Qt 实现炫酷锁屏源码分享
一、源码分享
1、效果展示

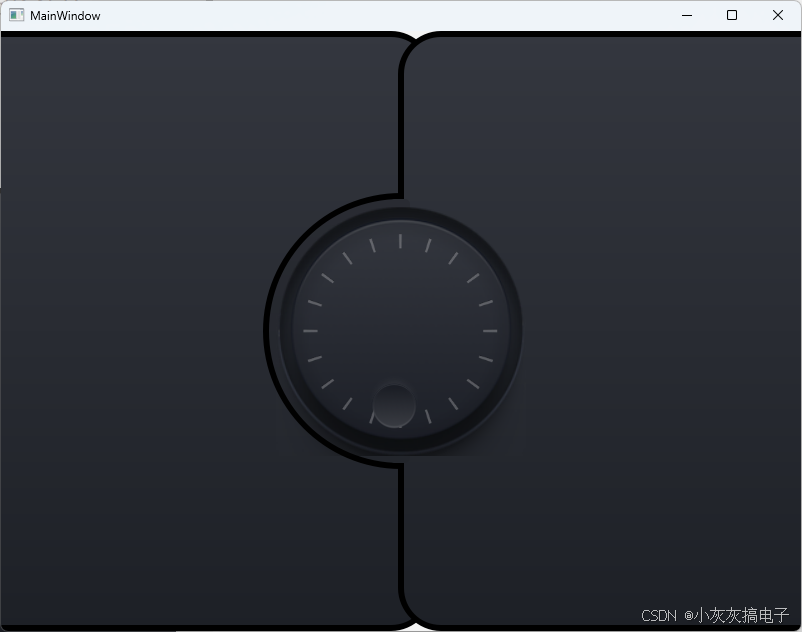
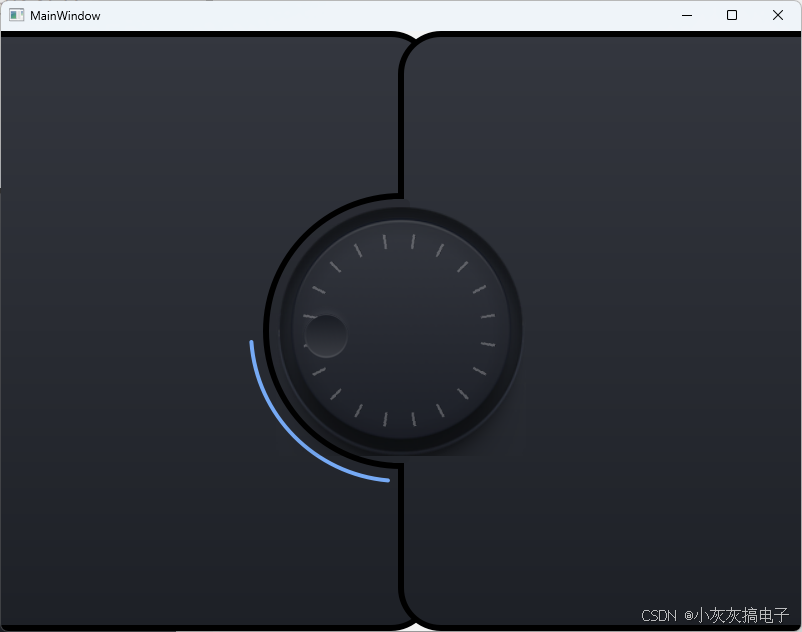

2、源码分享
2.1、工程结构

2.2、mainwindow.cpp
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include "ui_mainwindow.h"
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent)
: QMainWindow(parent)
, ui(new Ui::MainWindow)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
lockScreen = new LockScreen(this);
lockScreen->setGeometry(this->rect());
}
MainWindow::~MainWindow()
{
delete ui;
}
void MainWindow::on_pushButton_clicked()
{
lockScreen->lockScreen(true);
}
void MainWindow::keyPressEvent(QKeyEvent *e)
{
if(e->key() == Qt::Key_F1)
{
lockScreen->lockScreen(false);
}
}
void MainWindow::resizeEvent(QResizeEvent *event)
{
lockScreen->setGeometry(this->rect());
}
2.3、lockScreen.h
#ifndef LOCKSCREEN_H
#define LOCKSCREEN_H
#include <QWidget>
#include <QPaintEvent>
#include <QPainter>
#include <QPropertyAnimation>
#include <QPainterPath>
class LockScreen : public QWidget
{
Q_OBJECT
Q_PROPERTY(int doorLeftX READ getDoorLeftX WRITE setDoorLeftX NOTIFY doorLeftXChanged FINAL)
Q_PROPERTY(int doorRightX READ getDoorRightX WRITE setDoorRightX NOTIFY doorRightXChanged FINAL)
Q_PROPERTY(float ledOpacity READ getLedOpacity WRITE setLedOpacity NOTIFY ledOpacityChanged FINAL)
signals:
void doorLeftXChanged();
void doorRightXChanged();
void ledOpacityChanged();
public:
explicit LockScreen(QWidget *parent = nullptr);
void lockScreen(bool isLock);
int getDoorLeftX() const
{
return doorLeftX;
}
void setDoorLeftX(int newDoorLeftX)
{
if (doorLeftX == newDoorLeftX)
return;
doorLeftX = newDoorLeftX;
emit doorLeftXChanged();
}
int getDoorRightX() const
{
return doorRightX;
}
void setDoorRightX(int newDoorRightX)
{
if (doorRightX == newDoorRightX)
return;
doorRightX = newDoorRightX;
emit doorRightXChanged();
}
float getLedOpacity() const
{
return ledOpacity;
}
void setLedOpacity(float newLedOpacity)
{
if (qFuzzyCompare(ledOpacity, newLedOpacity))
return;
ledOpacity = newLedOpacity;
emit ledOpacityChanged();
}
protected:
void paintEvent(QPaintEvent *e) override;
bool eventFilter(QObject *obj, QEvent *e) override;
private:
float normalizeAngle(float angle) {
return fmod(angle + 360.0f, 360.0f);
}
float clamp(float val,float min,float max){
if(val < min)
return min;
else if(val > max)
return max;
else
return val;
}
