package cn.itcast.thread;
/*
自定义线程的创建方式:
方式一 :
1. 自定义一个类继承Thread类。
2. 重写Thread类的run方法,把自定义线程的任务代码写在run方法上。
3. 创建Thread的子类对象,并且调用start方法启动一个线程。
注意:千万不要直接调用run方法,调用start方法的时候线程就会开启,线程一旦开启就会执行run方法中代码,如果直接调用
run方法,那么就 相当于调用了一个普通的方法而已。
方式二:
1. 自定义一个类实现Runnable接口。
2. 实现Runnable接口 的run方法,把自定义线程的任务定义在run方法上。
3. 创建Runnable实现类对象。
4. 创建Thread类 的对象,并且把Runnable实现类的对象作为实参传递。
5. 调用Thread对象 的start方法开启一个线程。
问题1: 请问Runnable实现类的对象是线程对象吗?
Runnable实现类的对象并 不是一个线程对象,只不过是实现了Runnable接口 的对象而已。
只有是Thread或者是Thread的子类才是线程 对象。
问题2: 为什么要把Runnable实现类的对象作为实参传递给Thread对象呢?作用是什么?
作用就是把Runnable实现类的对象的run方法作为了线程的任务代码去执行了。
推荐使用: 第二种。 实现Runable接口的。
原因: 因为java单继承 ,多实现的。
*/
public class Demo3 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
/*System.out.println("this:"+ this);
System.out.println("当前线程:"+ Thread.currentThread());*/
for(int i = 0 ; i < 100 ; i++){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Runnable实现类的对象
Demo3 d = new Demo3();
//创建Thread类的对象, 把Runnable实现类对象作为实参传递。
Thread thread = new Thread(d,"狗娃"); //Thread类使用Target变量记录了d对象,
//调用thread对象的start方法开启线程。
thread.start();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 100 ; i++){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);
}
}
/*
Thread类 的run方法
* @Override
public void run() {
if (target != null) {
target.run(); //就相当于Runnable实现类的对象的run方法作为了Thread对象的任务代码了。
}
}
*/
}
package cn.itcast.thread;
class SaleTicket implements Runnable{
int num = 50; // 票数,
//多线程执行时,不用加static,因为只new了一个对象,
//将这个对象传给三个线程去执行,对象只有一个,所以没有线程安全问题
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
synchronized ("锁") {
if(num>0){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"售出了第"+ num+"号票");
num--;
}else{
System.out.println("售罄了..");
break;
}
}
}
}
}
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建了一个Runnable实现类的对象
SaleTicket saleTicket = new SaleTicket();
//创建三个线程对象模拟三个窗口
Thread thread1 = new Thread(saleTicket,"窗口1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(saleTicket,"窗口2");
Thread thread3 = new Thread(saleTicket,"窗口3");
//开启线程售票
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
}
}
**价格出现错乱的原因:
因为 产品共享,当生产一半时,就被消费者抢走了,所有消费者打印的
价格错乱了**
package cn.itcast.thread;
/*
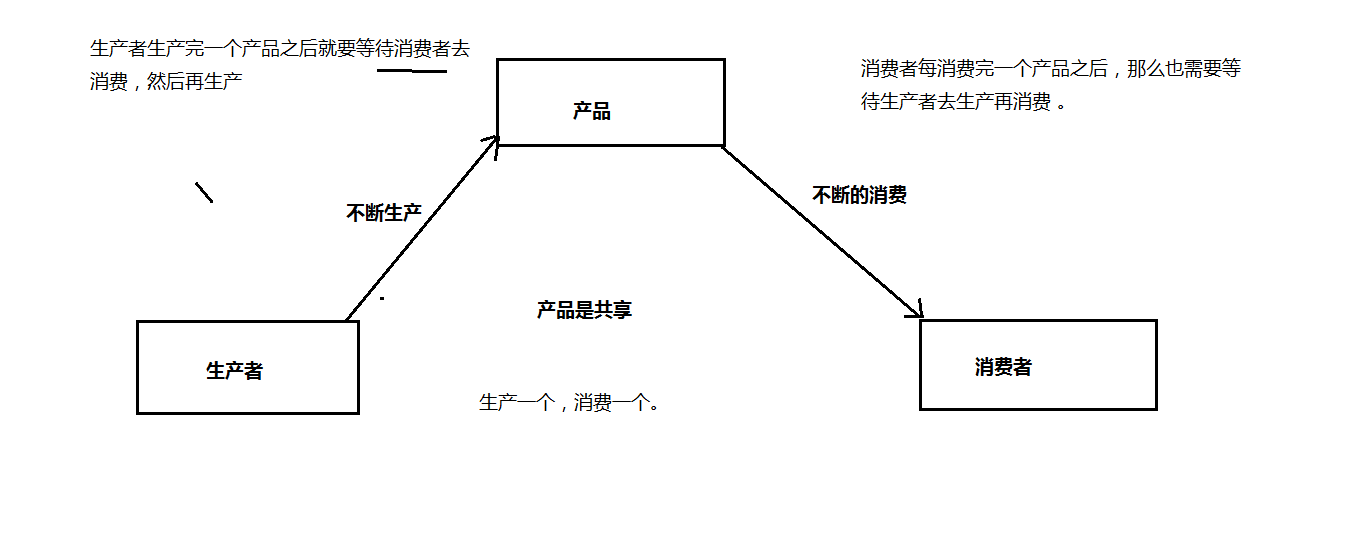
线程通讯: 一个线程完成了自己的任务时,要通知另外一个线程去完成另外一个任务.
