前言
最近比较忙,所以很久没更新。
之前玩过很多三维沙盒游戏,但是很好奇是如何实现那种三维投射的
于是最近写出来了一个三维引擎
过程
我还是用的qt(自从用qt就发现爱上qt了)去实现打开窗口、画线等功能,但是qt自带的三维支持我不用。
准备工作
导入库、创建qt应用、创建空间对象,都不多说。
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QWidget,QApplication
from PySide6.QtGui import QPainter,QColor,QPen,QCursor
from PySide6.QtCore import QTimer,Qt
import math
class Space():
def __init__(self):
self.objects=[]
qapp=QApplication([])
def run():
qapp.exec()
点对象和相机对象
组成图形的基本元素是点。为了方便描述三维空间坐标,我创建了一个点对象。
同时,需要一个相机,点会投射到相机上
class Point():
def __init__(self,x,y,z):
self.x=x
self.y=y
self.z=z
class Camera(QWidget):
def __init__(self,space,wwidth,wheight,caption,cwidth,cheight,cdeepth):
super().__init__()
self.resize(wwidth,wheight)#窗口宽高
self.setWindowTitle(caption)#窗口标题
self.space=space #相机所在的空间
self.movement=[0,0,0] #相机试试移动方向
self.rotatex=0
self.rotatey=90
self.rotatez=0 #相机旋转角度
self.posx=0
self.posy=0
self.posz=0 #相机的位置
self.controled=True #鼠标是否控制
self.movespeed=1 #移速
self.setCursor(Qt.CursorShape.BlankCursor)
self.objects2D=[]
self.cwidth=cwidth
self.cheight=cheight #相机宽高
self.cdeepth=cdeepth #相机视锥深度
def launch(self):
self.timer=QTimer()
self.timer.start(5)
self.timer.timeout.connect(self.update)
self.show()
投射
这是整个三维投影中最关键的一点。
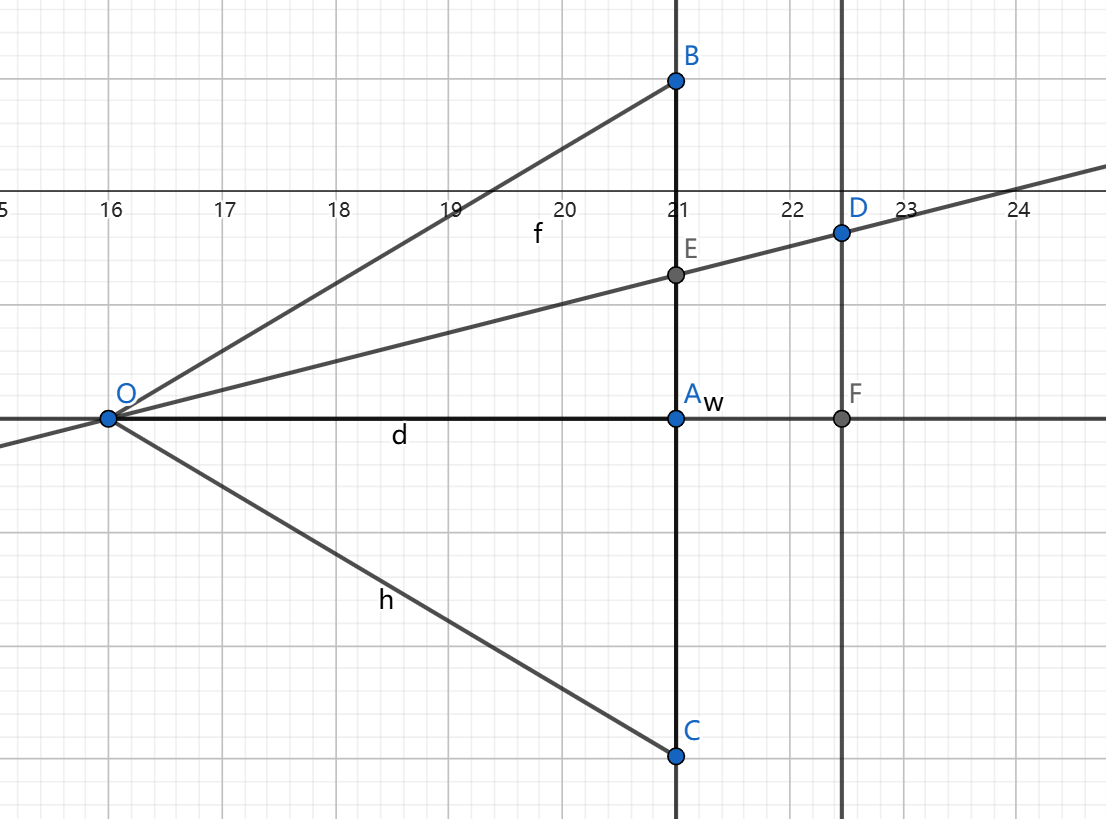
可见, △ O A E ∼ △ O F D \triangle OAE \sim \triangle OFD △OAE∼△OFD, O A OA OA是相机深度,D是我们要投射的点 ,O是相机的位置,求出BE就可以求出E点的位置,即显示在屏幕上的位置。
从上面看(x坐标)和从右边看(y坐标)这张图都适用。
但是要考虑相机会旋转角度的问题。不妨将相机到投射的点看作一个向量。
假设相机位置为 ( a x , a y , a z ) (a_{x},a_{y},a_{z}) (ax,ay,az),投射的点的位置为 ( c x , c y , c z ) (c_{x},c_{y},c_{z}) (cx,cy,cz),相机长 w w w,宽 h h h,深 d d d
先计算向量旋转后的新向量:
$$
\begin{bmatrix}
d_{x} \
d_{y} \
d_{z}
\end{bmatrix}
\begin{bmatrix}
1 & 0 & 0 \
0 & \cos (\theta_{x}) &\sin(\theta_{x}) \
0 & -\sin(\theta_{x})& \cos(\theta_{x})
\end{bmatrix}
\begin{bmatrix}
\cos(\theta_{y}) &0 & -\sin(\theta_{y}) \
0 & 1& 0 \
\sin(\theta_{y})& 0 & \cos(\theta_{y})
\end{bmatrix}
\begin{bmatrix}
