什么是链表?
链表是一种线性数据结构,包括一系列相连的结点。在这里,每个节点都存储数据和下一个节点的地址。例如:

链表有多种类型:单链表、双链表和循环链表。这里仅介绍单链表。
链表的简单示例
这里我用一个结构体来封装一个结点,对于每一个结点都包含:
- 数据域
- 指向下个结点的next指针
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
};下面我将创建一个包含三个结点的链表:

具体实现:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 创建一个结点
class Node {
public:
int value;
Node* next;
};
int main() {
Node* head;
Node* one = NULL;
Node* two = NULL;
Node* three = NULL;
// 为三个结点分配内存
one = new Node();
two = new Node();
three = new Node();
// 分配数据域的值
one->value = 1;
two->value = 2;
three->value = 3;
// 链接结点
one->next = two;
two->next = three;
three->next = NULL;
// 打印结点的值
head = one;
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->value;
head = head->next;
}
}遍历链表
当我们想要遍历一个链表时,需要一个临时结点来存储当前所遍历的结点,每次循环都指向它的下一个结点,直到这个临时结点指向NULL,跳出循环。
struct node *temp = head;
printf("\n\nList elements are - \n");
while(temp != NULL) {
printf("%d --->",temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}运行结果:
List elements are -
1 --->2 --->3 --->从链表中插入一个结点
1.在表头插入一个结点
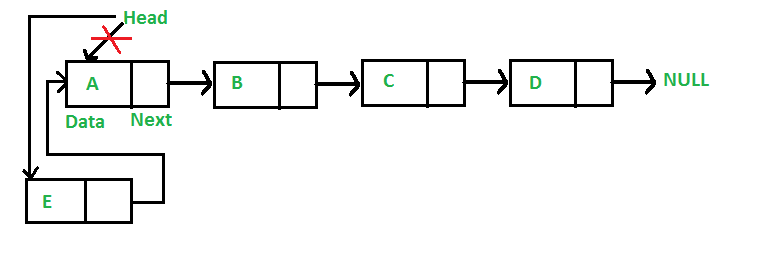
在表头插入一个结点的步骤:
- 为新结点分配内存
- 存储数据
- 改变新结点的next指针到头指针
- 改变头指针到新结点
struct node *newNode;
newNode = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newNode->data = 4;
newNode->next = head;
head = newNode;2.在表尾插入一个结点
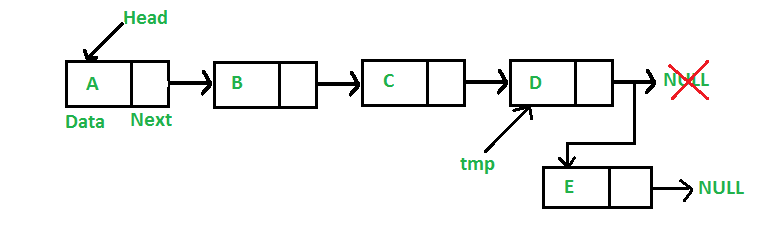
在表尾插入一个结点的步骤:
- 为新结点分配内存
- 存储数据
- 遍历最后一个结点
- 将最后结点的next指向新结点
struct node *newNode;
newNode = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newNode->data = 4;
newNode->next = NULL;
struct node *temp = head;
while(temp->next != NULL){
temp = temp->next;
}
temp->next = newNode;3.在中间位置插入一个结点
在中间位置插入一个结点的步骤:
- 为结点分配内存
- 存储数据
- 遍历到新节点所需位置前的节点
- 更改next指针到两者之间
struct node *newNode;
newNode = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newNode->data = 4;
struct node *temp = head;
for(int i=2; i < position; i++) {
if(temp->next != NULL) {
temp = temp->next;
}
}
newNode->next = temp->next;
temp->next = newNode;从链表中删除一个结点
1. 删除头结点
- 将头指针指向下一个结点
head = head->next;2. 删除尾结点
- 遍历到倒数第二个元素
- 更改它的next指针为NULL
struct node* temp = head;
while(temp->next->next!=NULL){
temp = temp->next;
}
temp->next = NULL;3. 在中间删除一个结点
- 遍历到要删除元素的前一个元素
- 更改next指针并将此结点删除
for(int i=2; i< position; i++) {
if(temp->next!=NULL) {
temp = temp->next;
}
}
temp->next = temp->next->next;在一个链表中查找一个元素
- 将头设为当前结点
- 执行该循环直到当前结点指向NULL
- 执行每一次的迭代,检查结点的键值是否与我们要找到键值相等,如果相等返回true,循环结束返回false
// 查找一个结点
bool searchNode(struct Node** head_ref, int key) {
struct Node* current = *head_ref;
while (current != NULL) {
if (current->data == key) return true;
current = current->next;
}
return false;
}对链接列表中的元素排序
下面我们将使用一种简单的排序算法--冒泡排序,对链表中的元素进行升序排序。
- 将头作为当前节点,并创建另一个节点索引供以后使用。
- 如果 head 为空,则返回。
- 否则,运行循环直到最后一个节点(即 NULL)。
- 每次迭代都要遵循以下步骤 5-6。
- 用索引存储当前节点的下一个节点。
- 检查当前节点的数据是否大于下一个节点。如果大于,则交换当前节点和索引。
// 排序此链表
void sortLinkedList(struct Node** head_ref) {
struct Node *current = *head_ref, *index = NULL;
int temp;
if (head_ref == NULL) {
return;
} else {
while (current != NULL) {
index = current->next;