private:
int doorLeftX = 0,doorRightX = 0;
const int dialSize = 250;
const int indictorSize = dialSize + 50;
float currentAngle = 95;
QRect rectDial;
float deltaDegrees;
float recordAngle;
const int startAngle = 95;
const int endAngle = 265;
float ledOpacity = 1.0f;
QPropertyAnimation *animDoorLeftX = nullptr,*animDoorRightX = nullptr;
QPropertyAnimation *animLedOpacity = nullptr;
QImage *imageDial,*imageLines,*imageNotch,*imgageLed;
};
#endif // LOCKSCREEN_H
2.4、lockScreen.cpp
#include "lockScreen.h"
LockScreen::LockScreen(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget{parent},
imageDial(new QImage(":/image/images/dial-frame.png")),
imageLines(new QImage(":/image/images/lines.png")),
imageNotch(new QImage(":/image/images/notch.png")),
imgageLed(new QImage(":/image/images/led-dark.png"))
{
this->animDoorLeftX = new QPropertyAnimation(this,"doorLeftX",this);
this->animDoorLeftX->setDuration(800);
this->animDoorLeftX->setEasingCurve(QEasingCurve::InExpo);
connect(this->animDoorLeftX,&QPropertyAnimation::valueChanged,this,
[=](const QVariant &value)
{
Q_UNUSED(value);
this->update();
//qDebug()<<value;
});
connect(this->animDoorLeftX,&QPropertyAnimation::finished,this,
[=]()
{
if(this->doorLeftX <= -this->width())
{
this->setVisible(false);
this->currentAngle = this->startAngle;
}
});
this->animDoorRightX = new QPropertyAnimation(this,"doorRightX",this);
this->animDoorRightX->setDuration(800);
this->animDoorRightX->setEasingCurve(QEasingCurve::InExpo);
this->animLedOpacity = new QPropertyAnimation(this,"ledOpacity",this);
this->animLedOpacity->setDuration(800);
this->animLedOpacity->setEasingCurve(QEasingCurve::InExpo);
this->animLedOpacity->setStartValue(1.0);
this->animLedOpacity->setEndValue(0.0);
this->animLedOpacity->setEasingCurve(QEasingCurve::InOutQuad);
this->animLedOpacity->start();
connect(this->animLedOpacity,&QPropertyAnimation::valueChanged,this,
[=](const QVariant &value)
{
Q_UNUSED(value);
this->update();
});
connect(this->animLedOpacity,&QPropertyAnimation::finished,this,
[=]()
{
if(ledOpacity == 1.0f)
{
this->animLedOpacity->setDirection(QAbstractAnimation::Forward);
this->animLedOpacity->start();
}
else
{
this->animLedOpacity->setDirection(QAbstractAnimation::Backward);
this->animLedOpacity->start();
}
});
this->setVisible(false);
this->installEventFilter(this);
}
