下面这个是骨架提取的代码实现
//两个方法吧,我记不得在哪看的了
enum
{
THINNING_ZHANGSUEN,
THINNING_GUOHALL
};
//骨架提取
void thinningIteration(cv::Mat img, int iter, int thinningType)
{
cv::Mat marker = cv::Mat::zeros(img.size(), CV_8UC1);
if (thinningType == THINNING_ZHANGSUEN) {
for (int i = 1; i < img.rows - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < img.cols - 1; j++)
{
uchar p2 = img.at<uchar>(i - 1, j);
uchar p3 = img.at<uchar>(i - 1, j + 1);
uchar p4 = img.at<uchar>(i, j + 1);
uchar p5 = img.at<uchar>(i + 1, j + 1);
uchar p6 = img.at<uchar>(i + 1, j);
uchar p7 = img.at<uchar>(i + 1, j - 1);
uchar p8 = img.at<uchar>(i, j - 1);
uchar p9 = img.at<uchar>(i - 1, j - 1);
int A = (p2 == 0 && p3 == 1) + (p3 == 0 && p4 == 1) +
(p4 == 0 && p5 == 1) + (p5 == 0 && p6 == 1) +
(p6 == 0 && p7 == 1) + (p7 == 0 && p8 == 1) +
(p8 == 0 && p9 == 1) + (p9 == 0 && p2 == 1);
int B = p2 + p3 + p4 + p5 + p6 + p7 + p8 + p9;
int m1 = iter == 0 ? (p2 * p4 * p6) : (p2 * p4 * p8);
int m2 = iter == 0 ? (p4 * p6 * p8) : (p2 * p6 * p8);
if (A == 1 && (B >= 2 && B <= 6) && m1 == 0 && m2 == 0)
marker.at<uchar>(i, j) = 1;
}
}
}
if (thinningType == THINNING_GUOHALL) {
for (int i = 1; i < img.rows - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < img.cols - 1; j++)
{
uchar p2 = img.at<uchar>(i - 1, j);
uchar p3 = img.at<uchar>(i - 1, j + 1);
uchar p4 = img.at<uchar>(i, j + 1);
uchar p5 = img.at<uchar>(i + 1, j + 1);
uchar p6 = img.at<uchar>(i + 1, j);
uchar p7 = img.at<uchar>(i + 1, j - 1);
uchar p8 = img.at<uchar>(i, j - 1);
uchar p9 = img.at<uchar>(i - 1, j - 1);
