LibSVM是是台湾林智仁(Chih-Jen Lin)教授2001年开发的一套支持向量机的库,可以很方便的对数据做分类或回归。由于LibSVM程序小,运用灵活,输入参数少,并且是开源的,易于扩展,因此成为目前国内应用最多的SVM的库,同时sklearn.svm也是使用的该库。
网络上对于LibSVM源码的讲解有很多,但个人感觉绝大多数讲解的不够清晰,很多都是贴个理论公式图片再粘段代码就一带而过。并且网络上基本都是对SVC的讲解,SVR部分几乎没有提及(虽然SVR只是SVC的扩展)。因此本篇博文将系统地讲解LibSVM中SVR训练与预测部分的源码(想学习SVC的同学同样适用)。
python复现LIBSVM中SVR部分功能可参见 https://github.com/KunBB/LibSVM_SVR_python
文章目录
- LibSVM整体流程
- svm.h文件解析
- svm.cpp文件解析
- Kernel类
- 成员变量
- 成员函数
- Kernel(int l, svm_node \* const \* x, const svm_parameter& param);
- static double dot(const svm_node \*px, const svm_node \*py);
- static double k_function(const svm_node \*x, const svm_node \*y, const svm_parameter& param);
- virtual Qfloat *get_Q(int column, int len);
- virtual void swap_index(int i, int j);
- virtual double \*get_QD();
- double (Kernel::\*kernel_function)(int i, int j);
- Solver类
- 成员变量
- 成员函数
- double get_C(int i);
- void swap_index(int i, int j);
- void reconstruct_gradient();
- virtual void do_shrinking();
- virtual int select_working_set(int &i, int &j);
- void Solve(int l, const QMatrix& Q, const double \*p_, const schar \*y_, double \*alpha_, double Cp, double Cn, double eps, SolutionInfo\* si, int shrinking);
- virtual double calculate_rho();
- SVR_Q类
- static void solve_epsilon_svr(const svm_problem \*prob, const svm_parameter \*param, double \*alpha, Solver::SolutionInfo\* si)
- static decision_function svm_train_one(const svm_problem \*prob, const svm_parameter \*param, double Cp, double Cn)
- svm_model \*svm_train(const svm_problem \*prob, const svm_parameter \*param);
- double svm_predict_values(const svm_model \*model, const svm_node \*x, double\* dec_values)
- Reference:
LibSVM整体流程
train:
//根据svm_type的不同进行初始化
svm_train()
//根据svm_type的不同调用不同的分类回归训练函数
svm_train_one()
//针对epsilon-SVR这一类型进行模型参数初始化
solve_epsilon_svr()
//使用SMO算法求解对偶问题(二次优化问题)
Solver::Solve()
//每隔若干次迭代进行一次shrinking,对样本集进行缩减降低计算成本
Solver::do_shrinking()
//若满足停止条件则进行梯度重建并跳出循环
Solver::reconstruct_gradient()
//选择出当前最大违反对i,j
Solver::select_working_set()
//计算参数优化后的rho
Solver::caculate_rho()
//得到优化后的alpha和SolutionInfo对象si
//得到优化后的alpha和SolutionInfo对象si
//得到decision_function对象f
//得到svm_model对象model
predict
//根据svm_type的不同开辟dec_value空间
svm_predict()
//根据svm_type的不同调用k_function函数
svm_predict_values()
//根据kernel_type的不同计算k(i,j)
Kernel::k_function()
//得到k(x_train[i],x_test[j])
//得到预测值y_pre[j]
//得到预测值y_pre[j]
svm.h文件解析
svm_node
//存储一个样本(假设为样本i)的一个特征
struct svm_node{
int index; //样本i的特征索引值,最后一个为-1
double value; //样本i第index个特征的值,最后一个为NULL
};
如:x[i]={0.23,1.2,3.5,1.5}
则需使用五个svm_node来表示x[i],具体映射如下:
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | -1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| value | 0.23 | 1.2 | 3.5 | 1.5 | NULL |
svm_problem
//存储参加运算的所有样本数据(训练集)
struct svm_problem{
int l; //样本总数
double *y; //样本输出值(所属类别)
struct svm_node **x; //样本输入值
};
下图中最右边的长条格同上表,存储了三维数据。
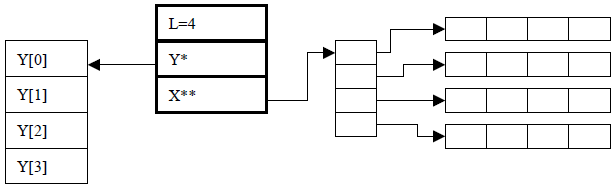
**svm_problem中的y与类Solver中的y并不完全一样!!!**对于一般SVC而言可以看出一样的,其值为-1与+1,对于多分类而言svm_problem.y[i]可以是1、2、3等,而多类计算其实是二分类的组合,因此在二分类中y[i]依然等于+1与-1.更特殊的,在SVR中,svm_problem的y[i]等于其目标值,如:11.234、56.24、5.23等,在计算时svm_problem.y[i]整合到了Solver.p[i]与Solver.p[i+svm_problem.l]中(具体的问题后续章节再详细解释),而在Solver.y[i]依然为+1和-1.
svm_parameter
//svm_type和svm_type可能取值
enum { C\_SVC, NU\_SVC, ONE\_CLASS, EPSILON\_SVR, NU\_SVR };/* svm_type */
enum { LINEAR, POLY, RBF, SIGMOID }; /* kernel_type */
//svm模型训练参数
struct svm_parameter
{
int svm_type;
int kernel_type;
int degree; /* for poly */
double gamma; /* for poly/rbf/sigmoid */
double coef0; /* for poly/sigmoid */
/* these are for training only */
double cache_size; /* in MB */
double eps; /* stopping criteria */
double C; /* for C_SVC, EPSILON_SVR and NU_SVR */
int nr_weight; /* for C_SVC */
int *weight_label; /* for C_SVC */
double* weight; /* for C_SVC */
double nu; /* for NU_SVC, ONE_CLASS, and NU_SVR */
double p; /* for EPSILON_SVR */
int shrinking; /* use the shrinking heuristics */
int probability; /* do probability estimates */
};
LibSVM中的核函数如下:
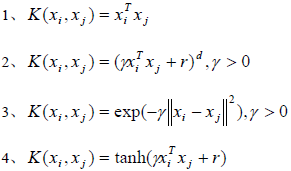
各参数解释如下:
| Parameter | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| degree | 2式中的d |
| gamma | 2,3,4式中的gamma |
| coef0 | 2,4式中的r |
| cache_size | 单位MB,训练所需内存,LibSVM2.5默认4M |
| eps | 停止条件需满足的最大误差值(文献[2]中式3.9) |
| C | 惩罚因子,越大模型过拟合越严重 |
| nr_weight | 权重的数目,目前在实例代码中只有两个值,一个是默认0,另外一个是svm_binary_svc_probability函数中使用数值2 |
| *weight_label | 权重,元素个数由nr_weight决定. |
| nu | NU_SVC,ONE_CLASS,NU_SVR中的nu |
| p | SVR中的间隔带epsilon |
| shrinking | 指明训练过程是否使用压缩 |
| probability | 指明是否做概率估计 |
svm_model
//保存训练后的模型参数
struct svm_model{
struct svm_parameter param; /* parameter */
int nr_class; /* number of classes, = 2 in regression/one class svm */
int l; /* total #SV */
struct svm_node **SV; /* SVs (SV[l]) */
double **sv_coef; /* coefficients for SVs in decision functions (sv_coef[k-1][l]) */
double *rho; /* constants in decision functions (rho[k*(k-1)/2]) */
double *probA; /* pariwise probability information */
double *probB;
int *sv_indices; /* sv_indices[0,...,nSV-1] are values in [1,...,num_traning_data] to indicate SVs in the training set */
/* for classification only */
int *label; /* label of each class (label[k]) */
int *nSV; /* number of SVs for each class (nSV[k]) */
/* nSV[0] + nSV[1] + ... + nSV[k-1] = l */
/* XXX */
int free_sv; /* 1 if svm_model is created by svm_load_model*/
/* 0 if svm_model is created by svm_train */
};
各参数解释如下:
| Parameter | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| param | 训练参数 |
| nr_class | 类别数 |
| l | 支持向量数 |
| **SV | 作为支持向量的样本集 |
| **sv_coef | 支持向量系数alpha |
| *rho | 判别函数中的b |
| *proA | 成对概率信息 |
| *proB | 成对概率信息 |
| *sv_indices | 记录支持向量在训练数据中的index |
| *label | 各类的标签 |
| *nSV | 各类的支持向量数 |
| free_SV | 若model由svm_load_model函数生成则为1,若为svm_train生成则为0 |
svm.cpp文件解析
下图为svm.cpp中的类继承和组合情况(实现表示继承关系,虚线表示组合关系):
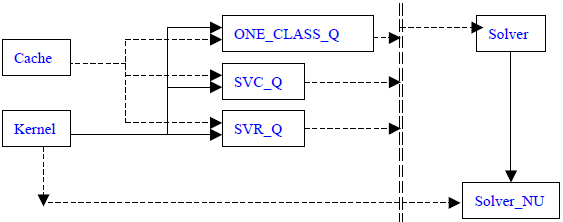
Cache类主要负责运算所涉及的内存的管理,包括申请、释放等。本篇博文主要讲解SVM求解过程,对于Cache类将不予解析。
Kernel类
class Kernel : public QMatrix {
public:
Kernel(int l, svm_node * const * x, const svm_parameter& param);
virtual ~Kernel();
static double k_function(const svm_node *x, const svm_node *y,
const svm_parameter& param);
virtual Qfloat *get_Q(int column, int len) const = 0;
virtual double *get_QD() const = 0;
virtual void swap_index(int i, int j) const // no so const...