while (index != NULL) {
if (current->data > index->data) {
temp = current->data;
current->data = index->data;
index->data = temp;
}
index = index->next;
}
current = current->next;
}
}
}链表在c++中的操作
// 链表在c++中的操作
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 创建一个结点
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
void insertAtBeginning(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data) {
// 为结点分配内存
struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// 插入这个数据
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
// 移动头到新结点
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// 在一个结点后插入一个结点
void insertAfter(struct Node* prev_node, int new_data) {
if (prev_node == NULL) {
cout << "the given previous node cannot be NULL";
return;
}
struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = prev_node->next;
prev_node->next = new_node;
}
// 在尾部插入
void insertAtEnd(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data) {
struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
struct Node* last = *head_ref; /* 用于步骤 5*/
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = NULL;
if (*head_ref == NULL) {
*head_ref = new_node;
return;
}
while (last->next != NULL) last = last->next;
last->next = new_node;
return;
}
// 删除节点
void deleteNode(struct Node** head_ref, int key) {
struct Node *temp = *head_ref, *prev;
if (temp != NULL && temp->data == key) {
*head_ref = temp->next;
free(temp);
return;
}
// 找到要删除的键值
while (temp != NULL && temp->data != key) {
prev = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// 如果键值不存在
if (temp == NULL) return;
// 删除此结点
prev->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
}
// 查找结点
bool searchNode(struct Node** head_ref, int key) {
struct Node* current = *head_ref;
while (current != NULL) {
if (current->data == key) return true;
current = current->next;
}
return false;
}
// 链表排序
void sortLinkedList(struct Node** head_ref) {
struct Node *current = *head_ref, *index = NULL;
int temp;
if (head_ref == NULL) {
return;
} else {
while (current != NULL) {
//索引指向当前的next
index = current->next;
while (index != NULL) {
if (current->data > index->data) {
temp = current->data;
current->data = index->data;
index->data = temp;
}
index = index->next;
}
current = current->next;
}
}
}
// 打印此链表
void printList(struct Node* node) {
while (node != NULL) {
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
}
// 驱动程序
int main() {
struct Node* head = NULL;
insertAtEnd(&head, 1);
insertAtBeginning(&head, 2);
insertAtBeginning(&head, 3);
insertAtEnd(&head, 4);
insertAfter(head->next, 5);
cout << "Linked list: ";
printList(head);
cout << "\nAfter deleting an element: ";
deleteNode(&head, 3);
printList(head);
int item_to_find = 3;
if (searchNode(&head, item_to_find)) {
cout << endl << item_to_find << " is found";
} else {
cout << endl << item_to_find << " is not found";
}
sortLinkedList(&head);
cout << "\nSorted List: ";
printList(head);
}





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










