提要
两年前的我写下了这篇文章 - 向量类的实现。现在看来,这代码真是略显丑陋。
于是,重新写吧。
参照了一下Unity3d 的Vector3类的接口。话不多说,上代码。
编译器:gcc 4.6.3
代码清单
vector3.h
#ifndef VECTOR3_H
#define VECTOR3_H
#include <math.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <iostream>
#define PI 3.14159265
using namespace std;
class Vector3
{
public:
float x;
float y;
float z;
Vector3();
Vector3(float x, float y, float z);
~Vector3();
bool HasNaNs() const;
void set(float _x, float _y, float _z);
//Static functions
static Vector3 back();
static Vector3 down();
static Vector3 forward();
static Vector3 left();
static Vector3 one();
static Vector3 right();
static Vector3 up();
static Vector3 zero();
float magnitude() const;
float sqrtMagnitude() const;
Vector3 normalized();
//Operators
//Add two Vectors
Vector3 operator+(const Vector3 &v) const;
//Subtracts one vector from another
Vector3 operator-(const Vector3 &v) const;
Vector3 operator*(float num) const;
Vector3 operator/(float num) const;
Vector3 &operator+=(const Vector3 &v);
Vector3 &operator-=(const Vector3 &v);
Vector3 &operator*=(float num);
Vector3 &operator/=(float num);
//Returns true if vectors different.
bool operator!=(Vector3 &v) const;
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& output,const Vector3& v)
{
output<<"("<<v.x<<","<<v.y<<","<<v.z<<")"<<"\n";
return output;
}
//Static Functions
//Calculate angle between two vectors.
static float Angle(const Vector3 &from, const Vector3 &to)
{
double c, d;
c = from.x*to.x + from.y*to.y + from.z*to.z;
d = sqrt(from.x*from.x + from.y*from.y + from.z*from.z) * sqrt(to.x*to.x + to.y*to.y + to.z*to.z);
return acos(c/d) * 180.0 / PI;
}
//Get dot result of two vector2.
static inline float Dot(const Vector3 &v1, const Vector3 &v2)
{
return v1.x * v2.x + v1.y * v2.y + v1.z * v2.z;
}
//Get cross result of two vector2.
static inline Vector3 Cross(const Vector3 &v1, const Vector3 &v2)
{
return Vector3((v1.y * v2.z) - (v1.z * v2.y),
(v1.z * v2.x) - (v1.x * v2.z),
(v1.x * v2.y) - (v1.y * v2.x));
}
//Get a normalized vector3 from a given vector3.
static inline Vector3 Normalize(const Vector3 &v1)
{
float tmpLength = v1.magnitude();
return Vector3(v1.x/tmpLength, v1.y/tmpLength, v1.z/tmpLength);
}
//Construct a coordinateSystem by a given vector3. v2 and v3 are output.
static inline void CoordinateSystem(const Vector3 &v1, Vector3 *v2, Vector3 *v3)
{
if(fabsf(v1.x) > fabsf(v1.y))
{
float invLen = 1.0f / sqrtf(v1.x*v1.x + v1.z*v1.z);
*v2 = Vector3(-v1.z * invLen, 0.0f, v1.x * invLen);
}else
{
float invLen = 1.0f / sqrt(v1.y*v1.y + v1.z*v1.z);
*v2 = Vector3(0.0f, v1.z * invLen, -v1.y * invLen);
}
*v3 = Vector3::Cross(v1, *v2);
}
static Vector3 ClampMagnitude();
static Vector3 Lerp(const Vector3 &v1, const Vector3 &v2);
static Vector3 OrthoNormalize();
protected:
private:
};
#endif // VECTOR3_H
vector3.cpp
#include "vector3.h"
Vector3::Vector3()
{
x = y = z = 0.0f;
}
Vector3::Vector3(float _x, float _y, float _z):x(_x),y(_y),z(_z)
{
assert(!HasNaNs());
}
Vector3::~Vector3()
{
//dtor
}
bool Vector3::HasNaNs() const
{
return isnan(x) || isnan(y) || isnan(z);
}
Vector3 Vector3::one()
{
return Vector3(1, 1, 1);
}
float Vector3::magnitude() const
{
return sqrt(x*x + y*y + z*z);
}
float Vector3::sqrtMagnitude() const
{
return x*x + y*y + z*z;
}
void Vector3::set(float _x, float _y, float _z)
{
x = _x;
y = _y;
z = _z;
}
Vector3 Vector3::operator+(const Vector3 &v) const
{
return Vector3(x + v.x, y+ v.y, z+ v.z);
}
Vector3 Vector3::operator-(const Vector3 &v) const
{
return Vector3(x - v.x, y - v.y, z - v.z);
}
Vector3 Vector3::operator*(float num) const
{
return Vector3(num*x, num*y, num*z);
}
Vector3 Vector3::operator/(float num) const
{
return Vector3(x/num, y/num, z/num);
}
Vector3& Vector3::operator*=(float num)
{
x *= num; y *= num; z *= num;
return *this;
}
Vector3& Vector3::operator/=(float num)
{
x /= num; y /= num; z /= num;
return *this;
}
Vector3& Vector3::operator+=(const Vector3 &v)
{
x += v.x; y += v.y; z += v.z;
return *this;
}
Vector3& Vector3::operator-=(const Vector3 &v)
{
x -= v.x; y -= v.y; z -= v.z;
return *this;
}
bool Vector3::operator!=(Vector3 &v) const
{
return x==v.x && y==v.y && z==v.z;
}
Vector3 Vector3::normalized()
{
float tmpLength = this->magnitude();
return Vector3(x/tmpLength, y/tmpLength, z/tmpLength);
}
测试代码
#include <iostream>
#include "vector3.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Vector3 v1,v2,v3;
v1=Vector3(1.0,-1.0,0.0);
v2=Vector3(-1.0,-1.0,0.0);
cout<<"v1: "<<v1<<endl;
v2=v2/2;
cout<<"v2: "<<v2<<endl;
cout<<"Angle: "<<Vector3::Angle(v1, v2)<<endl;
v3=Vector3::Cross(v1,v2);
float a=Vector3::Dot(v1,v2);
cout<<"v1 dotMul v2:"<<a<<endl;
cout<<"v3.Length:"<<v3.magnitude()<<endl;
Vector3 v4 = v3.normalized();
cout<<"v3 After nomarlize:"<<v4<<endl;
return 0;
}
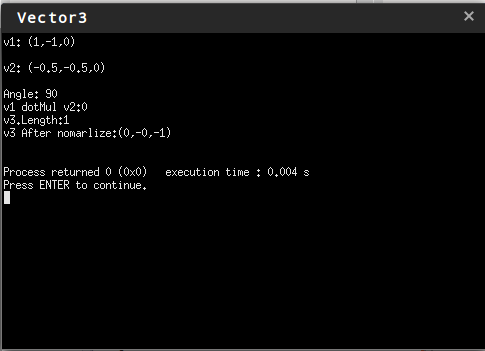
运行结果
代码说明
相对于前一个版本的代码,新版本的Vector3首先是包括了基本的向量运算,同时做了下面的改进:
1.重载了<<符号,这样就可以直接打印向量的内容了;
2.重载了基本的运算符号,包括返回引用和返回对象的,返回对象的不会改变本身,返回引用的会同时修改本省;
3.添加了一些静态的inline方法,用于向量的一些计算,关于static inline,可以理解是一个static的函数,加上了inline的属性。这个函数大部分表现和普通的static函数一样,只不过在调用这种函数的时候,gcc会在其调用处将其汇编码展开编译而不为这个函数生成独立的汇编码。
























 2028
2028

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