{
swap(x[i], x[j]);
if (x_square) swap(x_square[i], x_square[j]);
}
protected:
double (Kernel::*kernel_function)(int i, int j) const;
private:
const svm_node **x;
double *x_square;
// svm_parameter
const int kernel_type;
const int degree;
const double gamma;
const double coef0;
static double dot(const svm_node *px, const svm_node *py);
double kernel_linear(int i, int j) const
{
return dot(x[i], x[j]);
}
double kernel_poly(int i, int j) const
{
return powi(gamma*dot(x[i], x[j]) + coef0, degree);
}
double kernel_rbf(int i, int j) const
{
return exp(-gamma * (x_square[i] + x_square[j] - 2 * dot(x[i], x[j])));
}
double kernel_sigmoid(int i, int j) const
{
return tanh(gamma*dot(x[i], x[j]) + coef0);
}
double kernel_precomputed(int i, int j) const
{
return x[i][(int)(x[j][0].value)].value;
}
};
成员变量
| Parameter | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| svm_node **x | 训练样本数据 |
| *x_square | x[i]^T*x[i],使用RBF核会用到 |
| kernel_type | 核函数类型 |
| degree | svm_parameter |
| gamma | svm_parameter |
| coef0 | svm_parameter |
成员函数
Kernel(int l, svm_node * const * x, const svm_parameter& param);
构造函数。初始化类中的部分常量、指定核函数、克隆样本数据。
Kernel::Kernel(int l, svm_node * const * x_, const svm_parameter& param)
:kernel_type(param.kernel_type), degree(param.degree),
gamma(param.gamma), coef0(param.coef0)
{
switch (kernel_type) //根据kernel_type的不同定义相应的函数kernel_function()
{
case LINEAR:
kernel_function = &Kernel::kernel_linear;
break;
case POLY:
kernel_function = &Kernel::kernel_poly;
break;
case RBF:
kernel_function = &Kernel::kernel_rbf;
break;
case SIGMOID:
kernel_function = &Kernel::kernel_sigmoid;
break;
case PRECOMPUTED:
kernel_function = &Kernel::kernel_precomputed;
break;
}
clone(x, x_, l);
if (kernel_type == RBF) //如果使用RBF 核函数,则计算x_sqare[i],即x[i]^T*x[i]
{
x_square = new double[l];
for (int i = 0; i<l; i++)
x_square[i] = dot(x[i], x[i]);
}
else
x_square = 0;
}
static double dot(const svm_node *px, const svm_node *py);
点乘函数,点乘两个样本数据,按svm_node 中index (一般为特征)进行运算,一般来说,index为1,2,…直到-1。返回点乘总和。例如:x1={1,2,3} ,x2={4,5,6}总和为sum=1*4+2*5+3*6;在svm_node[3]中存储index=-1时,停止计算。
double Kernel::dot(const svm_node *px, const svm_node *py)
{
double sum = 0;
while (px->index != -1 && py->index != -1)
{
if (px->index == py->index)
{
sum += px->value * py->value;
++px;
++py;
}
else
{
if (px->index > py->index)
++py;
else
++px;
}
}
return sum;
}
static double k_function(const svm_node *x, const svm_node *y, const svm_parameter& param);
功能类似kernel_function,不过kerel_function用于训练,k_function用于预测。
double Kernel::k_function(const svm_node *x, const svm_node *y,
const svm_parameter& param) //输入数据为两个数据样本,其中一个为训练样本一个为测试样本
{
switch (param.kernel_type)
{
case LINEAR:
return dot(x, y);
case POLY:
return powi(param.gamma*dot(x, y) + param.coef0, param.degree);
case RBF:
{
double sum = 0;
while (x->index != -1 && y->index != -1)
{
if (x->index == y->index)
{
double d = x->value - y->value;
sum += d * d;
++x;
++y;
}
else
{
if (x->index > y->index)
{
sum += y->value * y->value;
++y;
}
else
{
sum += x->value * x->value;
++x;
}
}
}
while (x->index != -1)
{
sum += x->value * x->value;
++x;
}
while (y->index != -1)
{
sum += y->value * y->value;
++y;
}
return exp(-param.gamma*sum);
}
case SIGMOID:
return tanh(param.gamma*dot(x, y) + param.coef0);
case PRECOMPUTED: //x: test (validation), y: SV
return x[(int)(y->value)].value;
default:
return 0; // Unreachable
}
}
其中RBF部分很有讲究。因为存储时,0值不保留。如果所有0值都保留,第一个while就可以都做完了;如果第一个while做不完,在x,y中任意一个出现index=-1,第一个while就停止,剩下的代码中两个while只会有一个工作,该循环直接把剩下的计算做完。
virtual Qfloat *get_Q(int column, int len);
纯虚函数,将来在子类中实现(如class SVR_Q),计算Q值。相当重要的函数。
virtual Qfloat *get_Q(int column, int len) const = 0;
virtual void swap_index(int i, int j);
虚函数,x[i]和x[j]中所存储指针的内容。如果x_square不为空,则交换相应的内容。
virtual void swap_index(int i, int j) const // no so const...
