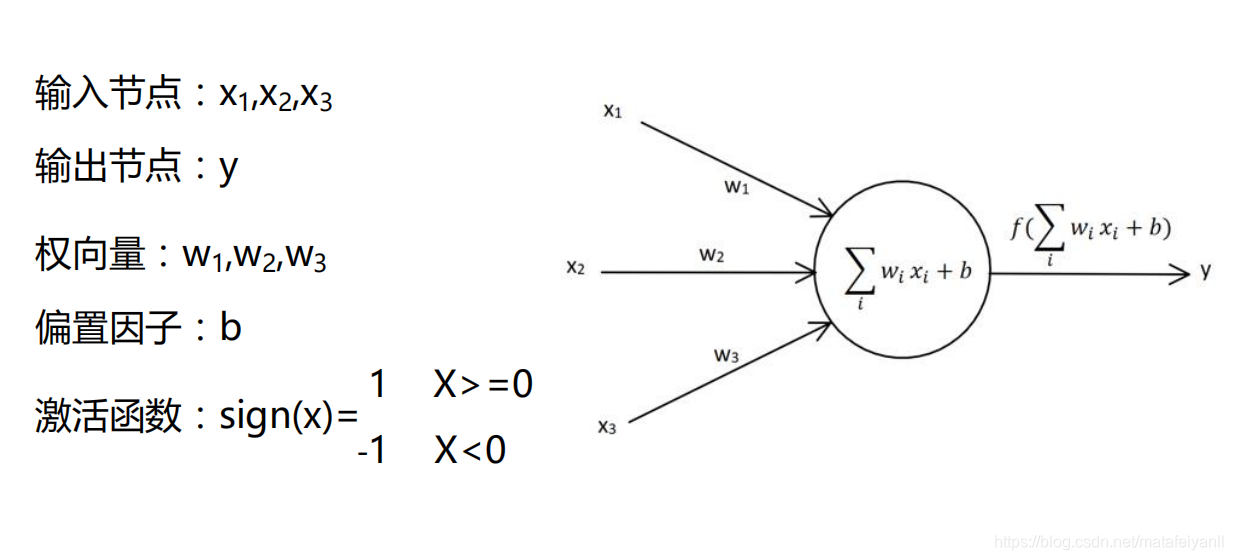
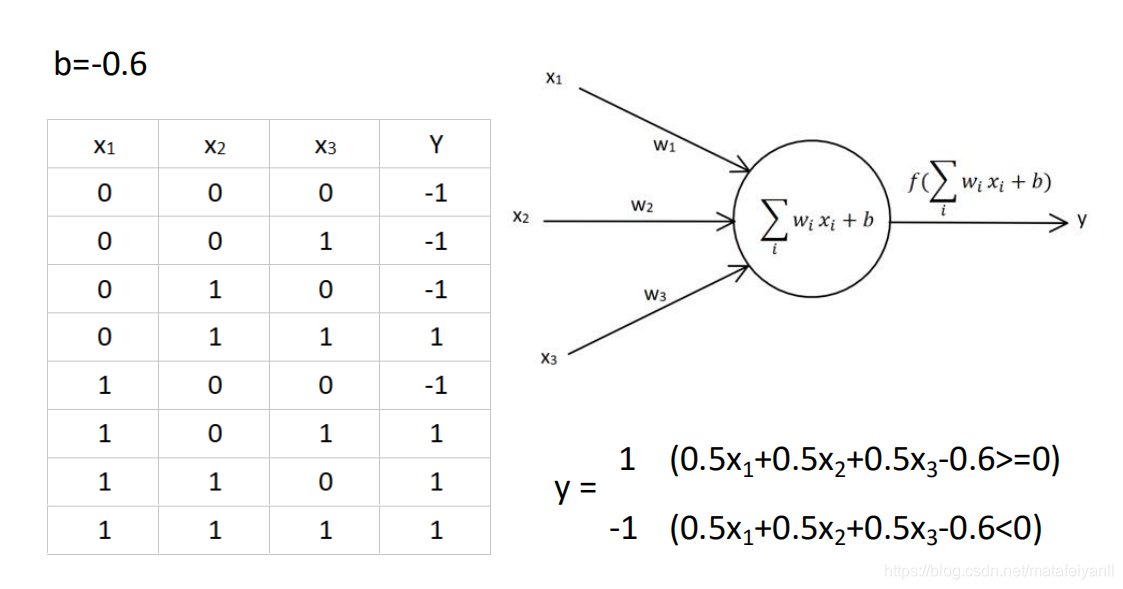
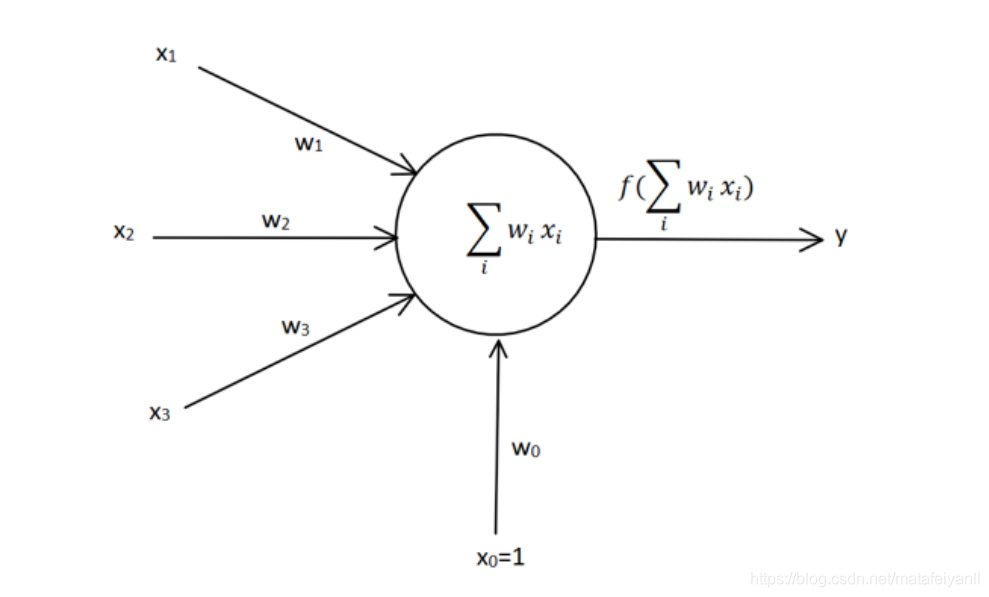
感知器学习规则