\cos(\theta_{z})&\sin(\theta_{z})& 0 \
-\sin(\theta_{z})&\cos(\theta_{z})&0 \
0&0&1
\end{bmatrix}
\begin{bmatrix}
a_{x}-c_{x} \
a_{y}-c_{y} \
a_{z}-c_{z}
\end{bmatrix}
利用相似三角形对应边成比例,得:
利用相似三角形对应边成比例,得:
利用相似三角形对应边成比例,得:
x=\frac{w}{2}-\frac{d}{d_{z}}d_{x}
y=\frac{h}{2}-\frac{d}{d_{z}}d_{y}
$$
因此我们有了代码:
# class Point():
def project(self,camera):
cx, cy, cz = camera.posx, camera.posy, camera.posz
thx, thy, thz = -camera.rotatex, camera.rotatey, camera.rotatez
x = self.x - cx
y = self.y - cy
z = self.z - cz
dx = math.cos(thy)*(math.sin(thz)*y+math.cos(thz)*x)-math.sin(thy)*z
dy = math.sin(thx)*(math.cos(thy)*z+math.sin(thy)*(math.sin(thz)*y+math.cos(thz)*x))+\
math.cos(thx)*(math.cos(thz)*y-math.sin(thz)*x)
dz = math.cos(thx)*(math.cos(thy)*z+math.sin(thy)*(math.sin(thz)*y+math.cos(thz)*x))-\
math.sin(thx)*(math.cos(thz)*y-math.sin(thz)*x)
newx= camera.cwidth/2-(camera.cdeepth/dz) * dx
newy= camera.cheight/2-(camera.cdeepth/dz) * dy
if camera.width()/camera.height()>camera.cwidth/camera.cheight:
rectw=camera.height()/camera.cheight*camera.cwidth
resultx=camera.width()/2-rectw/2+newx/camera.cwidth*rectw
resulty=newy/camera.cheight*camera.height()
else:
recth=camera.width()/camera.cwidth*camera.cheight
resultx=newx/camera.cwidth*camera.width()
resulty=camera.height()/2-recth/2+newy/camera.cheight*recth
return resultx,resulty,dz>0#当dz<=0时,即投影的点在相机的后面时,投射的位置不正确,需要特判处理
线段
连接两个点的是线段。将一个线段投影之后线段还是直的,所以只需连接两个投影后的端点即可得到投影后的线段。
class Segment():
def __init__(self,point1,point2):
self.point1=point1
self.point2=point2
def paint(self,camera):
x1,y1,m1=self.point1.project(camera)
x2,y2,m2=self.point2.project(camera)
if m1>0 and m2>0:
return x1,y1,x2,y2
elif m1>0:
return x1,y1,2*x1-x2,2*y1-y2
elif m2>0:
return 2*x2-x1,2*y2-y1,x2,y2 #这两都是将投影错误的端点绕着正确的端点旋转180度,即中心对称
else:
return -1,-1,-1,-1 #当两个端点都在后面,说明这条线段在摄像机后面,因此不用显示
相机的控制
监听键盘
用WSAD键移动,反引号键(Esc下面那个)呼出呼入鼠标。
# class Camera(QWidget):
def keyPressEvent(self, event):
