The technique that makes use of interference of electromagnetic waves that are transmitted and received by a SAR is called interferometric synthetic aperture radar, or InSAR. Very simply, InSAR involves the use of two or more SAR images of the same area—one arbitrarily chosen reference or master image and one or more additional images referred to as slave images—to extract land surface topography and deformation patterns.
1 高程和斜距差的关系
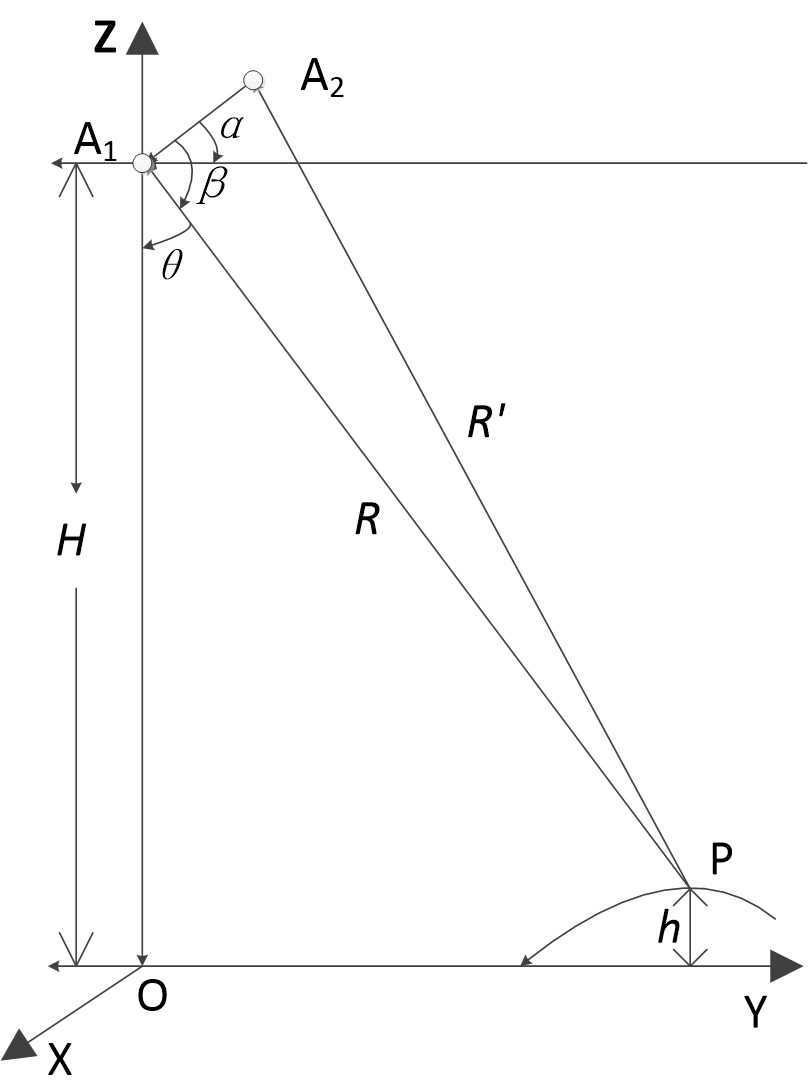
InSAR基本原理可以下图为例进行说明。设天线相位中心 A 1 的高程为 H ,地面点P的高程为 h ,天线相位中心 A 1 对目标点 成像时的侧视角为 θ ,两天线相位中心的距离为基线长度 B ,基线与水平方向的夹角为 α , R 和
干涉图像上,目标点对应的像点坐标为
(x p ,y p )
,天线相位中心到目标点的斜距
R
满足下式:
其中,
D S 0
为近距延迟,
M y
为图像距离向采样间隔。
根据InSAR的几何关系可知,地面点的高程为:
式中,侧视角 θ 与基线水平角 α 及角 β 的关系为:
在三角形中,有余弦定理:
则:
因此,地面点P的高程 h 为:
另外这里可以推导出一个重要的公式:
其中, B // 代表基线在平行于斜距方向上的分量。
2 斜距差和相位差的关系
SAR影像的一个像素为一个复数:包含振幅A和相位 φ ,
距离和相位的关系:
其中 λ、R fw 、R bw 、φ scatt 分别表示波长、发射天线到目标的距离、目标到接收天线的距离、地物散射特性引起的相位变化。下图分别为SAR影像的强读图像和相位图像,其中的相位信息并没有什么规律,因此也就不能加以利用。

But something very useful emerges when two otherwise useless SLC SAR images are combined, as explained below.
Interferometric SAR (InSAR) exploits the phase differences of at least two complex-valued SAR images acquired from different orbit positions and/or at different times.
也就是说,InSAR利用的是干涉图(interferogram)来反演信息的。
The interferogram is calculated by co-registering two SAR images
μ 1
、
μ 2
and differencing the corresponding phase values on a pixel-by-pixel basis, i.e., by a pixel-by-pixel complex multiplication of the master image
μ 1
with the complex conjugated slave image
μ 2
. Due to baseline
B
, the distances from the antennas to the scene differ by
Under the pre-condition φ scatt,1 =φ scatt,2 and the utilization of the same emitting horn for both images leading to R fw,1 =R fw,2 , which is the case for single-pass measurements, the interferometric phase is just related to the range difference of the two antennas:
On the other hand, for repeat-pass measurements,
























 7757
7757

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