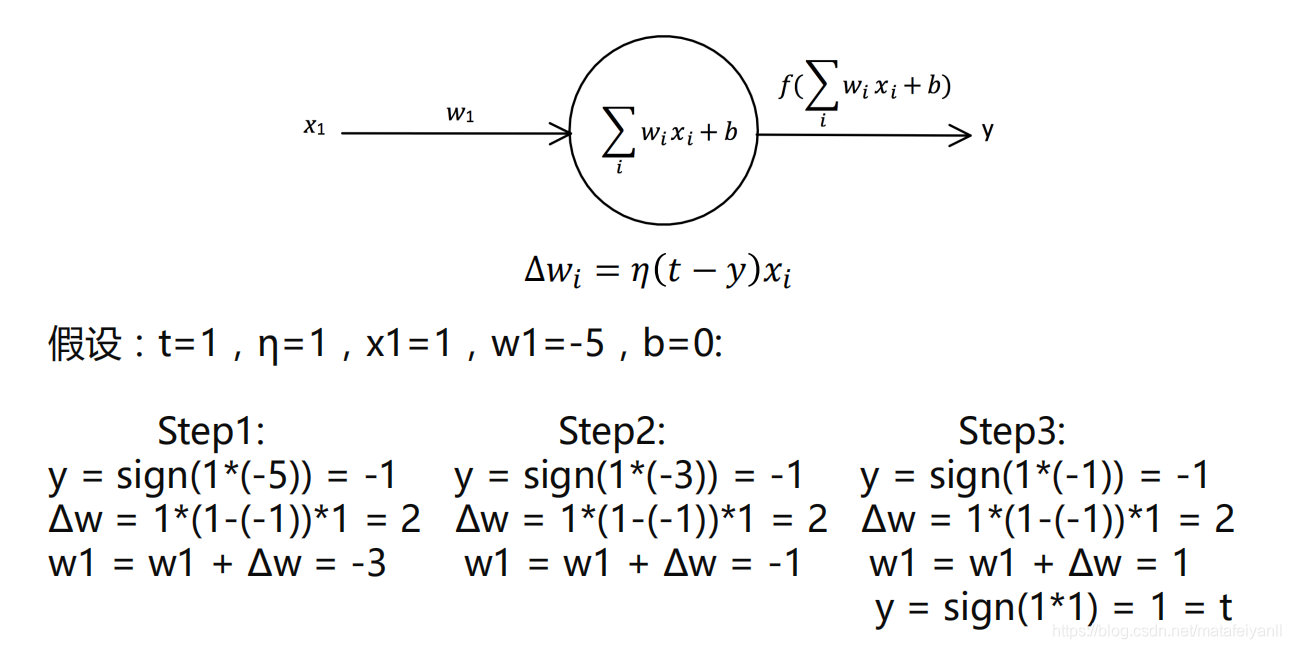
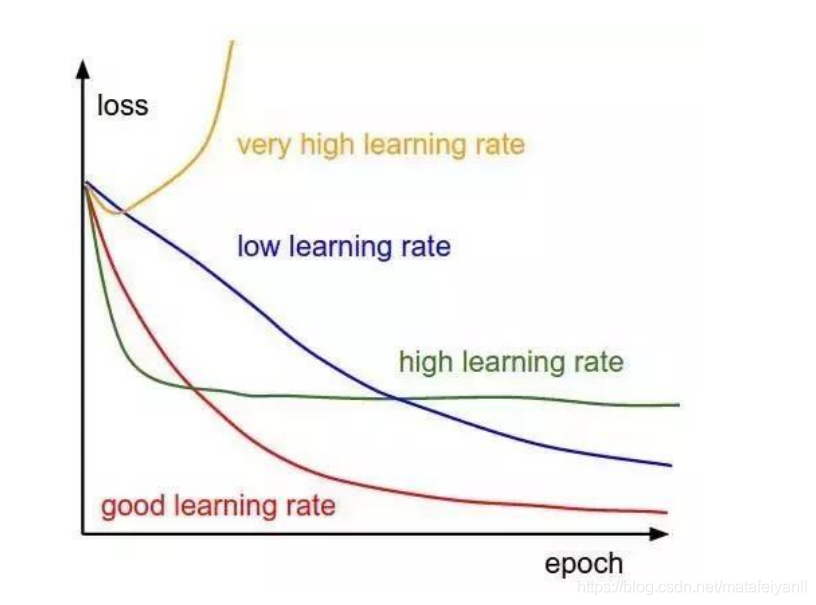
关于学习率
𝜂取值一般取0-1之间
学习率太大容易造成权值调整不稳定
学习率太小,权值调整太慢,迭代次数太多
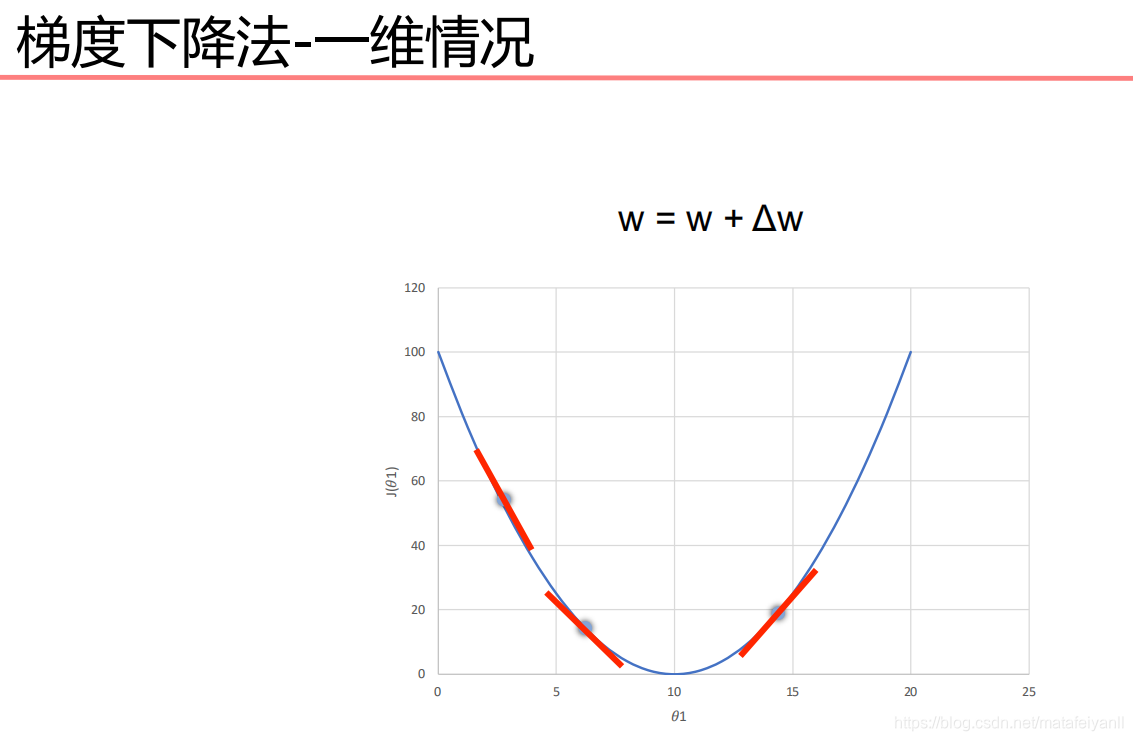
模型收敛条件
误差小于某个预先设定的较小的值
两次迭代之间的权值变化已经很小
设定最大迭代次数,当迭代超过最大次数就停止
线性神经网络
线性神经网络在结构上与感知器非常相似,只是激活函数不同。
在模型训练时把原来的sign函数改成了purelin函数:y = x
关于激活函数