生产者与消费者
wait(): 等待 如果线程执行了wait方法,那么该线程会进入等待的状态,等待状态下的线程必须要被其他线程调用notify方法才能唤醒。
notify(): 唤醒 唤醒线程池等待线程其中的一个。
notifyAll() : 唤醒线程池所有等待 线程。
wait与notify方法要注意的事项:
1. wait方法与notify方法是属于Object对象 的。
2. wait方法与notify方法必须要在同步代码块或者是同步函数中才能 使用。
3. wait方法与notify方法必需要由锁对象调用。
问题一:出现了线程安全问题。 价格错乱了...
*/
//产品类
class Product{
String name; //名字
double price; //价格
boolean flag = false; //产品是否生产完毕的标识,默认情况是没有生产完成。
}
//生产者
class Producer extends Thread{
Product p ; //产品
public Producer(Product p) {
this.p = p ;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 0 ;
while(true){
synchronized (p) {
if(p.flag==false){
if(i%2==0){
p.name = "苹果";
p.price = 6.5;
}else{
p.name="香蕉";
p.price = 2.0;
}
System.out.println("生产者生产出了:"+ p.name+" 价格是:"+ p.price);
p.flag = true;
i++;
p.notifyAll(); //唤醒消费者去消费
}else{
//已经生产 完毕,等待消费者先去消费
try {
p.wait(); //生产者等待
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
//消费者
class Customer extends Thread{
Product p;
public Customer(Product p) {
this.p = p;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
synchronized (p) {
if(p.flag==true){ //产品已经生产完毕
System.out.println("消费者消费了"+p.name+" 价格:"+ p.price);
p.flag = false;
p.notifyAll(); // 唤醒生产者去生产
}else{
//产品还没有生产,应该 等待生产者先生产。
try {
p.wait(); //消费者也等待了...
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Product p = new Product(); //产品
//创建生产对象
Producer producer = new Producer(p);
//创建消费者
Customer customer = new Customer(p);
//调用start方法开启线程
producer.start();
customer.start();
}
}
package cn.itcast.thread;
/*
线程的停止:
1. 停止一个线程 我们一般都会通过一个变量去控制的。
2. 如果需要停止一个处于等待状态下的线程,那么我们需要通过变量配合notify方法或者interrupt()来使用。
*/
public class Demo6 extends Thread {
boolean flag = true;
public Demo6(String name){
super(name);
}
@Override
public synchronized void run() {
int i = 0 ;
while(flag){
try {
this.wait(); //狗娃等待..
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("接收到了异常了....");
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);
i++;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo6 d = new Demo6("狗娃");
d.setPriority(10);
d.start();
for(int i = 0 ; i<100 ; i++){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);
//当主线程的i是80的时候停止狗娃线程。
//d.interrupt(); // interrupt()根本就是无法停止一个线程。
if(i==80){
d.flag = false;
d.interrupt(); //把线程的等待状态强制清除,被清除状态的线程会接收到一个InterruptedException。
/*synchronized (d) {
d.notify();
}*/
}
}
}
}
package cn.itcast.thread;
/*
守护线程(后台线程):在一个进程中如果只剩下 了守护线程,那么守护线程也会死亡。
需求: 模拟QQ下载更新包。
一个线程默认都不是守护线程。
*/
public class Demo7 extends Thread {
public Demo7(String name){
super(name);
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 1 ; i<=100 ; i++){
System.out.println("更新包目前下载"+i+"%");
if(i==100){
System.out.println("更新包下载完毕,准备安装..");
}
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo7 d = new Demo7("后台线程");
d.setDaemon(true); //setDaemon() 设置线程是否为守护线程,true为守护线程, false为非守护线程。
// System.out.println("是守护线程吗?"+ d.isDaemon()); //判断线程是否为守护线程。
d.start();
for(int i = 1 ; i<=100 ; i++){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);
}
}
}
package cn.itcast.thread;
/*
join方法。 加入
*/
//老妈
class Mon extends Thread{
public void run() {
System.out.println("妈妈洗菜");
System.out.println("妈妈切菜");
System.out.println("妈妈准备炒菜,发现没有酱油了..");
//叫儿子去打酱油
Son s= new Son();
s.start();
try {
s.join(); //加入。 一个线程如果执行join语句,那么就有新的线程加入,执行该语句的线程必须要让步给新加入的线程先完成任务,然后才能继续执行。
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("妈妈继续炒菜");
System.out.println("全家一起吃饭..");
}
}
class Son extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("儿子下楼..");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("儿子一直往前走");
System.out.println("儿子打完酱油了");
System.out.println("上楼,把酱油给老妈");
}
}
public class Demo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Mon m = new Mon();
m.start();
}
}
























 2081
2081

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








