During the kindergarten days, flymouse was the monitor of his class. Occasionally the head-teacher brought the kids of flymouse’s class a large bag of candies and had flymouse distribute them. All the kids loved candies very much and often compared the numbers of candies they got with others. A kid A could had the idea that though it might be the case that another kid B was better than him in some aspect and therefore had a reason for deserving more candies than he did, he should never get a certain number of candies fewer than B did no matter how many candies he actually got, otherwise he would feel dissatisfied and go to the head-teacher to complain about flymouse’s biased distribution.
snoopy shared class with flymouse at that time. flymouse always compared the number of his candies with that of snoopy’s. He wanted to make the difference between the numbers as large as possible while keeping every kid satisfied. Now he had just got another bag of candies from the head-teacher, what was the largest difference he could make out of it?
Input
The input contains a single test cases. The test cases starts with a line with two integers N and M not exceeding 30 000 and 150 000 respectively. N is the number of kids in the class and the kids were numbered 1 through N. snoopy and flymouse were always numbered 1 and N. Then follow M lines each holding three integers A, B and c in order, meaning that kid A believed that kid B should never get over c candies more than he did.
Output
Output one line with only the largest difference desired. The difference is guaranteed to be finite.
Sample Input
2 2
1 2 5
2 1 4
Sample Output
5
题解:
以下为转载
也是通过这个题第一次接触到差分约束这个东西,学习了下,很奇妙。
令x-y<=z表示x最大比y大z。
若b-a<=k1, c-b<=k2, c-a<=k3,那么c-a最大为多少呢?显然应该等于min(k1+k2, k3)。可以用下图来表示示(不擅图丑勿怪)
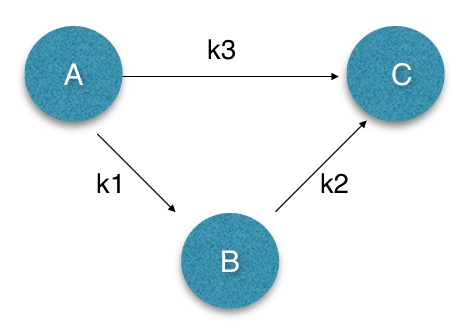
所以求Dijkstra最短路即可,注意vector会TLE
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int MAXN = 1000010;
struct qnode
{
int v;
int c;
qnode(int _v=0,int _c=0):v(_v),c(_c){}
bool operator < (const qnode &r) const
{
return c>r.c;
}
};
struct Edge
{
int v,cost;
int next;
};
Edge edge[200000];
int tol;
int head[MAXN];
bool vis[MAXN];
int dist[MAXN];
void Dijkstra(int n,int start)
{
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) dist[i]=INF;
priority_queue<qnode> que;
while(!que.empty()) que.pop();
dist[start]=0;
que.push(qnode(start,0));
qnode tmp;
while(!que.empty())
{
tmp=que.top();
que.pop();
int u = tmp.v;
if(vis[u]) continue;
vis[u]=true;
for(int i=head[u];i!=-1;i=edge[i].next)
{
int v = edge[i].v;
int cost = edge[i].cost;
if(!vis[v]&&dist[v]>dist[u]+cost)
{
dist[v] = dist[u]+cost;
que.push(qnode(v,dist[v]));
}
}
}
}
void addedge(int u,int v,int w)
{
edge[tol].v=v;
edge[tol].cost=w;
edge[tol].next=head[u];
head[u]=tol++;
}
int A[MAXN],B[MAXN],C[MAXN];
int main()
{
int n,m;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)==2)
{
tol=0;
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
int A,B,C;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&A,&B,&C);
addedge(A,B,C);
}
Dijkstra(n,1);
printf("%d\n",dist[n]);
}
return 0;
}






















 784
784

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