if event.key()==Qt.Key.Key_W:
self.movement[0]=1
if event.key()==Qt.Key.Key_S:
self.movement[0]=-1
if event.key()==Qt.Key.Key_A:
self.movement[2]=1
if event.key()==Qt.Key.Key_D:
self.movement[2]=-1
if event.key()==Qt.Key.Key_Space:
self.movement[1]=1
if event.key()==Qt.Key.Key_Shift:
self.movement[1]=-1
if event.key()==Qt.Key.Key_QuoteLeft:
if self.controled:
self.setCursor(Qt.CursorShape.ArrowCursor)
else:
self.setCursor(Qt.CursorShape.BlankCursor)
self.controled=not self.controled
def keyReleaseEvent(self,event):
self.movement=[0,0,0]
进行移动和旋转操作
刚刚已经改变了self.movement的值,现在只需要根据值来移动相机,如果鼠标已锁住,同时用鼠标到窗口正中心的偏移来旋转相机,然后把鼠标的位置设置到画面正中心。
当QWidget.update()被执行时,就会执行paintEvent(),重写这个函数就可以实现重复执行。
# class Camera(QWidget):
def paintEvent(self,event):
self.posx+= self.movement[0]*math.sin(self.rotatey)*self.movespeed*0.01
self.posx+= self.movement[2]*math.sin(self.rotatey+math.radians(90))*self.movespeed*0.01
self.posy+= self.movement[1]*self.movespeed*0.01
self.posz+= self.movement[0]*math.cos(self.rotatey)*self.movespeed*0.01
self.posz+= self.movement[2]*math.cos(self.rotatey+math.radians(90))*self.movespeed*0.01
if self.controled:
centerx=self.geometry().center().x()
centery=self.geometry().center().y()
mousex=QCursor.pos().x()
mousey=QCursor.pos().y()
offsetx=centerx-mousex
offsety=centery-mousey
self.rotatex+=offsety*0.001
self.rotatex=min(math.radians(90),self.rotatex)
self.rotatex=max(math.radians(-90),self.rotatex)#绕x轴旋转的极限
self.rotatey+=offsetx*0.001
if self.rotatey>math.radians(180):
self.rotatey-=math.radians(360)
if self.rotatey<math.radians(-180):
self.rotatey+=math.radians(360) #绕y轴旋转处理
QCursor.setPos(self.geometry().center())
多面体
将线段相接,得到多面体。
class Body():
def __init__(self,space,vertixes,edges):
self.vertixes=vertixes
self.edges=[]
for i in edges:
self.edges.append(Segment(Point(*(vertixes[i[0]])),Point(*(vertixes[i[1]]))))
self.space=space
self.space.objects.append(self)
矩体
矩体是一种特殊的多面体。