void LockScreen::lockScreen(bool isLock)
{
if(isLock)
this->setVisible(true);
this->animDoorLeftX->setStartValue(isLock?-this->width()-10:-this->width()/2 + 30);
this->animDoorLeftX->setEndValue(isLock?-this->width()/2 + 30:-this->width()-10);
this->animDoorLeftX->start();
this->animDoorRightX->setStartValue(isLock?this->width():this->width()/2 - indictorSize/2);
this->animDoorRightX->setEndValue(isLock?this->width()/2 - indictorSize/2:this->width());
this->animDoorRightX->start();
}
void LockScreen::paintEvent(QPaintEvent *e)
{
Q_UNUSED(e);
QPainter painter(this);
painter.setRenderHints(QPainter::Antialiasing|QPainter::SmoothPixmapTransform, true); // 开启抗锯齿
const int borderWidth = 6;
if(doorLeftX==0)
doorLeftX = -this->width()-10;
if(this->doorRightX == 0)
this->doorRightX = this->width();
//绘制左边门
painter.setPen(QPen(QColor("#000000"), 6, Qt::SolidLine, Qt::RoundCap, Qt::MiterJoin));
QLinearGradient gradient(this->width()/2, 0, this->width()/2,this->height());
gradient.setColorAt(0, QColor("#34373F"));
gradient.setColorAt(1, QColor("#1D2026")); // 尾部
painter.setBrush(gradient);
QRect rectDoorLeft(doorLeftX,borderWidth/2,this->width(),this->height() - borderWidth);
rectDoorLeft.setX(doorLeftX);
painter.drawRoundedRect(rectDoorLeft,40,40);
//绘制右边门
QRect rectDoorRight(doorRightX,borderWidth/2,this->width(),this->height() - borderWidth);
rectDoorRight.setX(doorRightX + indictorSize/2);
QLinearGradient gradient2(this->width()/2, 0, this->width()/2,this->height());
gradient2.setColorAt(0, QColor("#2e3037"));
gradient2.setColorAt(1, QColor("#1D2026")); // 尾部
painter.setBrush(gradient2);
QRect rectRoundBorder(doorRightX +15,(this->height() - (dialSize +20))/2,dialSize + 20,dialSize + 20);
painter.drawEllipse(rectRoundBorder);
painter.setBrush(gradient);
painter.drawRoundedRect(rectDoorRight,40,40);
QRectF rectIndictor(this->doorRightX,(this->height() - indictorSize)/2,indictorSize,indictorSize);//绘制蓝线
painter.setPen(QPen(QColor("#76AAF5"), 4, Qt::SolidLine, Qt::RoundCap, Qt::MiterJoin));
painter.drawArc(rectIndictor,-this->startAngle*16,-(this->currentAngle - this->startAngle)*16);
//绘制遮罩
painter.save();
painter.setPen(Qt::NoPen);
painter.setBrush(gradient2);
painter.drawRoundedRect(QRect(rectRoundBorder.center().x() - 10,rectRoundBorder.y()+3,20,rectRoundBorder.height()-6),5,5);
painter.restore();
//绘制dial