int C = ((!p2) & (p3 | p4)) + ((!p4) & (p5 | p6)) +
((!p6) & (p7 | p8)) + ((!p8) & (p9 | p2));
int N1 = (p9 | p2) + (p3 | p4) + (p5 | p6) + (p7 | p8);
int N2 = (p2 | p3) + (p4 | p5) + (p6 | p7) + (p8 | p9);
int N = N1 < N2 ? N1 : N2;
int m = iter == 0 ? ((p6 | p7 | (!p9)) & p8) : ((p2 | p3 | (!p5)) & p4);
if ((C == 1) && ((N >= 2) && ((N <= 3)) & (m == 0)))
marker.at<uchar>(i, j) = 1;
}
}
}
img &= ~marker;
}
// 这个是调用的方法,输入的图像需要是二值化后的图像
void thinning(cv::Mat input, cv::Mat& output, int thinningType)
{
output = input.clone();
// Enforce the range of the input image to be in between 0 - 255
output /= 255;
cv::Mat prev = cv::Mat::zeros(output.size(), CV_8UC1);
cv::Mat diff;
do {
thinningIteration(output, 0, thinningType);
thinningIteration(output, 1, thinningType);
absdiff(output, prev, diff);
output.copyTo(prev);
} while (countNonZero(diff) > 0);
output *= 255;
}
下面是提取最大的轮廓点,并且去除短的分支和自相交的轮廓点
int findLongContours(Mat img,vector<cv::Point2i> &contoursLong)
{
img /= 255;
for (int i = 2; i < img.rows-2;i++)
{
uchar* ptr0 = img.ptr<uchar>(i - 1);
uchar* ptr1 = img.ptr<uchar>(i);
uchar* ptr2 = img.ptr<uchar>(i + 1);
for (int j = 2; j < img.cols-2; j++)
{
if (ptr1[j]==1)
{
int hopCount = abs(ptr0[j] - ptr0[j-1]) + abs(ptr0[j+1] - ptr0[j])
+ abs(ptr1[j+1] - ptr0[j+1]) + abs(ptr2[j+1] - ptr1[j+1])
+ abs(ptr2[j] - ptr2[j+1]) + abs(ptr2[j-1] - ptr2[j])
+ abs(ptr1[j-1] - ptr2[j-1]) + abs(ptr0[j-1] - ptr1[j-1]);
if (hopCount>=5)
{
ptr0[j - 1] = 0, ptr0[j] = 0, ptr0[j + 1] = 0;
ptr1[j - 1] = 0, ptr1[j] = 0, ptr1[j + 1] = 0;