class Cubold(Body):
def __init__(self,space,x,y,z,length,width,height):
super().__init__(space,[[x,y,z],[x+length,y,z],[x,y,z+width],[x+length,y,z+height],
[x,y+height,z],[x+length,y+height,z],[x,y+height,z+width],[x+length,y+height,z+length]],#描述顶点坐标
[[0,1],[1,3],[2,0],[3,2],[4,5],[5,7],[6,4],[7,6],[0,4],[1,5],[2,6],[3,7]])#连棱
平面文字
没有什么特别的,但是设置了一个更新时会执行的函数
class Text2D():
def __init__(self,camera,x,y,content) :
self.x=x
self.y=y
self.camera=camera
self.content=content
self.camera.objects2D.append(self)
def update(camera):
pass
self.updatefunc=update
def setText(self,content):
self.content=content
def setUpdate(self,func):
self.updatefunc=func
更新相机画面
把当前相机所在空间中的每一个多面体的每一条棱画出来,同时也也要写文字,执行文字更新是的那个函数
使用QPainter。
# class Camera(QWidget):
# def paintEvent(self,event):
painter = QPainter(self)
color=QColor()
color.setRgb(0,0,255)
pen=QPen()
pen.setColor(color)
painter.setPen(pen)
if self.controled:
painter.drawLine(self.width()/2-2,self.height()/2,self.width()/2+2,self.height()/2)
painter.drawLine(self.width()/2,self.height()/2-2,self.width()/2,self.height()/2+2)
for i in self.space.objects:
for j in i.edges:
try:
x1,y1,x2,y2=j.paint(self)
painter.drawLine(x1,y1,x2,y2)
except:
pass
for i in self.objects2D:
if isinstance(i,Text2D):
painter.drawText(i.x,i.y,i.content)
i.updatefunc(self)
测试
我把这个文件叫做threedengine.py。同时建了一个测试文件demo.py。
测试代码
import threedengine
import math
space=threedengine.Space()
camera=threedengine.Camera(space,1000,500,'三维视图',800,400,300)
camera.launch()
body=threedengine.Cubold(space,1,0,0,1,1,1)
text=threedengine.Text2D(camera,10,10,'')
def update(camera):
text.setText('位置:(%f,%f,%f) 方向:%f° 俯仰:%f°'%(camera.posx,camera.posy,camera.posz,math.degrees(camera.rotatey),math.degrees(camera.rotatex)))
text.setUpdate(update)
threedengine.run()
效果
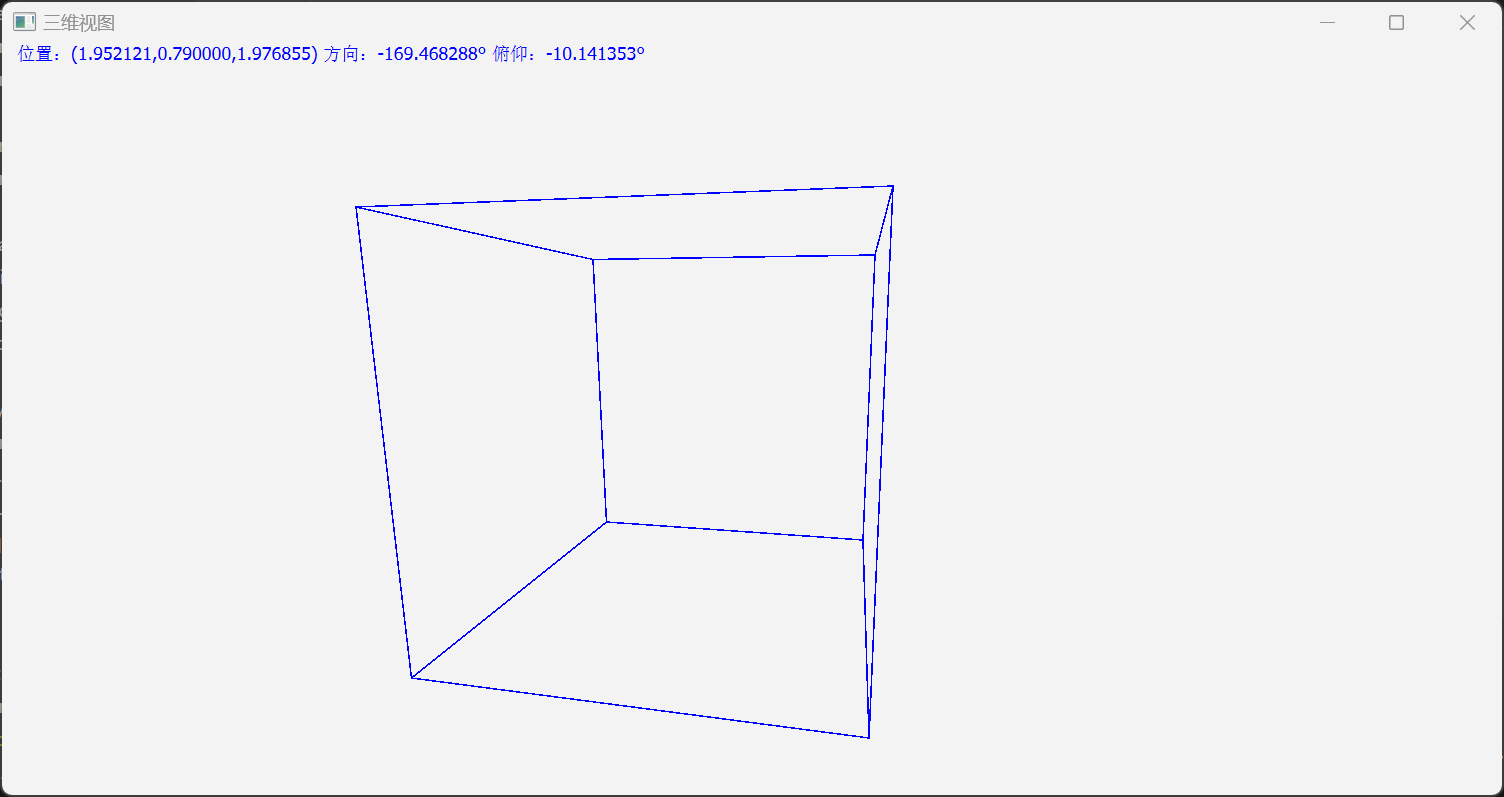
到这里这篇文章就结束了,886!























 675
675

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








