转载自http://blog.csdn.net/caimouse/article/details/60465975,仅用作个人学习。如需删除,请见谅并联系本人。为了不分原创浏览量,本人自己踩此文一下。
在机器学习课程里提到了这个矩阵,那么这个矩阵是从哪里来,又是用来作什么用呢?先来看一下定义:
黑塞矩阵(Hessian Matrix),又译作海森矩阵、海瑟矩阵、海塞矩阵等,是一个多元函数的二阶偏导数构成的方阵,描述了函数的局部曲率。黑塞矩阵最早于19世纪由德国数学家Ludwig Otto Hesse提出,并以其名字命名。黑塞矩阵常用于牛顿法解决优化问题。
一般来说, 牛顿法主要应用在两个方面, 1, 求方程的根; 2, 最优化.
在机器学习里,可以考虑采用它来计算n值比较少的数据,在图像处理里,可以抽取图像特征,在金融里可以用来作量化分析。
图像处理可以看这个连接:
http://blog.csdn.net/jia20003/article/details/16874237
量化分析可以看这个:
http://ookiddy.iteye.com/blog/2204127
下面使用TensorFlow并且使用黑塞矩阵来求解下面的方程:
代码如下:
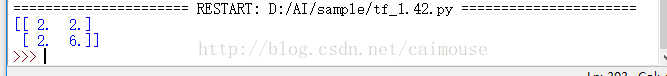
输出结果如下:
再来举多一个例子的源码,它就是用来计算量化分析,这个代码很值钱啊,如下:
输出结果如下:
====================== RESTART: D:/AI/sample/tf_1.43.py ======================
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: 0.000000
Iterations: 20
Function evaluations: 22
Gradient evaluations: 41
Hessian evaluations: 20
Result of minimizing Rosenbrock function via Newton-Conjugate-Gradient algorithm (Hessian):
fun: 1.47606641102778e-19
jac: array([ -3.62847530e-11, 2.68148992e-09, 1.16637362e-08,
4.81693414e-08, -2.76999090e-08])
message: 'Optimization terminated successfully.'
nfev: 22
nhev: 20
nit: 20
njev: 41
status: 0
success: True
x: array([ 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.])
>>>
可见hessian矩阵可以使用在很多地方了吧。
1. C++标准模板库从入门到精通
2.跟老菜鸟学C++
3. 跟老菜鸟学python
4. 在VC2015里学会使用tinyxml库
5. 在Windows下SVN的版本管理与实战
http://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/2579
6.Visual Studio 2015开发C++程序的基本使用
http://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/2570
可以看更多的网站:
http://blog.csdn.net/ubunfans/article/details/41520047
http://blog.csdn.net/baimafujinji/article/details/51167852
http://jacoxu.com/jacobian%E7%9F%A9%E9%98%B5%E5%92%8Chessian%E7%9F%A9%E9%98%B5/
http://www.cnblogs.com/logosxxw/p/4651413.html











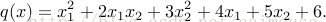













 1868
1868











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








