继续之前的源码学习,上一篇分析了InputFormat的getSplits()方法,接下来是createRecordReader()方法。
从这里可以看到该方法为一个split创建一个recordReader,并且在使用split之前会回调recordReader的初始化方法,该方法的具体实现在TextInputFormat中。
@Override
public RecordReader<LongWritable, Text>
createRecordReader(InputSplit split,
TaskAttemptContext context) {
String delimiter = context.getConfiguration().get(
"textinputformat.record.delimiter");
byte[] recordDelimiterBytes = null;
if (null != delimiter)
recordDelimiterBytes = delimiter.getBytes(Charsets.UTF_8);
return new LineRecordReader(recordDelimiterBytes);
}这段代码没什么作用,就是new了一个LineRecordReader对象,构造方法也没什么特别的,但是回想上面的注释说到:会调用一次初始化方法,所以看initialize()。
public void initialize(InputSplit genericSplit,
TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException {
FileSplit split = (FileSplit) genericSplit;
Configuration job = context.getConfiguration();
this.maxLineLength = job.getInt(MAX_LINE_LENGTH, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
start = split.getStart();
end = start + split.getLength();
final Path file = split.getPath();
// open the file and seek to the start of the split
final FileSystem fs = file.getFileSystem(job);
fileIn = fs.open(file);
CompressionCodec codec = new CompressionCodecFactory(job).getCodec(file);
if (null!=codec) {
isCompressedInput = true;
decompressor = CodecPool.getDecompressor(codec);
if (codec instanceof SplittableCompressionCodec) {
final SplitCompressionInputStream cIn =
((SplittableCompressionCodec)codec).createInputStream(
fileIn, decompressor, start, end,
SplittableCompressionCodec.READ_MODE.BYBLOCK);
in = new CompressedSplitLineReader(cIn, job,
this.recordDelimiterBytes);
start = cIn.getAdjustedStart();
end = cIn.getAdjustedEnd();
filePosition = cIn;
} else {
in = new SplitLineReader(codec.createInputStream(fileIn,
decompressor), job, this.recordDelimiterBytes);
filePosition = fileIn;
}
} else {
fileIn.seek(start);
in = new SplitLineReader(fileIn, job, this.recordDelimiterBytes);
filePosition = fileIn;
}
// If this is not the first split, we always throw away first record
// because we always (except the last split) read one extra line in
// next() method.
if (start != 0) {
start += in.readLine(new Text(), 0, maxBytesToConsume(start));
}
this.pos = start;
}这段代码主要作用就是初始化参数,将游标移动到split的起始位置,查看outline发现一些类似迭代功能的方法
但是没有找到方法的调用,应该是在其他的方法使用key,value,回想MR过程,联想到步骤二,所以应该是在Mapper类调用了这些方法。下面就进入步骤二的源码学习。
1.2自定义map函数,对<k1,v1>进行处理,转换成<k2,v2>输出。Mapper类中有一个map方法,正如注释所说一般我们都会重写map方法,添加自己的业务逻辑在里面,简单的例子就是单词计数,对v1进行切分。
/**
* Called once for each key/value pair in the input split. Most applications
* should override this, but the default is the identity function.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected void map(KEYIN key, VALUEIN value,
Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
context.write((KEYOUT) key, (VALUEOUT) value);
} /**
* Expert users can override this method for more complete control over the
* execution of the Mapper.
* @param context
* @throws IOException
*/
public void run(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
setup(context);
try {
while (context.nextKeyValue()) {
map(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getCurrentValue(), context);
}
} finally {
cleanup(context);
}
} /**
* The <code>Context</code> passed on to the {@link Mapper} implementations.
*/
public abstract class Context
implements MapContext<KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT> {
}MapContext只有定义了一个getInputSplit方法,所以继续找。MapContext继承了TaskInputOutputContext接口
public interface MapContext<KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT>
extends TaskInputOutputContext<KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT>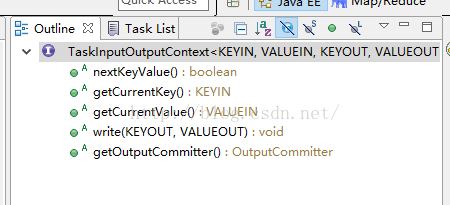
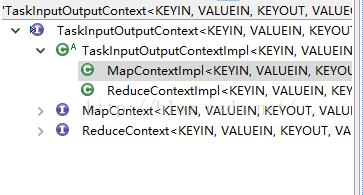
如下图,我们最终就找到了MapContextImpl类,熟悉JAVA的同学肯定不会对这个命名刚到陌生。
/**
* The context that is given to the {@link Mapper}.
* @param <KEYIN> the key input type to the Mapper
* @param <VALUEIN> the value input type to the Mapper
* @param <KEYOUT> the key output type from the Mapper
* @param <VALUEOUT> the value output type from the Mapper
*/
@InterfaceAudience.Private
@InterfaceStability.Unstable
public class MapContextImpl<KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT>
extends TaskInputOutputContextImpl<KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT>
implements MapContext<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT> {
private RecordReader<KEYIN,VALUEIN> reader;
private InputSplit split;
public MapContextImpl(Configuration conf, TaskAttemptID taskid,
RecordReader<KEYIN,VALUEIN> reader,
RecordWriter<KEYOUT,VALUEOUT> writer,
OutputCommitter committer,
StatusReporter reporter,
InputSplit split) {
super(conf, taskid, writer, committer, reporter);
this.reader = reader;
this.split = split;
}
/**
* Get the input split for this map.
*/
public InputSplit getInputSplit() {
return split;
}
@Override
public KEYIN getCurrentKey() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
return reader.getCurrentKey();
}
@Override
public VALUEIN getCurrentValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
return reader.getCurrentValue();
}
@Override
public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
return reader.nextKeyValue();
}
}







 本文深入剖析了Hadoop MapReduce的处理流程,重点讲解了InputFormat的createRecordReader方法及其实现细节,包括记录读取器的初始化过程,并探讨了Mapper类中map方法的调用机制。
本文深入剖析了Hadoop MapReduce的处理流程,重点讲解了InputFormat的createRecordReader方法及其实现细节,包括记录读取器的初始化过程,并探讨了Mapper类中map方法的调用机制。

















 789
789

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