QRectF rectDial(this->doorRightX + 25,(this->height() - dialSize)/2,dialSize,dialSize);//绘制转盘
this->rectDial.setX(rectDial.x());
this->rectDial.setY(rectDial.y());
this->rectDial.setWidth(rectDial.width());
this->rectDial.setHeight(rectDial.height());
painter.drawImage(rectDial,*this->imageDial);
//绘制指示线
painter.save();
int size = dialSize*1.1;
painter.setOpacity(0.3);
QRect rectLine(doorRightX+(indictorSize - size)/2,(this->height() - size)/2,size,size);
int lineWidth = this->imageLines->width();
int lineHeight = this->imageLines->height();
float width = sqrt(lineWidth*lineWidth+lineHeight*lineHeight);
QImage imageRoute((int)width,(int)width,QImage::Format_ARGB8565_Premultiplied);
imageRoute.fill(Qt::transparent);
QPainter p(&imageRoute);
p.translate(imageRoute.width()/2,imageRoute.height()/2);
p.rotate(this->currentAngle - this->startAngle);
p.setBrush(Qt::red);
// p.drawRect(QRect(-this->imageLines->width()/2,-this->imageLines->height()/2,
// this->imageLines->width(),this->imageLines->height()));
p.drawImage(QRect(- this->imageLines->width()/2,- this->imageLines->height()/2,
this->imageLines->width(),this->imageLines->height()),*this->imageLines);
p.end();
painter.drawImage(rectLine,imageRoute);
painter.setOpacity(1);
painter.restore();
//绘制缺口
int centerX = rectDial.x() + rectDial.width()/2;
int centerY = rectDial.y() + rectDial.height()/2;
int circleRadius = rectDial.width()/2 - 50;
QRectF rectNotch(this->doorRightX + 15,(this->height() - dialSize)/2,64,64);//绘制转盘
rectNotch.setX(centerX + circleRadius * cos(currentAngle * M_PI/180) - rectNotch.width()/2);
rectNotch.setY(centerY + circleRadius * sin(currentAngle * M_PI/180) - rectNotch.height()/2);
rectNotch.setWidth(64);
rectNotch.setHeight(64);
painter.drawImage(rectNotch,*this->imageNotch);
if(this->currentAngle == this->startAngle)
{
QRect rectLed(rectIndictor.x() + rectIndictor.width()/2 - 30,rectIndictor.y() + rectIndictor.height()-20,this->imgageLed->width(),this->imgageLed->height());
painter.setOpacity(ledOpacity);
painter.drawImage(rectLed,*this->imgageLed);
}
}
bool LockScreen::eventFilter(QObject *obj, QEvent *e)
{
static bool isPressed = false,isfirstTouch = false;
if(e->type() == QEvent::MouseButtonPress)
{
QMouseEvent *evt = static_cast<QMouseEvent *>(e);
if(evt->button() == Qt::LeftButton && this->rectDial.contains(evt->pos()))
{
isPressed = true;
