SoftMax---学习笔记
softMax分类函数
首先给一个图,这个图比较清晰地告诉大家softmax是怎么计算的。
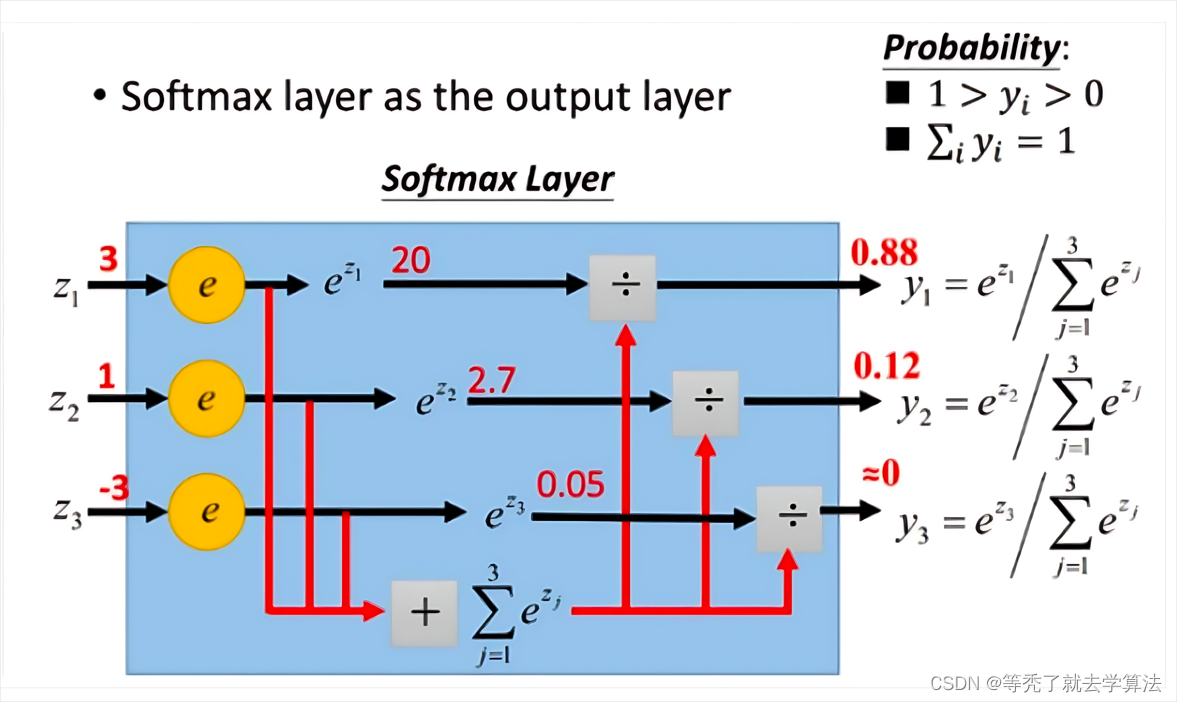 (图片来自网络)
(图片来自网络)
定义:
给定以歌
n
×
k
n×k
n×k矩阵
W
=
(
w
1
,
w
2
,
.
.
.
,
w
k
)
W=(w_1,w_2,...,w_k)
W=(w1,w2,...,wk),其中,
w
j
∈
R
n
w_j\in R^n
wj∈Rn为
n
×
1
n×1
n×1列向量(
1
≤
j
≤
k
1\leq j\leq k
1≤j≤k),Softmax模型
h
w
:
R
n
→
R
k
h_w:R^n →R^k
hw:Rn→Rk为:
h
W
(
x
)
=
(
e
<
w
1
,
x
>
∑
t
=
1
k
e
<
w
t
,
x
>
,
e
<
w
2
,
x
>
∑
t
=
1
k
e
<
w
t
,
x
>
,
.
.
.