{
swap(x[i], x[j]);
if (x_square) swap(x_square[i], x_square[j]);
}
virtual double *get_QD();
纯虚函数,将来在子类中实现(如class SVR_Q),计算Q[i,i]值。
virtual Qfloat *get_Q(int column, int len) const = 0;
double (Kernel::*kernel_function)(int i, int j);
函数指针,根据相应的核函数类型,来决定所使用的函数。在计算矩阵Q时使用。
double (Kernel::*kernel_function)(int i, int j) const;
Solver类
class Solver {
public:
Solver() {};
virtual ~Solver() {};
struct SolutionInfo {
double obj;
double rho;
double upper_bound_p;
double upper_bound_n;
double r; // for Solver_NU
};
void Solve(int l, const QMatrix& Q, const double *p_, const schar *y_,
double *alpha_, double Cp, double Cn, double eps,
SolutionInfo* si, int shrinking);
protected:
int active_size;
schar *y;
double *G; // gradient of objective function
enum { LOWER_BOUND, UPPER_BOUND, FREE };
char *alpha_status; // LOWER_BOUND, UPPER_BOUND, FREE
double *alpha;
const QMatrix *Q;
const double *QD;
double eps;
double Cp, Cn;
double *p;
int *active_set;
double *G_bar; // gradient, if we treat free variables as 0
int l;
bool unshrink; // XXX
double get_C(int i)
{
return (y[i] > 0) ? Cp : Cn;
}
void update_alpha_status(int i)
{
if (alpha[i] >= get_C(i))
alpha_status[i] = UPPER_BOUND;
else if (alpha[i] <= 0)
alpha_status[i] = LOWER_BOUND;
else alpha_status[i] = FREE;
}
bool is_upper_bound(int i) { return alpha_status[i] == UPPER_BOUND; }
bool is_lower_bound(int i) { return alpha_status[i] == LOWER_BOUND; }
bool is_free(int i) { return alpha_status[i] == FREE; }
void swap_index(int i, int j);
void reconstruct_gradient();
virtual int select_working_set(int &i, int &j);
virtual double calculate_rho();
virtual void do_shrinking();
private:
bool be_shrunk(int i, double Gmax1, double Gmax2);
};
成员变量
结构体SolutionInfo为求解优化中的参数信息。
各参数解释如下:
| Parameter | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| SolutionInfo.obj | 求解优化过程中的目标函数值 |
| SolutionInfo.rho | 判别函数中的b |
| SolutionInfo.upper_bound_p | 对于不平衡数据集,该值对应惩罚因子Cp |
| SolutionInfo.upper_bound_n | 对于不平衡数据集,该值对应惩罚因子Cn |
| SolutionInfo.r | 用于Solver_NU |
| active_size | 计算时实际参加运算的样本数目,经过shrink处理后,该数目会小于全部样本总数。 |
| *y | 样本所属类别,该值只取+1/-1 。虽然可以处理多类,最终是用两类SVM 完成的。 |
| *G | 梯度G=Qα+P |
| *alpha_status | α[i]的状态,根据情况分为α[i]≤0,α[i]≥c和0<α[i]<\c,分别对应内部点(非SV),错分点(BSV)和支持向量(SV)。 |
| *alpha | α[i] |
| *Q | 对应公式中Q的某一列 |
| *QD | 对应公式中的Q[i][i] |
| eps | 停止条件的误差限 |
| Cp,Cn | 对应不平衡数据的惩罚因子,若不为不平数据或是对于SVR来说Cp=Cn=C |
| *p | 对应梯度公式中的p,即SVR中的间隔带epsilon |
| *active_set | active对应的index |
| *G_bar | sum(C*Q) |
| l | 数据样本个数 |
| unshrink | 是否被压缩 |
成员函数
double get_C(int i);
返回对应于样本的C。设置不同的Cp 和Cn 是为了处理数据的不平衡。见[1]中的Unbalanced data.对于一般样本数据Cp=Cn。
double get_C(int i)
{
return (y[i] > 0) ? Cp : Cn;
}
void swap_index(int i, int j);
完全交换样本i和样本j的内容,包括所申请的内存的地址。
void Solver::swap_index(int i, int j)
{
Q->swap_index(i, j);
swap(y[i], y[j]);
swap(G[i], G[j]);
swap(alpha_status[i], alpha_status[j]);
swap(alpha[i], alpha[j]);
swap(p[i], p[j]);
swap(active_set[i], active_set[j]);
swap(G_bar[i], G_bar[j]);
}
template <class T> static inline void swap(T& x, T& y) { T t = x; x = y; y = t; }
void reconstruct_gradient();
重新计算梯度。
void Solver::reconstruct_gradient()
{
// reconstruct inactive elements of G from G_bar and free variables
if (active_size == l) return;
int i, j;
int nr_free = 0;
for (j = active_size; j<l; j++)
G[j] = G_bar[j] + p[j];
for (j = 0; j<active_size; j++)
if (is_free(j))
nr_free++;
if (2 * nr_free < active_size)
info("\nWARNING: using -h 0 may be faster\n");
if (nr_free*l > 2 * active_size*(l - active_size))
{
for (i = active_size; i<l; i++)
{
const Qfloat *Q_i = Q->get_Q(i, active_size);
for (j = 0; j<active_size; j++)
if (is_free(j))
G[i] += alpha[j] * Q_i[j];
}
}
else
{
for (i = 0; i<active_size; i++)
if (is_free(i))
{
const Qfloat *Q_i = Q->get_Q(i, l);
double alpha_i = alpha[i];
for (j = active_size; j<l; j++)
G[j] += alpha_i * Q_i[j];
}
}
}
G_bar[i]在初始化时并未加入p[i],所以程序首先增加p[i]。Shrink后依然参加运算的样本位于active_size和l-1位置上。在0~active_size之间的alpha[i]如果在区间(0,c)上,才有必要更新相应的active_size和l-1位置上的样本的梯度。
virtual void do_shrinking();
对样本集做缩减。当0<α<C时(还有两种情况),程序认为该样本可以不参加下次迭代。(0<α<C时,为内部点)程序会减小active_size,为内部点增加位置。active_size表明了不可以参加下次迭代的样本的最小标签号,在active_size与l之间的元素都对分类没有贡献。
void Solver::do_shrinking()
{
int i;
double Gmax1 = -INF; // max { -y_i * grad(f)_i | i in I_up(\alpha) }
double Gmax2 = -INF; // max { y_i * grad(f)_i | i in I_low(\alpha) }
// find maximal violating pair first
for (i = 0; i<active_size; i++)
{
if (y[i] == +1)
{
if (!is_upper_bound(i)) // < C
{
if (-G[i] >= Gmax1)
Gmax1 = -G[i];
}
if (!is_lower_bound(i))
{
if (G[i] >= Gmax2)
Gmax2 = G[i];
}
}
else
{
if (!is_upper_bound(i))
{
if (-G[i] >= Gmax2)
Gmax2 = -G[i];
}
if (!is_lower_bound(i))
{
if (G[i] >= Gmax1)
Gmax1 = G[i];
}
}