}
}
else if(e->type() == QEvent::MouseButtonRelease)
{
QMouseEvent *evt = static_cast<QMouseEvent *>(e);
if(evt->button() == Qt::LeftButton)
{
isPressed = false;
isfirstTouch = false;
}
}
else if(e->type() == QEvent::MouseMove)
{
QMouseEvent *evt = static_cast<QMouseEvent *>(e);
if(isPressed)
{
int dx = evt->pos().x() - this->rectDial.center().x();
int dy = evt->pos().y() - this->rectDial.center().y();
// 计算角度(弧度)
float angleRad = atan2(dy, dx);
float newAngle = angleRad * (180 / M_PI);
qDebug()<<angleRad<<" "<<newAngle;
newAngle = normalizeAngle(newAngle);
if(!isfirstTouch){
isfirstTouch = true;
deltaDegrees = newAngle;
recordAngle = currentAngle;
}
else
{
currentAngle = clamp(recordAngle + (newAngle - deltaDegrees),this->startAngle,this->endAngle);
}
this->update();
if(currentAngle >= this->endAngle)
this->lockScreen(false);
// root.isClose = false
}
}
return QWidget::eventFilter(obj,e);
}
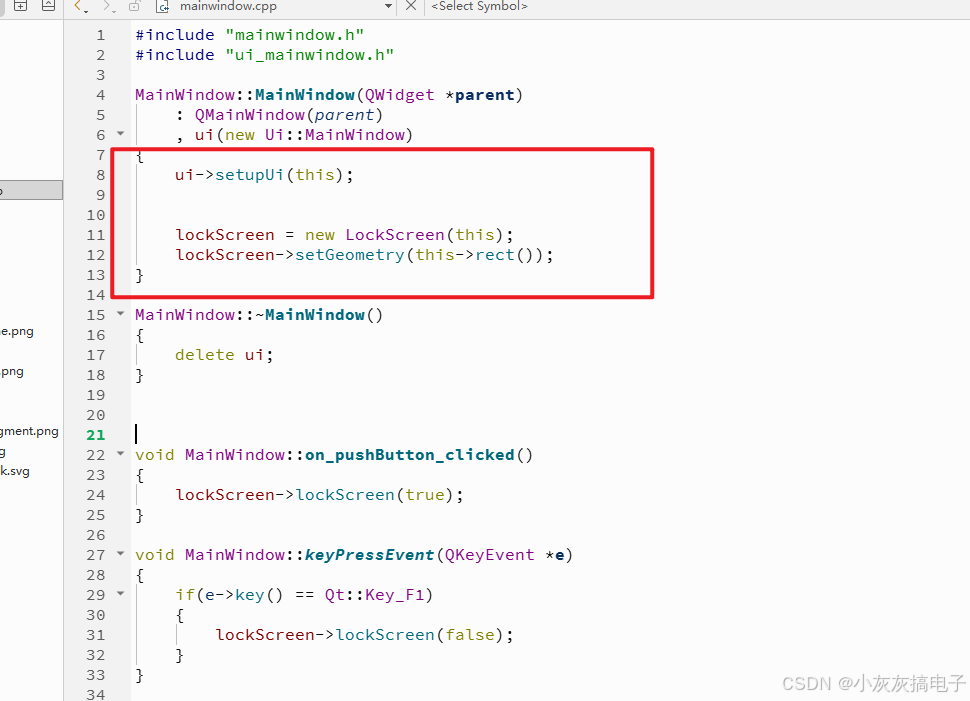
2.5、使用方法
直接在需要锁屏的界面new一个就可以。
2.6、完整工程下载
文章顶部下载。
二、实现原理
主要是通过QPainter和QPropertyAnimation来实现
1、QPainter详解
1、 QPainter 概述
QPainter 是 Qt 框架中用于执行低级别绘制的核心类。它提供了丰富的功能,允许你在各种绘图设备(如 QPixmap, QImage, QWidget, QPrinter 等)上绘制图形、文本和图像。其设计遵循“画家模式”(Painter’s Model),即在一个“画布”上使用不同的“工具”(画笔、画刷等)进行绘制。
2、核心概念
- 绘图设备 (
QPaintDevice): 这是绘制的目标表面,可以是窗口部件、像素图、图像或打印机页面。 - 画笔 (
QPen): 控制绘制线条(如形状的轮廓线)的属性,包括颜色、宽度、线型(实线、虚线、点线等)、端点样式和连接样式。- 示例:
pen.setColor(Qt::blue); pen.setWidth(2); pen.setStyle(Qt::DotLine);
- 示例:
- 画刷 (
QBrush): 控制填充形状内部的属性,包括颜色、样式(实心、渐变、纹理等)。- 示例:
brush.setColor(Qt::green); brush.setStyle(Qt::SolidPattern);
- 示例:
- 字体 (
QFont): 控制绘制文本时使用的字体属性,如字体族、大小、粗细、斜体等。- 示例:
font.setFamily("Arial"); font.setPointSize(12); font.setBold(true);
- 示例:
- 变换 (
QTransform): 提供坐标系变换功能,包括平移、缩放、旋转和剪切。这允许你在不同的坐标系下绘制相同的图形。- 示例:
painter.translate(100, 50); painter.rotate(45); painter.scale(2.0, 1.5);
- 示例:
- 视口 (
Viewport) 和 窗口 (Window): 用于逻辑坐标到物理设备坐标的映射。视口定义物理设备上的矩形区域,窗口定义逻辑坐标空间中的矩形区域。QPainter负责将窗口坐标映射到视口坐标。
3、核心功能
- 绘制基本图形:
drawPoint,drawPoints: 绘制点。drawLine,drawLines: 绘制直线。drawRect,drawRects: 绘制矩形。drawEllipse: 绘制椭圆(包括圆)。drawArc,drawChord,drawPie: 绘制弧线、弦形、扇形。drawPolyline,drawPolygon: 绘制折线、多边形。drawConvexPolygon: 绘制凸多边形(优化性能)。
- 绘制文本:
drawText: 绘制文本字符串。有多种重载形式,可以在指定点、矩形或路径上绘制文本。- 示例:
painter.drawText(rect, Qt::AlignCenter, "Hello Qt!");
- 绘制图像:
drawImage: 在指定位置绘制QImage。drawPixmap: 在指定位置绘制QPixmap。- 示例:
painter.drawImage(QPoint(10, 10), myImage);
- 路径 (
QPainterPath): 提供一种创建复杂形状(由直线、曲线和其他路径元素组成)并进行绘制或填充的方式。路径可以复用,并支持布尔运算(并集、交集等)。QPainterPath path; path.moveTo(20, 80); path.lineTo(20, 30); path.cubicTo(80, 0, 50, 50, 80, 80); // 绘制贝塞尔曲线 painter.drawPath(path); - 渐变填充 (
QGradient): 使用线性渐变 (QLinearGradient)、径向渐变 (QRadialGradient) 或锥形渐变 (QConicalGradient) 来填充形状,创建平滑的颜色过渡效果。QLinearGradient gradient(0, 0, 100, 100); gradient.setColorAt(0.0, Qt::white); gradient.setColorAt(1.0, Qt::green); QBrush brush(gradient); painter.setBrush(brush); painter.drawRect(0, 0, 100, 100); - 合成模式 (
CompositionMode): 控制新绘制的像素如何与目标设备上已有的像素进行混合。例如,SourceOver(默认,源覆盖目标)、Source(直接替换)、DestinationIn(目标在源内)等。通过setCompositionMode()设置。 - 反走样 (
Antialiasing): 通过setRenderHint(QPainter::Antialiasing, true)启用,可以平滑图形的边缘,减少锯齿感,提升视觉质量(但可能略微增加性能开销)。 - 裁剪区域 (
Clipping): 使用setClipRect(),setClipRegion(),setClipPath()限制绘制只发生在特定的区域内。通过setClipping(true/false)启用或禁用裁剪。
4、 使用模式
- 在
QWidget::paintEvent中使用: 这是最常见的用法。在QWidget子类的paintEvent(QPaintEvent *event)方法中创建QPainter对象,并传入this(指向该部件的指针)作为绘图设备。void MyWidget::paintEvent(QPaintEvent *event) { QPainter painter(this); // 创建QPainter,目标设备是这个部件 painter.setPen(...); painter.setBrush(...); // ... 绘制操作 ... } // 析构函数自动调用end(),确保资源释放 - 在图像或像素图上绘制: 创建
QImage或QPixmap,然后创建QPainter指向它们。绘制完成后,可以保存图像或显示在界面上。QImage image(800, 600, QImage::Format_ARGB32); image.fill(Qt::white); // 初始填充白色背景 QPainter painter(&image); painter.drawText(...); // ... 绘制操作 ... painter.end(); // 或者让QPainter析构自动结束 image.save("output.png"); - 打印: 创建
QPrinter对象,在打印作业开始后创建QPainter指向QPrinter,绘制内容将被发送到打印机。
5、 重要注意事项
- 生命周期管理:
QPainter的构造函数 (QPainter(QPaintDevice *)) 会隐式调用begin()。必须确保在绘图设备有效且准备好绘制时创建QPainter。QPainter的析构函数会自动调用end()。如果在同一个设备上需要多次绘制,最好在每次绘制之间显式调用begin()和end()(或让局部QPainter对象析构)。 - 状态保存:
save()和restore()方法用于保存和恢复当前的状态(画笔、画刷、字体、变换、视口窗口等)。这在嵌套绘制或需要临时改变状态时非常有用。painter.save(); // 保存当前状态 painter.setPen(Qt::red); painter.drawLine(...); painter.restore(); // 恢复到保存的状态(原来的画笔) - 性能: 避免在
paintEvent外创建QPainter。尽量减少在paintEvent中的计算量。重用预先生成的图像、路径或渐变对象。谨慎使用复杂的变换和反走样。 - 坐标系统: 默认原点 (0, 0) 在设备的左上角,x轴向右增加,y轴向下增加。使用
translate,scale,rotate,shear可以改变坐标系。setViewport和setWindow提供了另一种坐标映射方式。 - 设备独立性:
QPainter旨在提供设备无关的绘制。相同的绘制代码可以在屏幕、图像或打印机上工作,尽管不同设备的物理特性(如分辨率)可能不同。
6、 示例代码片段 (绘制一个简单的自定义部件)
#include <QWidget>
#include <QPainter>
#include <QPainterPath>