,
e
<
w
k
,
x
>
∑
t
=
1
k
e
<
w
t
,
x
>
)
(
样本
m
×
k
)
h_W(x)=(\frac{e^{<w_1,x>}}{\sum_{t=1}^{k}e^{<w_t,x>}},\frac{e^{<w_2,x>}}{\sum_{t=1}^{k}e^{<w_t,x>}},...,\frac{e^{<w_k,x>}}{\sum_{t=1}^{k}e^{<w_t,x>}})_{(样本m×k)}
hW(x)=(∑t=1ke<wt,x>e<w1,x>,∑t=1ke<wt,x>e<w2,x>,...,∑t=1ke<wt,x>e<wk,x>)(样本m×k)
样本
x
1
x_1
x1的softmax值为:
h
W
(
x
1
)
=
(
e
<
w
1
,
x
1
>
∑
t
=
1
k
e
<
w
t
,
x
1
>
,
e
<
w
2
,
x
1
>
∑
t
=
1
k
e
<
w
t
,
x
1
>
,
.
.
.
,
e
<
w
k
,
x
1
>
∑
t
=
1
k
e
<
w
t
,
x
1
>
)
(
1
×
k
)
h_W(x_1)=(\frac{e^{<w_1,x_1>}}{\sum_{t=1}^{k}e^{<w_t,x_1>}},\frac{e^{<w_2,x_1>}}{\sum_{t=1}^{k}e^{<w_t,x_1>}},...,\frac{e^{<w_k,x_1>}}{\sum_{t=1}^{k}e^{<w_t,x_1>}})_{(1×k)}
hW(x1)=(∑t=1ke<wt,x1>e<w1,x1>,∑t=1ke<wt,x1>e<w2,x1>,...,∑t=1ke<wt,x1>e<wk,x1>)(1×k)
且可知
∑
1
k
h
w
(
x
1
)
=
1
\sum_1^kh_w(x_1) = 1
1∑khw(x1)=1
类别数k要小于特征维度n
如果类别数大于特征维度,那么就会出现过多的未知参数需要学习,导致模型过于复杂,难以训练和泛化。因此,通常是将类别数设定为特征维度的一个较小的值,以保证模型的简洁性和可行性。
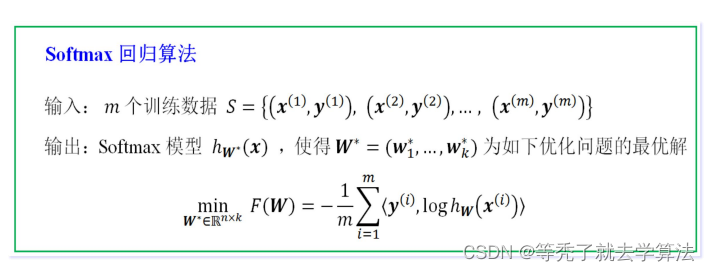
softmax分类损失函数
交叉熵的理论部分在上一篇文章:Logistic回归
前面提到,在多分类问题中,我们经常使用交叉熵作为损失函数
L
o
s
s
=
−
∑
t
i
l
n
y
i
Loss = -\sum t_ilny_i
Loss=−∑tilnyi
其中
t
i
t_i
ti表示真实值,
y
i
y_i
yi表示求出的softmax值。当预测第i个时,可以认为
t
i
t_i
ti=1.此时损失函数变成了
L
o
s
s
i
=
−
l
n
y
i
Loss_i=-lny_i
Lossi=−lnyi
代入
y
i
=
h
W
(
x
i
)
y_i=h_W(x_i)
yi=hW(xi),求梯度
▽
L
o
s
s
i
=
y
i
−
1
▽Loss_i=y_i-1
▽Lossi=yi−1上面的结果表示,我们只需要正向求出
y
i
y_i
yi,将结果减1就是反向更新的梯度,导数的计算是不是非常简单!