}
//如果程序在缩减一次后没有达到结束条件,就重新构造梯度矢量,并再缩减一次。
if (unshrink == false && Gmax1 + Gmax2 <= eps * 10)
{
unshrink = true;
reconstruct_gradient();
active_size = l;
info("*");
}
//程序中active_size--是为了消除交换后的影响,使重新换来的样本也被检查一次。
for (i = 0; i<active_size; i++)
if (be_shrunk(i, Gmax1, Gmax2))
{
active_size--;
while (active_size > i)
{
if (!be_shrunk(active_size, Gmax1, Gmax2))
{
swap_index(i, active_size);
break;
}
active_size--;
}
}
}
virtual int select_working_set(int &i, int &j);
该函数求解出违反KKT条件最严重的目标对i与j。
我们先来了解一下working set的选择原理。参考文献[3]。
选择i
SVM的对偶问题为:
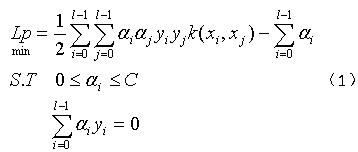
SVM收敛的充分必要条件(KKT条件)为:
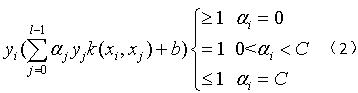
对(1)式求导可以得到:
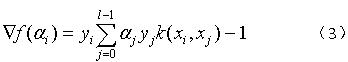
①yi=1,αi<C,由(2)和(3)可得:
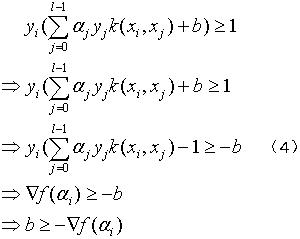
②yi=-1,αi>0,由(2)和(3)可得:
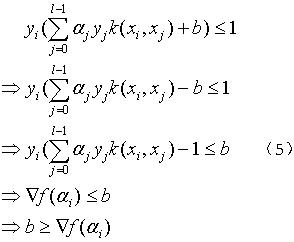
③yi=-1,αi<C,由(2)和(3)可得:
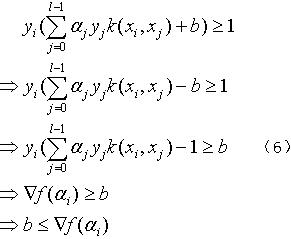
④yi=1,αi>0,由(2)和(3)可得:
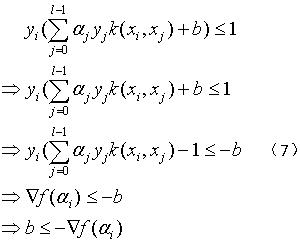
对式(4)、(5)、(6)、(7)进行约简得到式(8):
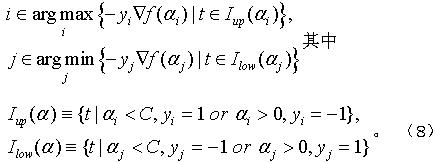
可以发现,(4)和(5)都是b大于某个数,(6)和(7)都是b小于某个数。因为b是个常量,那么根据上述条件,我们可以得到以下结论,在合理的αi和αj下,有:
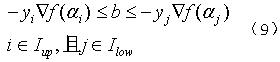
我们就是要从中挑选违反上述条件的αi和αj,来进行重新的迭代和更新,使得所有的αi和αj都满足上述条件。那么我们可以很容易得到违反条件为:
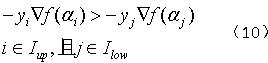
则根据式(8)中关于i的选择就可以明白select_working_set函数中关于选择i的部分了。
选择j
当yiyjK(i,j)为半正定矩阵时,当且仅当待优化乘子为“违反对”时,目标函数是严格递减的。LibSVM在做选择的时候,采用的是second order information方法。那么我们挑选出了i之后,剩下的任务就是挑选出既是“违反对”同时使目标函数值最小。补充一下:挑选了“违反对”,自然就使得目标函数自然递减了,那么我们挑选目标函数最小,自然使得迭代速度加快。这是我们希望看到的结果。
使用泰勒展开式:
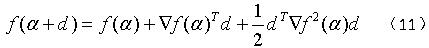
则优化问题变为:
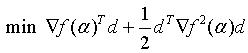
由约束条件可知:
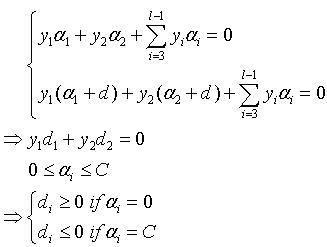
因为0≤α≤c,所以当α取到极值的时候,d的取值是有限制的,使得最终的α+d的值不会超出α取值范围。
则原优化问题可转换为下述优化问题:
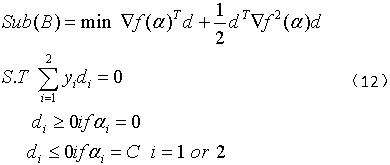
最小值为:
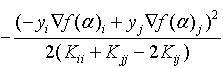
证明如下(可参考文献[3]的Theorem 3):

结论貌似挺复杂的,其实不然,仔细观察发现式(13)其实就是一个一元二次函数,对其求极值,得该函数的最小值。

下面我们来看一下代码:
int Solver::select_working_set(int &out_i, int &out_j)
{
// return i,j such that
// i: maximizes -y_i * grad(f)_i, i in I_up(\alpha)
// j: minimizes the decrease of obj value
// (if quadratic coefficeint <= 0, replace it with tau)
// -y_j*grad(f)_j < -y_i*grad(f)_i, j in I_low(\alpha)
double Gmax = -INF; //-yi*G(alphai)
double Gmax2 = -INF; //yj*G(alphaj)
int Gmax_idx = -1;
int Gmin_idx = -1;
double obj_diff_min = INF;
//寻找working set B中的i
for (int t = 0; t<active_size; t++)
if (y[t] == +1)
{
if (!is_upper_bound(t)) //对应于yi=1,alphai<c
if (-G[t] >= Gmax)
{
Gmax = -G[t]; //寻找最大的-yi*G(alphai),以使违反条件最严重
Gmax_idx = t;
}
}
else
{
if (!is_lower_bound(t)) //对应于yi=1,alphai>0
if (G[t] >= Gmax)
{
Gmax = G[t];
Gmax_idx = t;
}
}
int i = Gmax_idx; //得到i
const Qfloat *Q_i = NULL;
if (i != -1) // NULL Q_i not accessed: Gmax=-INF if i=-1
Q_i = Q->get_Q(i, active_size);
//寻找working set B中的j
for (int j = 0; j<active_size; j++)
{
if (y[j] == +1)
{
if (!is_lower_bound(j))
{
double grad_diff = Gmax + G[j]; //分子(-yi*Gi+yj*Gj)
if (G[j] >= Gmax2) //寻找最小的-yj*G(alphaj)
Gmax2 = G[j];
if (grad_diff > 0) //保证不满足KKT条件
{
double obj_diff;
double quad_coef = QD[i] + QD[j] - 2.0*y[i] * Q_i[j]; //分母(Kii+Kjj-2*Kij),注意Kij和Qij的关系(SVR_Q类中会讲)
if (quad_coef > 0)
obj_diff = -(grad_diff*grad_diff) / quad_coef;
else
obj_diff = -(grad_diff*grad_diff) / TAU; //当quad_coef小于0时令其等于一个很小很小的值。
if (obj_diff <= obj_diff_min)
{
Gmin_idx = j;
obj_diff_min = obj_diff;
}
}
}
}
else
{
if (!is_upper_bound(j))
{
double grad_diff = Gmax - G[j];
if (-G[j] >= Gmax2)
Gmax2 = -G[j];
if (grad_diff > 0)
{
double obj_diff;
double quad_coef = QD[i] + QD[j] + 2.0*y[i] * Q_i[j];
if (quad_coef > 0)
obj_diff = -(grad_diff*grad_diff) / quad_coef;
else
obj_diff = -(grad_diff*grad_diff) / TAU;
if (obj_diff <= obj_diff_min)
{
Gmin_idx = j;
obj_diff_min = obj_diff;
}
}
}
}
}
if (Gmax + Gmax2 < eps || Gmin_idx == -1) //达到停止条件或再没有需要优化的alpha,表示已经完全优化
return 1;
out_i = Gmax_idx;
out_j = Gmin_idx;
return 0;
}
void Solve(int l, const QMatrix& Q, const double *p_, const schar *y_, double *alpha_, double Cp, double Cn, double eps, SolutionInfo* si, int shrinking);
Solve函数用于求解更新alpha,下面讲解一下其求解原理,主要是SMO算法原理。这里主要还是以C-SVC为例,在后面讲解SVR_Q类时会解释如何将其扩展至回归分析。
SVM寻找超平面的公式为:
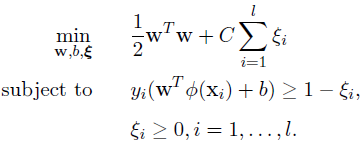
其对偶问题为:
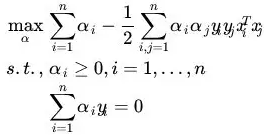
将其表示为矩阵形式可变换为:
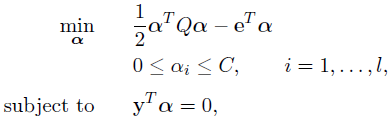
其中C>0为上界,e是数值全为1的行向量,Q是l*l的半正定矩阵,Qij=yi*yj*K(i,j),K(i,j)=φ(Xi)^T*φ(Xj)为核函数。
当然,这只是LIBSVM中的C-SVC的目标公式,LIBSVM采用的是更加通用的目标公式:
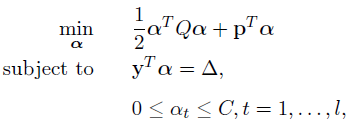
其中p是长度为l的行向量,△为常数。
其求导为:
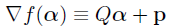
于是令aij = Kii+Kjj-2*Kij,假设选定的working set B为i和j,将其带入上式。(见文献[2]的Algorithm 1)
当aij>0时得:

当aij≤0时,约束同上式,令:
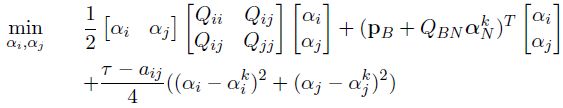