Delta学习规则


算法实现
简单的单层感知器

import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#载入数据
X=np.array([[1,3,3],
[1,4,3],
[1,1,1],
[1,0,2]])
#标签
Y=np.array([[1],
[1],
[-1],
[-1]])
#权值初始化 ,3个输入,1个输出,3行1列,取值范围-1~1,本身取值范围为0~1
W=(np.random.random([3,1])-0.5)*2
print(W)
#设置学习率
lr=0.11
#神经网络输出
O=1
#权值更新
def update():
global X,Y,W,lr
O=np.sign(np.dot(X,W))
W_C=lr*(X.T.dot(Y-O))/int(X.shape[0])
W=W+W_C
[[ 0.68420477]
[ 0.25176422]
[-0.38435113]]
for i in range(100):
update() #更新权值
print(W) #打印权值
print(i) #打印当前迭代次数
O=np.sign(np.dot(X,W)) #计算当前输出
if(O==Y).all():
print("Finished")
print("epoch:",i)
break
#正样本
x1=[3,4]
y1=[3,3]
#负样本
x2=[1,0]
y2=[1,2]
#计算分界线的斜率以及截距
k=-W[1]/W[2]
d=-W[0]/W[2]
print('k=',k)
print('d=',d)
xdata=(0,5)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(xdata,xdata*k+d,'r')
plt.scatter(x1,y1,c='b')
plt.scatter(x2,y2,c='r')
plt.show()

线性感知器
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#输入数据
X = np.array([[1,3,3],
[1,4,3],
[1,1,1],
[1,0,2]])
#标签
Y = np.array([[1],
[1],
[-1],
[-1]])
#权值初始化,3行1列,取值范围-1到1
W = (np.random.random([3,1])-0.5)*2
print(W)
#学习率设置
lr = 0.11
#神经网络输出
O = 0
def update():
global X,Y,W,lr
O = np.dot(X,W) #y=x线性激活函数
W_C = lr*(X.T.dot(Y-O))/int(X.shape[0])
W = W + W_C
for _ in range(1000):
update()#更新权值
#正样本
x1 = [3,4]
y1 = [3,3]
#负样本
x2 = [1,0]
y2 = [1,2]
#计算分界线的斜率以及截距
k = -W[1]/W[2]
d = -W[0]/W[2]
print('k=',k)
print('d=',d)
xdata = (0,5)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(xdata,xdata*k+d,'r')
plt.scatter(x1,y1,c='b')
plt.scatter(x2,y2,c='y')
plt.show()