总结一下:


练习题:红酒产地预测

本实验使用softmax回归模型进行红酒品质分类。首先,导入红酒数据,并将类标签转换为one-hot向量表示, 特征组向量前面置1(为了将线性回归b吸收到w中)。
rwine = load_wine() # 导入红酒数据
X = rwine.data
y = rwine.target
m, n = X.shape
y = convert_to_vectors(y)
X = np.concatenate((np.ones((m, 1)), X), axis=1)
然后,进行数据预处理,包括特征归一化和随机划分训练集和测试集。
# 正则化,原因是e = np.exp(scores)会溢出,将x正则化[]
X = normalize(X)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2)
接着,使用softmax回归模型对训练集进行训练,并在测试集上进行预测和模型评估。得到的Accuracy值是:0.9444444444444444
# 使用自定义的SoftMax回归模型
model = SoftmaxRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
model.predict(X_test)
y_score = model.proba
y_true = max_indices = np.argmax(y_test, axis=1)
# 精确率计算
def t_pre(y_pre, y_true):
count = 0
for i in range(len(y_pre)):
if y_pre[i] - y_true[i] == 0:
count += 1
return count
acc = (t_pre(np.argmax(model.proba, axis=1), y_true)) / len(y_true)
print(acc)
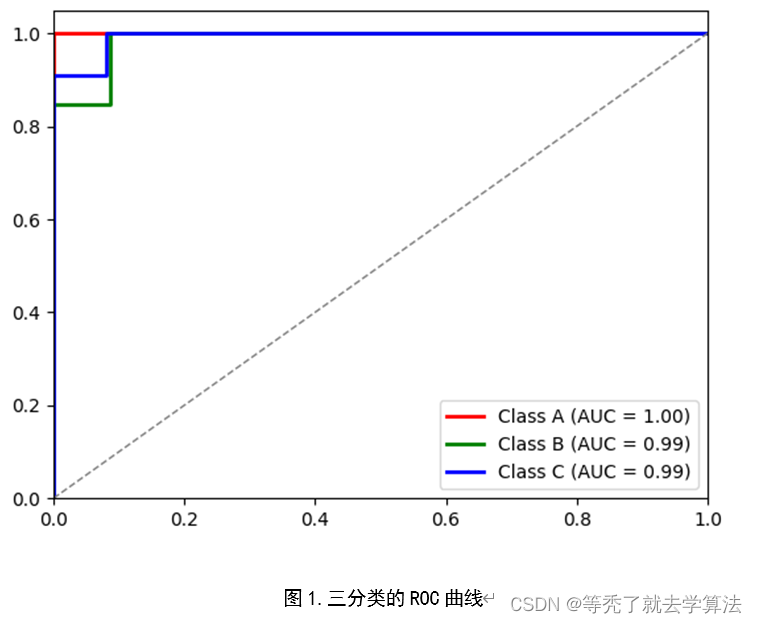
最后,绘制ROC曲线和计算AUC值,以进一步评估模型性能。
# 绘制ROC曲线:调用skelearn库中方法
# 将每个标签作为正例,其他两个标签合并作为负例,计算ROC曲线和AUC值
fpr, tpr, roc_auc = {}, {}, {}
for i in range(3):
fpr[i], tpr[i], _ = roc_curve(y_true == i, y_score[:, i])
roc_auc[i] = auc(fpr[i], tpr[i])
plt.figure()
colors = ['red', 'green', 'blue']
labels = ['Class A', 'Class B', 'Class C']
for i in range(3):
plt.plot(fpr[i], tpr[i], color=colors[i], lw=2,
label='{0} (AUC = {1:0.2f})'
''.format(labels[i], roc_auc[i]))
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='gray', lw=1, linestyle='--')
plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.ylim([0.0, 1.05])
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.show()
完整代码:
from sklearn.datasets import load_wine
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc, accuracy_score
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def normalize(X):
X_min = np.min(X, axis=0)
X_max = np.max(X, axis=0)
print(X_max)
denom = X_max - X_min
# 将所有分母为零的元素置为一个小值
denom[denom == 0] = 1e-8
return (X - X_min) / denom
def softmax(scores):
e = np.exp(scores)
s = e.sum(axis=1)
for i in range(len(s)):
e[i] /= s[i]
return e
def threshold(t, proba):
return (proba >= t).astype(np.int)
def plot_roc_curve(proba, y):
fpr, tpr = [], []
for i in range(100):
z = threshold(0.01 * i, proba)
tp = (y * z).sum()
fp = ((1 - y) * z).sum()
tn = ((1 - y) * (1 - z)).sum()
fn = (y * (1 - z)).sum()
fpr.append(1.0 * fp / (fp + tn))
tpr.append(1.0 * tp / (tp + fn))
plt.plot(fpr, tpr)
plt.show()
class SoftmaxRegression:
def __init__(self):