上式加的一项看似复杂,其实就是函数select_working_set中写的,当aij小于0时令其等于一个很小很小的值。
工作集i,j的选择
参见select_working_set函数的讲解。
αi,αj的更新
参考文献[2]的“5 Unbalanced Data”。
令:
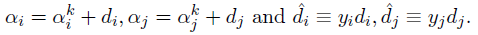
则问题:
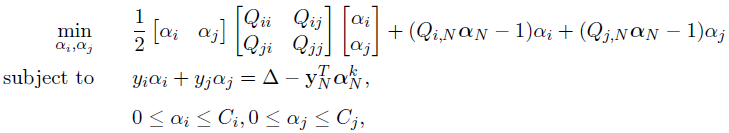
可转化为问题:

进而求解出di,dj可以得到更新后的α,即:
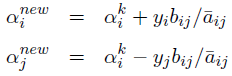
其中:
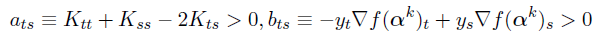
以不考虑非均衡样本为例(即Cp=Cn)。
当yi≠yj时:

当yi=yj时:

梯度G的更新
G[α(k)] = Q[α(k)] + p
G[α(k+1)] = Q[α(k+1)] + p
则:
G[α(k+1)] = G[α(k)] + Q[α(k+1)-α(k)]
G_bar的更新
G_bar[i] = {C * sum(Q[i,j]) while α[j]=C} i = 1,2,3,… l
因此,若α更新前后状态(alpha_status)不变,如都为C或都小于C,则G_bar不变。
否则:
①迭代前不为C,迭代后为C,则:
G_bar(k+1)[i] = {C * sum(Q[i,j]) while α[j]=C}
②迭代前为C,迭代后不为C,则:
G_bar(k+1)[i] = G_bar(k)[i] - {C * sum(Q[i,j]) while α[j]=C}
下面我们开始看代码。
void Solver::Solve(int l, const QMatrix& Q, const double *p_, const schar *y_,
double *alpha_, double Cp, double Cn, double eps,
SolutionInfo* si, int shrinking)
{
this->l = l;
this->Q = &Q;
QD = Q.get_QD();
clone(p, p_, l);
clone(y, y_, l);
clone(alpha, alpha_, l);
this->Cp = Cp;
this->Cn = Cn;
this->eps = eps;
unshrink = false;
// initialize alpha_status
{
alpha_status = new char[l];
for (int i = 0; i<l; i++)
update_alpha_status(i);
}
// initialize active set (for shrinking)
{
active_set = new int[l];
for (int i = 0; i<l; i++)
active_set[i] = i;
active_size = l;
}
// initialize gradient,根据梯度定义公式进行初始化
{
G = new double[l];
G_bar = new double[l];
int i;
for (i = 0; i<l; i++)
{
G[i] = p[i];
G_bar[i] = 0;
}
for (i = 0; i<l; i++)
if (!is_lower_bound(i))
{
const Qfloat *Q_i = Q.get_Q(i, l);
double alpha_i = alpha[i];
int j;
for (j = 0; j<l; j++)
G[j] += alpha_i * Q_i[j];
if (is_upper_bound(i))
for (j = 0; j<l; j++)
G_bar[j] += get_C(i) * Q_i[j];
}
}
// optimization step
int iter = 0;
int max_iter = max(10000000, l>INT_MAX / 100 ? INT_MAX : 100 * l);
int counter = min(l, 1000) + 1;
while (iter < max_iter)
{
// show progress and do shrinking
if (--counter == 0)
{
counter = min(l, 1000);
if (shrinking) do_shrinking();
info("do shrinking.\n");
}
int i, j;
if (select_working_set(i, j) != 0)
{
// reconstruct the whole gradient
reconstruct_gradient();
// reset active set size and check
active_size = l;
info("reconstruct G*\n");
if (select_working_set(i, j) != 0) {
info("======break======");
break;
}
else
counter = 1; // do shrinking next iteration
}
++iter;
// update alpha[i] and alpha[j], handle bounds carefully
const Qfloat *Q_i = Q.get_Q(i, active_size);
const Qfloat *Q_j = Q.get_Q(j, active_size);
double C_i = get_C(i);
double C_j = get_C(j);
double old_alpha_i = alpha[i];
double old_alpha_j = alpha[j];
if (y[i] != y[j]) //# yi,yj异号
{
double quad_coef = QD[i] + QD[j] + 2 * Q_i[j]; //最后一个为+号因为Qij为kij*y[i]*y[j]
if (quad_coef <= 0)
quad_coef = TAU;
double delta = (-G[i] - G[j]) / quad_coef; //alpha改变量
double diff = alpha[i] - alpha[j]; //根据此项判断alpha(i)-alpha(j)=constant与约束框(0~c)的交点
alpha[i] += delta;
alpha[j] += delta;
if (diff > 0)
{
if (alpha[j] < 0)
{
alpha[j] = 0;
alpha[i] = diff;
}
}
else
{
if (alpha[i] < 0)
{
alpha[i] = 0;
alpha[j] = -diff;
}
}
if (diff > C_i - C_j)
{
if (alpha[i] > C_i)
{
alpha[i] = C_i;
alpha[j] = C_i - diff;
}
}
else
{
if (alpha[j] > C_j)
{
alpha[j] = C_j;
alpha[i] = C_j + diff;
}
}
}
else
{
double quad_coef = QD[i] + QD[j] - 2 * Q_i[j];
if (quad_coef <= 0)
quad_coef = TAU;
double delta = (G[i] - G[j]) / quad_coef;
double sum = alpha[i] + alpha[j];
alpha[i] -= delta;
alpha[j] += delta;
if (sum > C_i)
{
if (alpha[i] > C_i)
{
alpha[i] = C_i;
alpha[j] = sum - C_i;
}
}
else
{
if (alpha[j] < 0)
{
alpha[j] = 0;
alpha[i] = sum;
}
}
if (sum > C_j)
{
if (alpha[j] > C_j)
{
alpha[j] = C_j;
alpha[i] = sum - C_j;
}
}
else
{
if (alpha[i] < 0)
{
alpha[i] = 0;
alpha[j] = sum;
}
}
}
// update G
double delta_alpha_i = alpha[i] - old_alpha_i;
double delta_alpha_j = alpha[j] - old_alpha_j;
for (int k = 0; k<active_size; k++)
{
G[k] += Q_i[k] * delta_alpha_i + Q_j[k] * delta_alpha_j;
}
// update alpha_status and G_bar
{
bool ui = is_upper_bound(i);
bool uj = is_upper_bound(j);
update_alpha_status(i);
update_alpha_status(j);
int k;
if (ui != is_upper_bound(i))
{
Q_i = Q.get_Q(i, l);
if (ui)
for (k = 0; k<l; k++)
G_bar[k] -= C_i * Q_i[k];
else
for (k = 0; k<l; k++)
G_bar[k] += C_i * Q_i[k];
}
if (uj != is_upper_bound(j))
{
Q_j = Q.get_Q(j, l);
if (uj)
for (k = 0; k<l; k++)
G_bar[k] -= C_j * Q_j[k];
else
for (k = 0; k<l; k++)
G_bar[k] += C_j * Q_j[k];
}
}
printf("i:%d, j:%d, alpha_i:%f, alpha_j:%f\n", i, j, alpha[i], alpha[j]);
}
if (iter >= max_iter)
{
if (active_size < l)
{
// reconstruct the whole gradient to calculate objective value
reconstruct_gradient();
active_size = l;
info("*");
}
fprintf(stderr, "\nWARNING: reaching max number of iterations\n");
}