线性感知器不能解决异或问题
‘’’
异或
0^0 = 0
0^1 = 1
1^0 = 1
1^1 = 0
‘’’

找不到一条直线将两个类分开
异或问题的解决
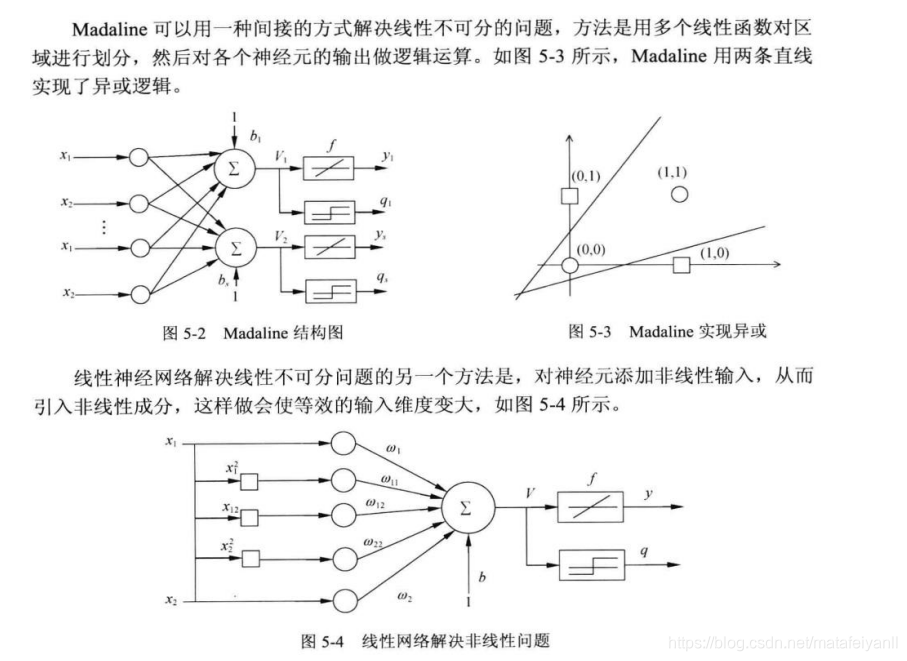
这里采用引入非线性输入
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#输入数据
X = np.array([[1,0,0,0,0,0],
[1,0,1,0,0,1],
[1,1,0,1,0,0],
[1,1,1,1,1,1]])
#标签
Y = np.array([[-1],
[1],
[1],
[-1]])
#权值初始化,3行1列,取值范围-1到1
W = (np.random.random([6,1])-0.5)*2
print(W)
#学习率设置
lr = 0.11
#计算迭代次数
n = 0
#神经网络输出
O = 0
def update():
global X,Y,W,lr,n
n+=1
O = np.dot(X,W) #y=x线性激活函数
W_C = lr*(X.T.dot(Y-O))/int(X.shape[0])
W = W + W_C
[[-0.25710504]
[ 0.43289465]
[-0.02744922]
[ 0.50894635]
[ 0.96606606]
[-0.91572789]]
for _ in range(1000):
update()#更新权值
#正样本
x1 = [0,1]
y1 = [1,0]
#负样本
x2 = [0,1]
y2 = [0,1]
#画图,计算x2的值,root=1返回正根
def calculate(x,root):
a=W[5]
b=W[2]+W[4]*x
c=W[1]*x+W[3]*x*x+W[0]
if(root==1):
return((-b+np.sqrt(b*b-4*a*c))/2/a)
if(root==0):
return((-b-np.sqrt(b*b-4*a*c))/2/a)
xdata = np.linspace(0,1)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(xdata,calculate(xdata,1),'r')
plt.plot(xdata,calculate(xdata,0),'r')
plt.plot(x1,y1,'bo')
plt.plot(x2,y2,'yo')
plt.show()























 1594
1594











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