class MyCustomWidget : public QWidget {
Q_OBJECT
public:
using QWidget::QWidget;
protected:
void paintEvent(QPaintEvent *event) override {
QPainter painter(this); // 针对此部件创建QPainter
painter.setRenderHint(QPainter::Antialiasing); // 开启反走样
// 设置画笔和画刷
QPen pen(Qt::darkBlue, 2);
painter.setPen(pen);
QBrush brush(Qt::lightGray);
painter.setBrush(brush);
// 绘制一个矩形
painter.drawRect(10, 10, 100, 50);
// 改变画笔颜色,绘制一条线
pen.setColor(Qt::red);
painter.setPen(pen);
painter.drawLine(10, 70, 110, 70);
// 创建一个路径并绘制(一个简单的箭头)
QPainterPath path;
path.moveTo(150, 30);
path.lineTo(180, 30);
path.lineTo(170, 20);
path.lineTo(180, 30);
path.lineTo(170, 40);
painter.drawPath(path);
// 绘制文本
QFont font("Arial", 12);
painter.setFont(font);
painter.drawText(50, 100, "Qt 6 QPainter Demo");
}
};
7、调试技巧
- 确保
paintEvent被正确调用(例如,在需要重绘时调用update())。 - 检查画笔颜色是否设置正确(忘记设置画笔可能导致图形不可见)。
- 注意坐标范围是否超出设备边界。
- 使用
save()和restore()避免状态设置错误的影响范围过大。
QPainter 是 Qt 图形编程的基石。掌握其核心概念、功能和使用模式,能够帮助你创建各种自定义的、高性能的图形界面元素和应用程序。
2、QPropertyAnimation详解
QPropertyAnimation 是 Qt 框架中 QVariantAnimation 类的一个子类。它是 Qt 动画框架的核心组成部分,专门用于对 QObject 或其子类对象的特定属性进行动画插值。简单来说,它能让一个对象的属性(比如位置、大小、颜色、透明度等)在一段时间内平滑地从起始值变化到结束值。
1、 核心概念
- 目标对象 (
targetObject): 你想要施加动画效果的那个 QObject (或其子类) 实例。例如,一个QWidget, 一个QGraphicsItem等。 - 目标属性 (
propertyName): 目标对象中你想要动态改变的属性的名称。这个属性必须是:- 通过
Q_PROPERTY宏声明过的。 - 拥有读 (
READ) 和写 (WRITE) 函数。 - 其类型能够被
QVariant表示(大多数 Qt 的基本类型和自定义类型只要注册过都可以)。
- 通过
- 起始值 (
startValue): 动画开始时属性的值。类型必须与属性类型兼容。 - 结束值 (
endValue): 动画结束时属性的值。类型必须与属性类型兼容。 - 持续时间 (
duration): 动画从开始到结束所持续的时间长度,单位是毫秒 (ms)。 - 插值器 (
easingCurve): 定义动画过程中值变化的速率模式(匀速、加速、减速、弹跳等)。QEasingCurve类提供了多种预定义的曲线。
2、 工作原理
- 时间驱动:
QPropertyAnimation内部使用一个计时器。 - 插值计算: 在动画运行的每一帧(由 Qt 的主事件循环驱动),根据当前动画已进行的时间占总持续时间的比例(一个介于 0.0 到 1.0 的值),结合设置的
easingCurve,计算出当前应该达到的插值值。 - 属性更新: 将计算出的插值值通过目标对象的属性写函数 (
WRITE) 设置回去,从而改变属性的当前值。 - 信号通知: 在动画开始、结束、状态改变以及每一帧属性值更新时,
QPropertyAnimation会发出相应的信号(如valueChanged,finished),便于应用程序进行响应。
3、 基本用法
以下是一个使用 QPropertyAnimation 移动一个 QPushButton 的简单示例:
#include <QApplication>
#include <QPushButton>
#include <QPropertyAnimation>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
QApplication app(argc, argv);
QPushButton button("Animate Me!");
button.resize(100, 50);
button.show();
// 1. 创建动画对象,指定目标对象和属性名
QPropertyAnimation *animation = new QPropertyAnimation(&button, "geometry");
// 设置父对象为按钮,方便内存管理 (Qt 的对象树机制)