// calculate rho
si->rho = calculate_rho();
// calculate objective value
{
double v = 0;
int i;
for (i = 0; i<l; i++)
v += alpha[i] * (G[i] + p[i]);
si->obj = v / 2; //目标值为(alpha^T*Q*alpha + p^T*alpha)
}
// put back the solution
{
for (int i = 0; i<l; i++)
alpha_[active_set[i]] = alpha[i];
}
// juggle everything back
/*{
for(int i=0;i<l;i++)
while(active_set[i] != i)
swap_index(i,active_set[i]);
// or Q.swap_index(i,active_set[i]);
}*/
si->upper_bound_p = Cp;
si->upper_bound_n = Cn;
info("\noptimization finished, #iter = %d\n", iter);
/*for (int g = 0; g < l/2; g++) {
printf("alpha_%d:%f\n", g, (alpha[g]-alpha[g+l/2]));
}*/
delete[] p;
delete[] y;
delete[] alpha;
delete[] alpha_status;
delete[] active_set;
delete[] G;
delete[] G_bar;
}
virtual double calculate_rho();
该函数用于计算判别函数中的b(rho为b的相反数),参考文献[2]的3.6。
这里仅写出结果:
当yi=1时:
假设0<αi<C,则r1 = G[α](i)
为避免出现数值错误,一般将其写成平均值:
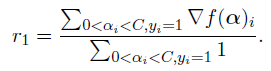
如果没有这样的αi,则r1必须满足:
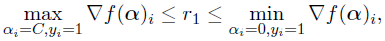
此时将ri取为范围中点。
当yi=-1时,计算过程类似,得到r2。
得到r1、r2后,通过计算得到:

double Solver::calculate_rho()
{
double r;
int nr_free = 0;
double ub = INF, lb = -INF, sum_free = 0;
for (int i = 0; i<active_size; i++)
{
double yG = y[i] * G[i];
if (is_upper_bound(i))
{
if (y[i] == -1)
ub = min(ub, yG);
else
lb = max(lb, yG);
}
else if (is_lower_bound(i))
{
if (y[i] == +1)
ub = min(ub, yG);
else
lb = max(lb, yG);
}
else
{
++nr_free;
sum_free += yG;
}
}
if (nr_free>0)
r = sum_free / nr_free;
else
r = (ub + lb) / 2;
return r;
}
SVR_Q类
class SVR_Q : public Kernel
{
public:
SVR_Q(const svm_problem& prob, const svm_parameter& param)
:Kernel(prob.l, prob.x, param)
{
l = prob.l;
cache = new Cache(l, (long int)(param.cache_size*(1 << 20)));
QD = new double[2 * l];
sign = new schar[2 * l];
index = new int[2 * l];
for (int k = 0; k<l; k++)
{
sign[k] = 1;
sign[k + l] = -1;
index[k] = k;
index[k + l] = k;
QD[k] = (this->*kernel_function)(k, k);
QD[k + l] = QD[k];
}
buffer[0] = new Qfloat[2 * l];
buffer[1] = new Qfloat[2 * l];
next_buffer = 0;
}
void swap_index(int i, int j) const
{
swap(sign[i], sign[j]);
swap(index[i], index[j]);
swap(QD[i], QD[j]);
}
Qfloat *get_Q(int i, int len) const
{
Qfloat *data;
int j, real_i = index[i];
if (cache->get_data(real_i, &data, l) < l)
{
for (j = 0; j<l; j++)
data[j] = (Qfloat)(this->*kernel_function)(real_i, j);
}
// reorder and copy
Qfloat *buf = buffer[next_buffer];
next_buffer = 1 - next_buffer;
schar si = sign[i];
for (j = 0; j<len; j++)
buf[j] = (Qfloat)si * (Qfloat)sign[j] * data[index[j]];
return buf;
}
double *get_QD() const
{
return QD;
}
~SVR_Q()
{
delete cache;
delete[] sign;
delete[] index;
delete[] buffer[0];
delete[] buffer[1];
delete[] QD;
}
private:
int l;
Cache *cache;
schar *sign;
int *index;
mutable int next_buffer;
Qfloat *buffer[2];
double *QD;
};
成员变量
主要参数解释如下:
| Parameter | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| *sign | 同SVC_Q中的y,即为公式中的y。sign[i]=1,sign[i+l]=-1,i=1,2,3,…,l |
成员函数
SVR_Q(const svm_problem& prob, const svm_parameter& param):Kernel(prob.l, prob.x, param);
初始化有关SVR的计算参数。与SVC不同的是优化公式中的y并不是SVR样本数据的目标值,优化公式中的l为两倍的SVR数据样本数量,详见solve_epsilon_svr函数解析。
SVR_Q(const svm_problem& prob, const svm_parameter& param)
:Kernel(prob.l, prob.x, param)
{
l = prob.l; //l为样本数据的数量
cache = new Cache(l, (long int)(param.cache_size*(1 << 20)));
//对于SVR而言需要开辟2*l的空间
QD = new double[2 * l];
sign = new schar[2 * l];
index = new int[2 * l];
for (int k = 0; k<l; k++)
{
//sign[i]=1,sign[i+l]=-1,i=1,2,3,...,l
sign[k] = 1;
sign[k + l] = -1;
index[k] = k;
index[k + l] = k;
QD[k] = (this->*kernel_function)(k, k);
QD[k + l] = QD[k];
}
buffer[0] = new Qfloat[2 * l];
buffer[1] = new Qfloat[2 * l];
next_buffer = 0;
}
Qfloat *get_Q(int i, int len) const;
计算SVR公式中所使用的Q[i],此处为第i列,不过一般而言Q[i,j]=Q[j,i]。
Qfloat *get_Q(int i, int len) const
{
Qfloat *data;
int j, real_i = index[i];
if (cache->get_data(real_i, &data, l) < l)
{
for (j = 0; j<l; j++)
data[j] = (Qfloat)(this->*kernel_function)(real_i, j); //计算得到K[i,j]
}
// reorder and copy
Qfloat *buf = buffer[next_buffer];
next_buffer = 1 - next_buffer;
schar si = sign[i];
for (j = 0; j<len; j++)
buf[j] = (Qfloat)si * (Qfloat)sign[j] * data[index[j]]; //为了与Solver类中的公式相匹配,此处定义Q[i,j]=sign[i]*sign[j]*K[i,j]
return buf;
}
static void solve_epsilon_svr(const svm_problem *prob, const svm_parameter *param, double *alpha, Solver::SolutionInfo* si)
该函数用于计算优化公式中的p,并定义Solver中的y与α,调用Solver类。
epsilon-SVR原始公式为:
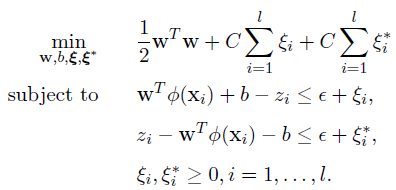
其对偶式为:
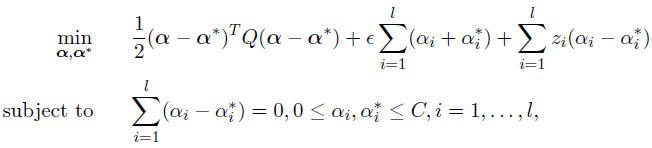
其中:
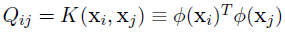
决策函数为:
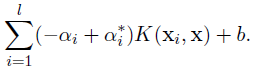
将其化为矩阵形式:
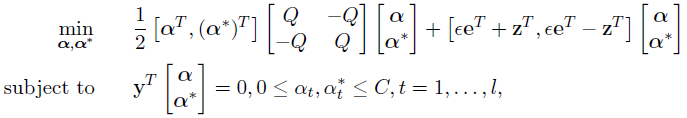
其中y为2l*1的矩阵,yt=1,t=1,…,l; yt=-1,t=l+1,…,2l.
