一、合并分割
tf.concat()函数:张量拼接函数
a = tf.ones([4,2,3])
b = tf.ones([2,2,3])
c = tf.concat([a,b],axis=0)
print(c.shape) #Tensorshape([6,2,3])tf.stack()函数:创造新的维度
d = tf.stack([a,b],axis=0) #注:stack必须所有维度相等
#Tensorshape([2,4,2,3])tf.unstack()函数:分割操作。
a = tf.ones([4,2,3])
b = tf.ones([2,2,3])
c = tf.concat([a,b],axis=0)
d = tf.unstack(c,axis=0)
d = tf.unstack(c,axis=0)
print(d[0].shape)#Tensorshape([2,3])
print(d[3].shape)#Tensorshape([2,3])tf.split()函数:按照规则打散分割
e = tf.split(c,axis=0,num_or_size_splits=[3,5])
for i in range(len(e)):
print(e[i].shape) #(3, 2, 3) (5, 2, 3)二、数据统计
张量的范数:

tf.norm()函数:
-
支持在维度上进行各种范数计算
-
axis=a:指的是在a上各个小单元进行的范数计算,即:第i列第a行所有元素的范数计算
a = tf.ones([3,2])
c = tf.norm(a,ord = 2,axis=0)
#tf.Tensor([1.7320508 1.7320508], shape=(2,), dtype=float32)tf.reduce_min/max/mean():求解最小最大值
a = tf.random.normal([2,3])
b = tf.reduce_min(a,axis=0)
print(a)
print(b)#同样的也是每个第0维度(每一列的一行所有值)的最大最小值,[min((1,1),(2,1),min((1,2),(2,2)]tf.argmax()函数:求出最大值的索引位置
tf.equal()函数:比较两个张量,常用于求解准确度
tf.unique()函数:求解张量中不重复的值的位置索引
a = tf.random.normal([4,3])
b = tf.argmax(a,axis=0)
print(b.shape) #(3,)
c = tf.constant([1,1,3,4,4])
d = tf.range(5)
print('d:',d) #d: tf.Tensor([0 1 2 3 4], shape=(5,), dtype=int32)
e = tf.equal(c,d)
print('e:',e) #e: tf.Tensor([False True False False True], shape=(5,), dtype=bool)
unique,idx = tf.unique(c)
print('unique:',unique) #unique: tf.Tensor([1 3 4], shape=(3,), dtype=int32)
print('idx:',idx) #idx: tf.Tensor([0 0 1 2 2], shape=(5,), dtype=int32)
f = tf.gather(unique,idx)
print(f) #tf.Tensor([1 1 3 4 4], shape=(5,), dtype=int32)三、张量排序
tf.random.shuffle()函数:随机打乱某一维度的排序
tf.argsort()函数:张量排序后的序号
tf.sort(,direction='DESCENDING')函数:张量排序(降序)
tf.argsort()函数:张量排序后的序号
a = tf.random.uniform([3,3],maxval = 10,dtype=tf.int32)
b = tf.sort(a,direction='DESCENDING')
print(b)
idx = tf.argsort(a,direction='DESCENDING')
print(idx)
a = tf.random.uniform([3,3],maxval = 10,dtype=tf.int32)
print(a)
b = tf.math.top_k(a,3).indices
print(b)
b = tf.math.top_k(a,3)函数:返回前多少个最大的值的value和indices(值和排序)
a = tf.random.uniform([3,3],maxval=10)
b = tf.math.top_k(a,3).indices
print(b)
#tf.Tensor(
# [[6 5 2]
# [4 0 7]
# [8 8 4]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=int32)
# tf.Tensor(
# [[0 1 2]
# [2 0 1]
# [0 1 2]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=int32)四、数据填充与复制
tf.pad():数据的填充
tf.tile():数据的复制
tf.broadcast_to()
#pad()填充示例:
a = tf.random.uniform([3,3],maxval=9)
a = tf.pad(a,[[1,1],[0,1]])
#效果即在行上:上边和下边都加了一排0,列上:只有右边加了一排0
#tile()复制示例:
a = tf.constant([[0,1,2],[3,4,5],[6,7,8]])
b = tf.tile(a,[2,2])
#结果即:在行、列上分别复制了两次
# tf.Tensor(
# [[0 1 2 0 1 2]
# [3 4 5 3 4 5]
# [6 7 8 6 7 8]
# [0 1 2 0 1 2]
# [3 4 5 3 4 5]
# [6 7 8 6 7 8]], shape=(6, 6), dtype=int32)五、张量的限幅
clip_by_value():
a = tf.range(10) #tf.Tensor([0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9], shape=(10,), dtype=int32) b = tf.maximum(a,2) #tf.Tensor([2 2 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9], shape=(10,), dtype=int32)
c = tf.minimum(a,8) #tf.Tensor([0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 8], shape=(10,), dtype=int32) d = tf.clip_by_value(a,2,8) #tf.Tensor([2 2 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 8], shape=(10,), dtype=int32)<p>
tf.nn.relu():relu激活函数
</p>a = tf.range(10)
a = a-5
b = tf.nn.relu(a) #tf.Tensor([0 0 0 0 0 0 1 2 3 4], shape=(10,), dtype=int32)tf.norm():保持方向不变,只改变模的大小,通过除以一个范数,再乘以模来实现
a = tf.random.normal([2,2],mean=10)
b = tf.clip_by_norm(a,15) #tf.Tensor([8.2,6.8,7.34,7.43]) 裁剪后整体的数norm,也就是一次范数的范数和为15
aa = tf.norm(b) #numpy=15.0001六、高阶OP(高阶操作)
6.1找到特定坐标的tensor:
#找到大于0的tensor
a = tf.random.normal([3,3])
print(a)
mask = a>0
print(mask)
indices = tf.where(mask)
b = tf.gather_nd(a,indices)
print(b)6.2跟新底板操作:tf.scatter_nd():其中的shape必须是空的模板即tensor底板
shape = tf.constant([8])
print(shape)
indices = tf.constant([[0],[2],[4],[7]])
updates = tf.constant([9,10,11,12])
a = tf.scatter_nd(indices,updates,shape) #tf.Tensor([ 9 0 10 0 11 0 0 12], shape=(8,), dtype=int32)6.3 meshgrid()生成三维图像#找到大于0的tensor a = tf.random.normal([3,3]) print(a) mask = a>0 print(mask) indices = tf.where(mask) b = tf.gather_nd(a,indices) print(b)
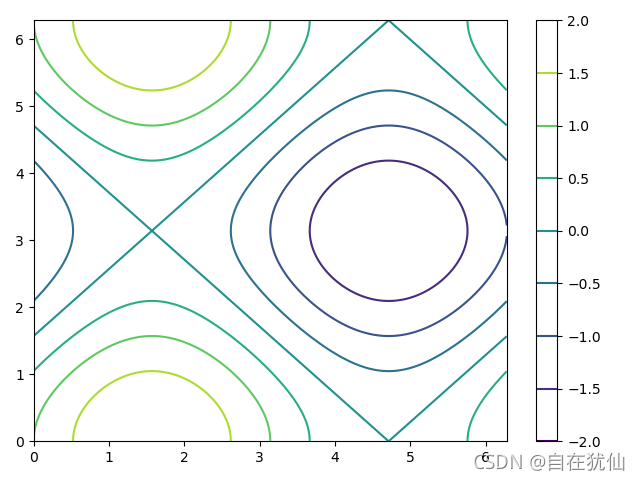
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def fun(points):
z = tf.math.sin(points[...,0])+tf.math.cos(points[...,1])
return z
x = tf.linspace(0.,2*3.14,500)
y = tf.linspace(0.,2*3.14,500)
mesh_x,mesh_y = tf.meshgrid(x,y)
points = tf.stack([mesh_x,mesh_y],axis=2)
print(points.shape)
z= fun(points)
print(z.shape)
# plt.figure('2d')
# plt.contourf((x,y),fun(points))
# plt.colorbar()
plt.figure('hight')
plt.contour(mesh_x,mesh_y ,z)
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()






















 384
384











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