ptr2[j - 1] = 0, ptr2[j] = 0, ptr2[j + 1] = 0;
vector<vector<cv::Point2i>> countours;
findContours(img, countours, cv::RETR_LIST, cv::CHAIN_APPROX_NONE);
vector<Point2i> vecSize;
for (int m = 0; m < countours.size();m++)
{
vecSize.push_back(cv::Point2i(m,countours[m].size()));
}
sort(vecSize.begin(), vecSize.end(), comparePoint2iY);
img = Mat::zeros(img.size(), CV_8UC1);
if (vecSize.size() <= 2) //去除自交的轮廓点,有优化空间,去判断自交的轮廓
{
cv::polylines(img, countours[vecSize[0].x], false, 1);
continue;
}
cv::polylines(img, countours[vecSize[0].x], false, 1);
cv::polylines(img, countours[vecSize[1].x], false, 1);
//补齐断点
ptr1[j] = 1;
uchar* ptrCur = img.data;
for (int m = i - 2; m < i + 3;m++)
{
for (int n = j - 2; n < j + 3;n++)
{
if (ptrCur[m*img.cols + n] != 0)
{
int xClose = (n+j)/2;
int yClose = (m + i) / 2;
ptrCur[yClose*img.cols + xClose] = 1;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
vector<vector<cv::Point2i>> contoursOut;
findContours(img, contoursOut, cv::RETR_TREE, cv::CHAIN_APPROX_NONE);
for (int i = 0; i < contoursOut.size();i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < contoursOut[i].size();j++)
{
contoursLong.push_back(contoursOut[i][j]);
}
}
return 1;
}
效果如下:
二值化图像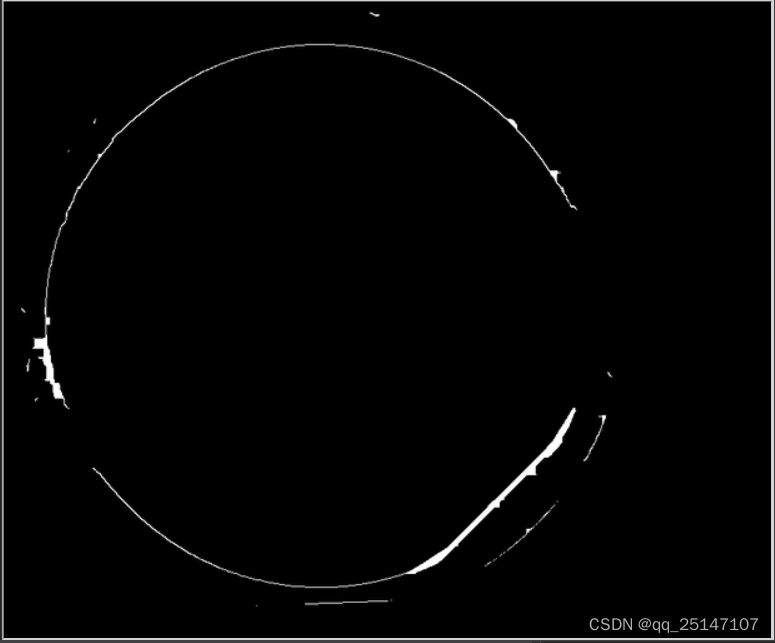
提取骨架的图像
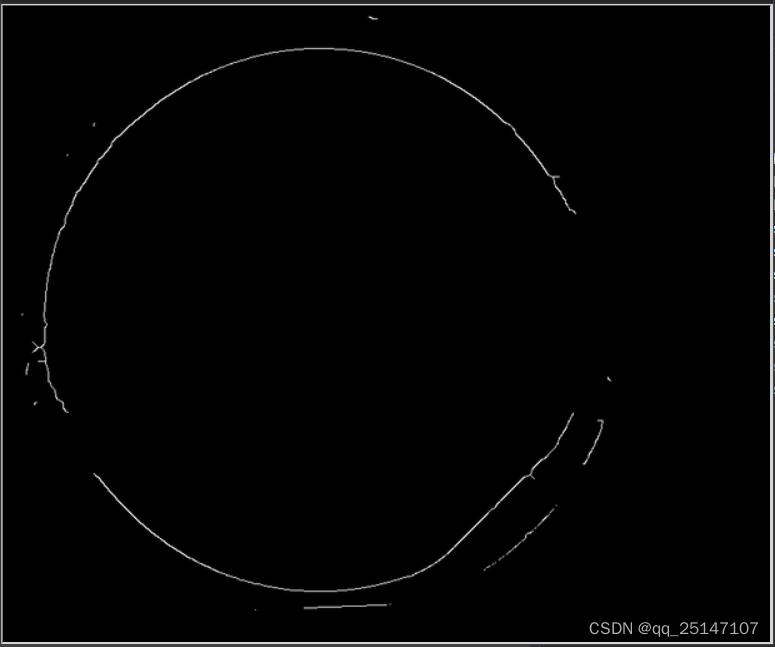

抽出最大的轮廓,去除分支点和自相交的分支点(对于后面拟合圆,拟合直线能够去除很大的干扰)
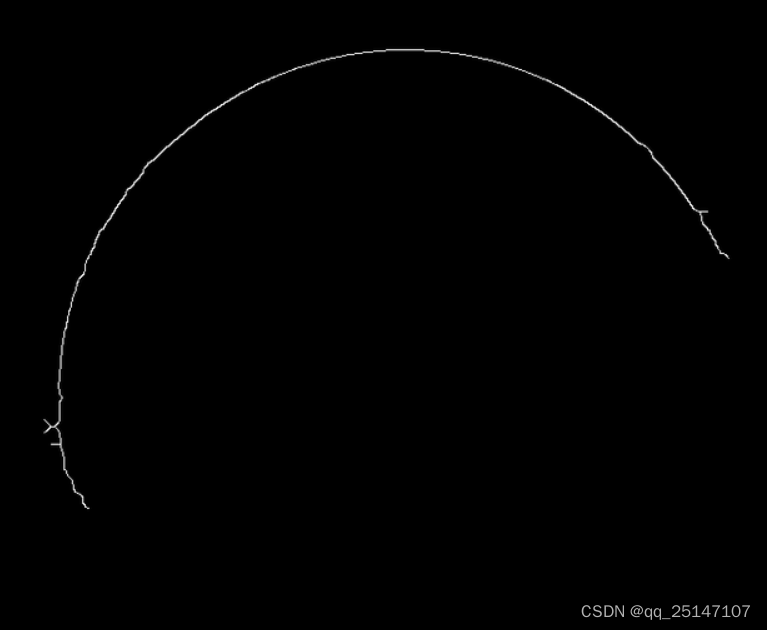
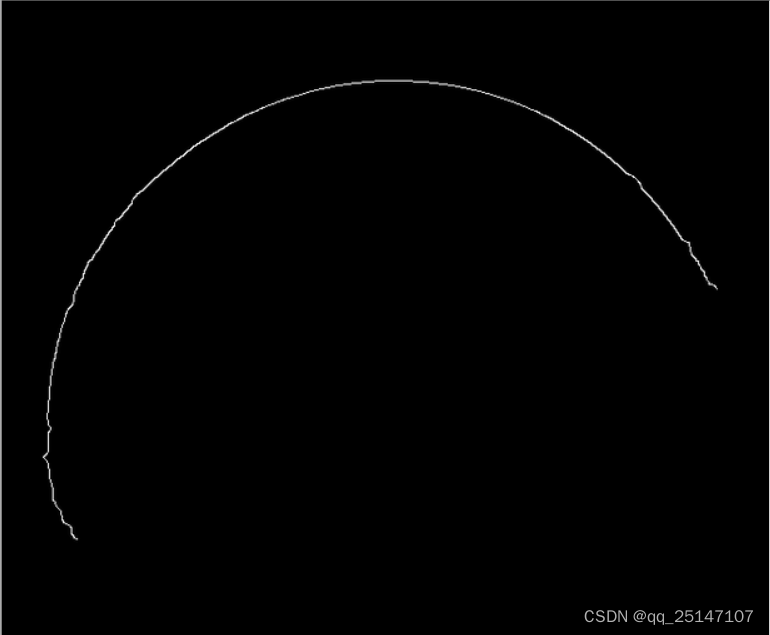



























 2599
2599











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