将上式与前述的通用目标公式相比较,记上标t为通用公式的参数,则可知:
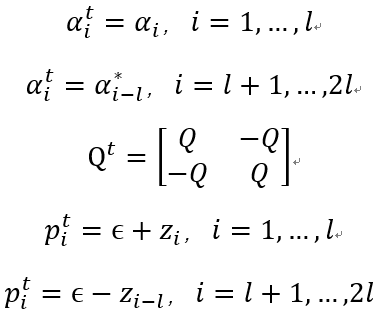
static void solve_epsilon_svr(
const svm_problem *prob, const svm_parameter *param,
double *alpha, Solver::SolutionInfo* si)
{
int l = prob->l;
double *alpha2 = new double[2 * l];
double *linear_term = new double[2 * l];
schar *y = new schar[2 * l]; //新定义了y值,对应Solver的y
int i;
for (i = 0; i<l; i++)
{
alpha2[i] = 0;
linear_term[i] = param->p - prob->y[i]; //epsilon*e-z,epsilon为间隔带,e为全为1的行向量,z为样本数据的目标值
y[i] = 1;
alpha2[i + l] = 0;
linear_term[i + l] = param->p + prob->y[i]; //epsilon*e+z
y[i + l] = -1;
}
Solver s;
s.Solve(2 * l, SVR_Q(*prob, *param), linear_term, y,
alpha2, param->C, param->C, param->eps, si, param->shrinking);
double sum_alpha = 0;
for (i = 0; i<l; i++)
{
alpha[i] = alpha2[i] - alpha2[i + l]; //将alpha[i]-alpha[i+1]得到数据样本x前的最终系数
sum_alpha += fabs(alpha[i]);
}
info("nu = %f\n", sum_alpha / (param->C*l));
delete[] alpha2;
delete[] linear_term;
delete[] y;
}
static decision_function svm_train_one(const svm_problem *prob, const svm_parameter *param, double Cp, double Cn)
根据kernel_type的不同调用不同的求解函数,并计算支持向量的个数与处于边界的支持向量个数。
static decision_function svm_train_one(
const svm_problem *prob, const svm_parameter *param,
double Cp, double Cn)
{
double *alpha = Malloc(double, prob->l);
Solver::SolutionInfo si;
switch (param->svm_type)
{
case C_SVC:
solve_c_svc(prob, param, alpha, &si, Cp, Cn);
break;
case NU_SVC:
solve_nu_svc(prob, param, alpha, &si);
break;
case ONE_CLASS:
solve_one_class(prob, param, alpha, &si);
break;
case EPSILON_SVR:
solve_epsilon_svr(prob, param, alpha, &si);
break;
case NU_SVR:
solve_nu_svr(prob, param, alpha, &si);
break;
}
info("obj = %f, rho = %f\n", si.obj, si.rho);
// output SVs
int nSV = 0;
int nBSV = 0;
for (int i = 0; i<prob->l; i++)
{
if (fabs(alpha[i]) > 0)
{
++nSV;
if (prob->y[i] > 0)
{
if (fabs(alpha[i]) >= si.upper_bound_p)
++nBSV;
}
else
{
if (fabs(alpha[i]) >= si.upper_bound_n)
++nBSV;
}
}
}
info("nSV = %d, nBSV = %d\n", nSV, nBSV);
decision_function f;
f.alpha = alpha;
f.rho = si.rho;
return f;
}
svm_model *svm_train(const svm_problem *prob, const svm_parameter *param);
根据不同svm_type开辟不同空间,最后返回训练好的svm model。
svm_model *svm_train(const svm_problem *prob, const svm_parameter *param)
{
svm_model *model = Malloc(svm_model, 1);
model->param = *param;
model->free_sv = 0; // XXX
if (param->svm_type == ONE_CLASS ||
param->svm_type == EPSILON_SVR ||
param->svm_type == NU_SVR)
{
// regression or one-class-svm
model->nr_class = 2;
model->label = NULL;
model->nSV = NULL;
model->probA = NULL; model->probB = NULL;
model->sv_coef = Malloc(double *, 1);
/*if (param->probability &&
(param->svm_type == EPSILON_SVR ||
param->svm_type == NU_SVR))
{
model->probA = Malloc(double, 1);
model->probA[0] = svm_svr_probability(prob, param);
}*/
decision_function f = svm_train_one(prob, param, 0, 0);
model->rho = Malloc(double, 1);
model->rho[0] = f.rho;
int nSV = 0;
int i;
for (i = 0; i<prob->l; i++)
if (fabs(f.alpha[i]) > 0) ++nSV;
model->l = nSV;
model->SV = Malloc(svm_node *, nSV);
model->sv_coef[0] = Malloc(double, nSV);
model->sv_indices = Malloc(int, nSV);
int j = 0;
for (i = 0; i<prob->l; i++)
if (fabs(f.alpha[i]) > 0)
{
model->SV[j] = prob->x[i];
model->sv_coef[0][j] = f.alpha[i];
model->sv_indices[j] = i + 1;
++j;
}
free(f.alpha);
}
else
{
// classification
int l = prob->l;
int nr_class;
int *label = NULL;
int *start = NULL;
int *count = NULL;
int *perm = Malloc(int, l);
// group training data of the same class
svm_group_classes(prob, &nr_class, &label, &start, &count, perm);
if (nr_class == 1)
info("WARNING: training data in only one class. See README for details.\n");
svm_node **x = Malloc(svm_node *, l);
int i;
for (i = 0; i<l; i++)
x[i] = prob->x[perm[i]];
// calculate weighted C
double *weighted_C = Malloc(double, nr_class);
for (i = 0; i<nr_class; i++)
weighted_C[i] = param->C;
for (i = 0; i<param->nr_weight; i++)
{
int j;
for (j = 0; j<nr_class; j++)
if (param->weight_label[i] == label[j])
break;
if (j == nr_class)
fprintf(stderr, "WARNING: class label %d specified in weight is not found\n", param->weight_label[i]);
else
weighted_C[j] *= param->weight[i];
}
// train k*(k-1)/2 models
bool *nonzero = Malloc(bool, l);
for (i = 0; i<l; i++)
nonzero[i] = false;
decision_function *f = Malloc(decision_function, nr_class*(nr_class - 1) / 2);
double *probA = NULL, *probB = NULL;
if (param->probability)
{
probA = Malloc(double, nr_class*(nr_class - 1) / 2);
probB = Malloc(double, nr_class*(nr_class - 1) / 2);
}
int p = 0;
for (i = 0; i<nr_class; i++)
for (int j = i + 1; j<nr_class; j++)
{
svm_problem sub_prob;
int si = start[i], sj = start[j];
int ci = count[i], cj = count[j];
sub_prob.l = ci + cj;
sub_prob.x = Malloc(svm_node *, sub_prob.l);
sub_prob.y = Malloc(double, sub_prob.l);
int k;
for (k = 0; k<ci; k++)
{
sub_prob.x[k] = x[si + k];
sub_prob.y[k] = +1;
}
for (k = 0; k<cj; k++)
{
sub_prob.x[ci + k] = x[sj + k];
sub_prob.y[ci + k] = -1;
}
if (param->probability)
svm_binary_svc_probability(&sub_prob, param, weighted_C[i], weighted_C[j], probA[p], probB[p]);