self.w = None
self.proba = None
def fit(self, X, y, eta_0=50, eta_1=100, N=1000):
m, n = X.shape
m, k = y.shape
w = np.zeros(n * k).reshape(n, k)
if self.w is None:
self.w = np.zeros(n * k).reshape(n, k)
for t in range(N):
i = np.random.randint(m)
x = X[i].reshape(1, -1)
print(x.dot(w))
proba = softmax(x.dot(w))
g = x.T.dot(proba - y[i])
w = w - eta_0 / (t + eta_1) * g
self.w += w
self.w /= N
def predict_proba(self, X):
return softmax(X.dot(self.w))
def predict(self, X):
self.proba = self.predict_proba(X)
return np.argmax(self.proba, axis=1)
def convert_to_vectors(c): # 转换成 m*k 矩阵(one-hot向量), m样本数,k类别数
# c为类标签列向量 m*1,c[i]{0,1,..,k-1}
m = len(c)
k = np.max(c) + 1
y = np.zeros(m * k).reshape(m, k)
for i in range(m):
y[i][c[i]] = 1 # y[i]的第c[i]位置1,其余位为0
return y
rwine = load_wine() # 导入红酒数据
X = rwine.data
y = rwine.target
m, n = X.shape
y = convert_to_vectors(y)
X = np.concatenate((np.ones((m, 1)), X), axis=1)
# 正则化,原因是e = np.exp(scores)会溢出,将x正则化[]
X = normalize(X)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2)
# 使用自定义的SoftMax回归模型
model = SoftmaxRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
model.predict(X_test)
y_score = model.proba
y_true = max_indices = np.argmax(y_test, axis=1)
# 精确率计算
def t_pre(y_pre, y_true):
count = 0
for i in range(len(y_pre)):
if y_pre[i] - y_true[i] == 0:
count += 1
return count
acc = (t_pre(np.argmax(model.proba, axis=1), y_true)) / len(y_true)
print(acc)
# 绘制ROC曲线:调用skelearn库中方法
# 将每个标签作为正例,其他两个标签合并作为负例,计算ROC曲线和AUC值
fpr, tpr, roc_auc = {}, {}, {}
for i in range(3):
fpr[i], tpr[i], _ = roc_curve(y_true == i, y_score[:, i])
roc_auc[i] = auc(fpr[i], tpr[i])
plt.figure()
colors = ['red', 'green', 'blue']
labels = ['Class A', 'Class B', 'Class C']
for i in range(3):
plt.plot(fpr[i], tpr[i], color=colors[i], lw=2,
label='{0} (AUC = {1:0.2f})'
''.format(labels[i], roc_auc[i]))
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='gray', lw=1, linestyle='--')
plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.ylim([0.0, 1.05])
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.show()
- 在用自定义的Softmax回归,对于没有正则化的X,它在进入softmax(scores)函数,会出现溢出情况,需要控制X.dot(w)的值的大小。这里的正则化是指的数据预处理的归一化(将每个特征值都缩放到0和1之间) 公式:x’ = (x - min(x)) / (max(x) - min(x)),不会影响分类结果(会影响W值,但是并不需要关注W值)
- ROC曲线:对于多分类的ROC曲线的绘制,可以分别将各个类别作为正例,其他类别作为反例,最后可以取平均AUC值作为该模型的AUC值























 2737
2737











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