animation->setParent(&button);
// 2. 设置持续时间 (2 秒)
animation->setDuration(2000);
// 3. 设置起始值 (按钮的初始位置和大小)
animation->setStartValue(QRect(0, 0, 100, 50));
// 4. 设置结束值 (移动到 (200, 150) 位置,大小不变)
animation->setEndValue(QRect(200, 150, 100, 50));
// 5. (可选) 设置缓动曲线 (例如,OutBounce 弹跳效果)
animation->setEasingCurve(QEasingCurve::OutBounce);
// 6. 启动动画
animation->start();
return app.exec();
}
4、 关键成员函数
setTargetObject(QObject *object): 设置要动画的目标对象。setPropertyName(const QByteArray &propertyName): 设置要动画的属性名称。setDuration(int msecs): 设置动画持续时间。setStartValue(const QVariant &value): 显式设置动画的起始值。setEndValue(const QVariant &value): 显式设置动画的结束值。setEasingCurve(const QEasingCurve &curve): 设置动画的缓动曲线。start(QAbstractAnimation::DeletionPolicy policy = KeepWhenStopped): 启动动画。stop(): 停止动画。pause(): 暂停动画。resume(): 从暂停状态恢复动画。currentValue() const: 获取当前动画的插值值。state() const: 获取动画的当前状态 (Stopped,Paused,Running)。
5、 高级用法与技巧
- 自动起始/结束值: 如果不显式调用
setStartValue(),动画启动时会自动使用目标属性的当前值作为起始值。类似地,也可以不调用setEndValue()而在运行时通过槽函数动态改变结束值。 - 关键帧动画: 虽然
QPropertyAnimation本身只支持两点间的线性插值(加上缓动曲线),但你可以通过QSequentialAnimationGroup或QParallelAnimationGroup组合多个QPropertyAnimation来实现更复杂的序列或并行动画效果。对于更精细的控制,可以使用QVariantAnimation并重写virtual void updateCurrentValue(const QVariant &value)函数,或者使用QAnimationDriver(更底层)。 - 动画组: 使用
QSequentialAnimationGroup(顺序执行) 或QParallelAnimationGroup(并行执行) 来管理多个动画。 - 状态改变信号: 连接
stateChanged()信号可以知道动画何时开始、暂停或停止。连接finished()信号知道动画何时正常结束。连接valueChanged()信号可以实时获取属性变化的值(注意频率可能很高)。 - 循环动画: 使用
setLoopCount(int count)可以设置动画的循环次数。设置为-1表示无限循环。 - 方向: 使用
setDirection(QAbstractAnimation::Direction direction)可以设置动画是正向 (Forward) 播放还是反向 (Backward) 播放。
6、 注意事项
- 属性支持: 确保目标属性是用
Q_PROPERTY声明过的,并且有可用的读写函数。尝试动画一个没有WRITE函数或类型不兼容的属性会导致运行时警告或错误。 - 线程安全:
QPropertyAnimation以及整个 Qt 动画框架都不是线程安全的。动画操作必须在主线程(GUI线程)中进行。 - 对象生命周期: 确保目标对象在动画执行期间一直有效。通常将动画对象设置为目标对象的子对象(利用 Qt 对象树机制)是一种安全的做法,这样当目标对象被删除时,动画对象也会被自动删除。
- 性能: 对于非常高频的属性更新(比如每帧更新位置),确保操作本身是高效的,避免在
valueChanged()的槽函数中进行复杂计算。对于 UI 动画,Qt 通常能很好地处理。 - 与 QML 的对比: Qt Quick (QML) 有自己更声明式的动画系统 (
PropertyAnimation,NumberAnimation等)。QPropertyAnimation主要用于 Qt Widgets 模块的 C++ 开发。
7、 总结
QPropertyAnimation 是 Qt Widgets 应用程序中为对象属性添加平滑动画效果的有力工具。通过设置目标对象、属性名、持续时间、起始值、结束值和缓动曲线,你可以轻松创建出各种视觉效果。结合动画组和信号槽机制,可以实现非常复杂的动画交互逻辑。理解其核心概念和正确使用方式是关键。
























 1636
1636

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