f[p] = svm_train_one(&sub_prob, param, weighted_C[i], weighted_C[j]);
for (k = 0; k<ci; k++)
if (!nonzero[si + k] && fabs(f[p].alpha[k]) > 0)
nonzero[si + k] = true;
for (k = 0; k<cj; k++)
if (!nonzero[sj + k] && fabs(f[p].alpha[ci + k]) > 0)
nonzero[sj + k] = true;
free(sub_prob.x);
free(sub_prob.y);
++p;
}
// build output
model->nr_class = nr_class;
model->label = Malloc(int, nr_class);
for (i = 0; i<nr_class; i++)
model->label[i] = label[i];
model->rho = Malloc(double, nr_class*(nr_class - 1) / 2);
for (i = 0; i<nr_class*(nr_class - 1) / 2; i++)
model->rho[i] = f[i].rho;
if (param->probability)
{
model->probA = Malloc(double, nr_class*(nr_class - 1) / 2);
model->probB = Malloc(double, nr_class*(nr_class - 1) / 2);
for (i = 0; i<nr_class*(nr_class - 1) / 2; i++)
{
model->probA[i] = probA[i];
model->probB[i] = probB[i];
}
}
else
{
model->probA = NULL;
model->probB = NULL;
}
int total_sv = 0;
int *nz_count = Malloc(int, nr_class);
model->nSV = Malloc(int, nr_class);
for (i = 0; i<nr_class; i++)
{
int nSV = 0;
for (int j = 0; j<count[i]; j++)
if (nonzero[start[i] + j])
{
++nSV;
++total_sv;
}
model->nSV[i] = nSV;
nz_count[i] = nSV;
}
info("Total nSV = %d\n", total_sv);
model->l = total_sv;
model->SV = Malloc(svm_node *, total_sv);
model->sv_indices = Malloc(int, total_sv);
p = 0;
for (i = 0; i<l; i++)
if (nonzero[i])
{
model->SV[p] = x[i];
model->sv_indices[p++] = perm[i] + 1;
}
int *nz_start = Malloc(int, nr_class);
nz_start[0] = 0;
for (i = 1; i<nr_class; i++)
nz_start[i] = nz_start[i - 1] + nz_count[i - 1];
model->sv_coef = Malloc(double *, nr_class - 1);
for (i = 0; i<nr_class - 1; i++)
model->sv_coef[i] = Malloc(double, total_sv);
p = 0;
for (i = 0; i<nr_class; i++)
for (int j = i + 1; j<nr_class; j++)
{
// classifier (i,j): coefficients with
// i are in sv_coef[j-1][nz_start[i]...],
// j are in sv_coef[i][nz_start[j]...]
int si = start[i];
int sj = start[j];
int ci = count[i];
int cj = count[j];
int q = nz_start[i];
int k;
for (k = 0; k<ci; k++)
if (nonzero[si + k])
model->sv_coef[j - 1][q++] = f[p].alpha[k];
q = nz_start[j];
for (k = 0; k<cj; k++)
if (nonzero[sj + k])
model->sv_coef[i][q++] = f[p].alpha[ci + k];
++p;
}
free(label);
free(probA);
free(probB);
free(count);
free(perm);
free(start);
free(x);
free(weighted_C);
free(nonzero);
for (i = 0; i<nr_class*(nr_class - 1) / 2; i++)
free(f[i].alpha);
free(f);
free(nz_count);
free(nz_start);
}
return model;
}
double svm_predict_values(const svm_model *model, const svm_node *x, double* dec_values)
该函数用于预测单个测试样本数据,因此对于一组测试样本需要调用n次。
double svm_predict_values(const svm_model *model, const svm_node *x, double* dec_values)
{
int i;
if (model->param.svm_type == ONE_CLASS ||
model->param.svm_type == EPSILON_SVR ||
model->param.svm_type == NU_SVR)
{
double *sv_coef = model->sv_coef[0];
double sum = 0;
for (i = 0; i<model->l; i++)
sum += sv_coef[i] * Kernel::k_function(x, model->SV[i], model->param); //对应决策公式的前半部分,即αi*K(xi,x)
sum -= model->rho[0]; //加上决策函数的常数项
*dec_values = sum;
if (model->param.svm_type == ONE_CLASS)
return (sum>0) ? 1 : -1;
else
return sum;
}
else
{
int nr_class = model->nr_class;
int l = model->l;
double *kvalue = Malloc(double, l);
for (i = 0; i<l; i++)
kvalue[i] = Kernel::k_function(x, model->SV[i], model->param);
int *start = Malloc(int, nr_class);
start[0] = 0;
for (i = 1; i<nr_class; i++)
start[i] = start[i - 1] + model->nSV[i - 1];
int *vote = Malloc(int, nr_class);
for (i = 0; i<nr_class; i++)
vote[i] = 0;
int p = 0;
for (i = 0; i<nr_class; i++)
for (int j = i + 1; j<nr_class; j++)
{
double sum = 0;
int si = start[i];
int sj = start[j];
int ci = model->nSV[i];
int cj = model->nSV[j];
int k;
double *coef1 = model->sv_coef[j - 1];
double *coef2 = model->sv_coef[i];
for (k = 0; k<ci; k++)
sum += coef1[si + k] * kvalue[si + k];
for (k = 0; k<cj; k++)
sum += coef2[sj + k] * kvalue[sj + k];
sum -= model->rho[p];
dec_values[p] = sum;
if (dec_values[p] > 0)
++vote[i];
else
++vote[j];
p++;
}
int vote_max_idx = 0;
for (i = 1; i<nr_class; i++)
if (vote[i] > vote[vote_max_idx])
vote_max_idx = i;
free(kvalue);
free(start);
free(vote);
return model->label[vote_max_idx];
}
}
Reference:
[1] Smola A J, Schölkopf B. A tutorial on support vector regression[J]. Statistics & Computing, 2004, volume 14(3):199-222(24).
[2] Chang C C, Lin C J. LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines[M]. ACM, 2011.
[3] Fan R E, Chen P H, Lin C J, et al. Working Set Selection Using Second Order Information for Training Support Vector Machines[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2005, 6(4):1889-1918.
[4] Svm O F. Sequential Minimal Optimization for SVM[J]. 2007.
[5] LibSVM中select_working_set函数:http://blog.csdn.net/le_zhou/article/details/40505465
[6] libsvm最新源代码(版本3.21)理解解析(三):http://blog.csdn.net/xiaoqiangqiangjie/article/details/53886907
[7] LibSVM源码剖析(java版):http://makaidong.com/bentuwuying/21760_40631.html
[8] LibSVM-2.6 程序代码注释,上交
本博客与https://xuyunkun.com同步更新
























 3243
3243

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








