Introduction
Epigenetics(表观遗传学)
在核苷酸序列不发生改变的情况下,基因表达的可遗传的变化的一门遗传学分支学科。
方向:
1、组蛋白修饰(accessibility/compaction可接近性和紧束状态)
2、甲基化![]()
甲基化种类: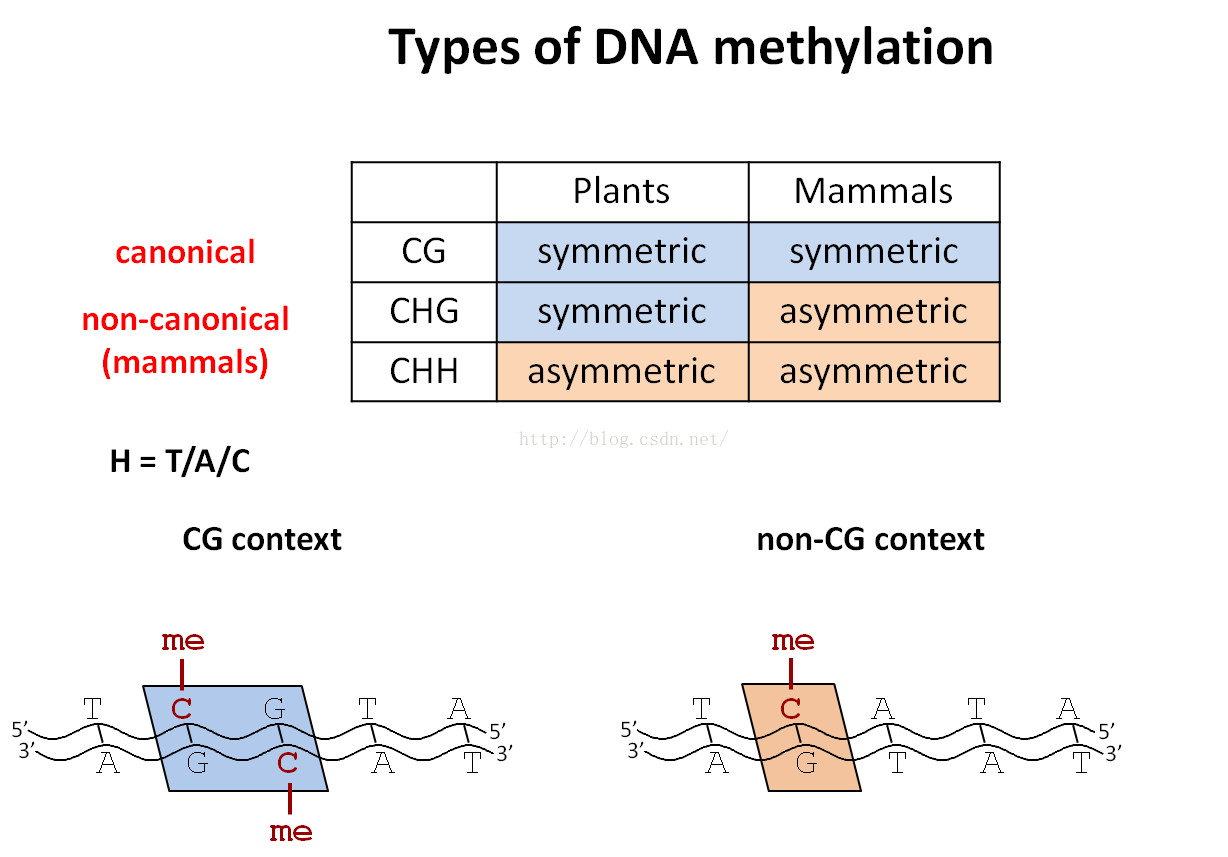

维持性甲基化作用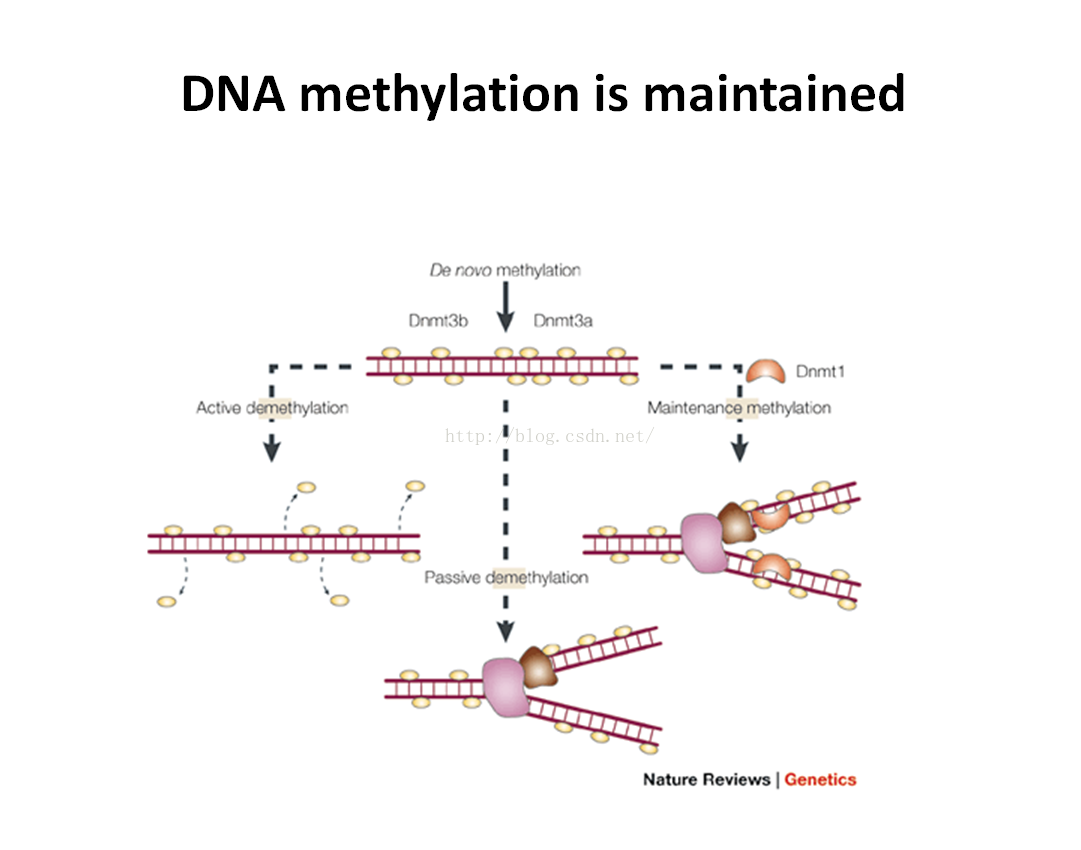

DNA甲基化可以调节
1、沉默基因表达
2、重复序列可以保持基因组稳定性
错误的甲基化会导致:
1、早期发育错误
2、表观遗传综合征
3、癌症
等位基因的不同表达:起因是 CGI(CpG island)的DNA甲基化
(PS:CpG表示核苷酸对,其中G在DNA链中紧随C后。CpG对很少出现在人类基因中。然而,在许多基因的启动子(promotor)或转录起始位点(transcription start site,TSS)区域周围,甲基化经常被抑制。这些区域包含浓度相对较高的CpG对,与染色体一起称作CpG岛,其长度通常在几百到几千核苷酸的长度内变化。)
而且DNA甲基化会在DNA重组的时候重置。
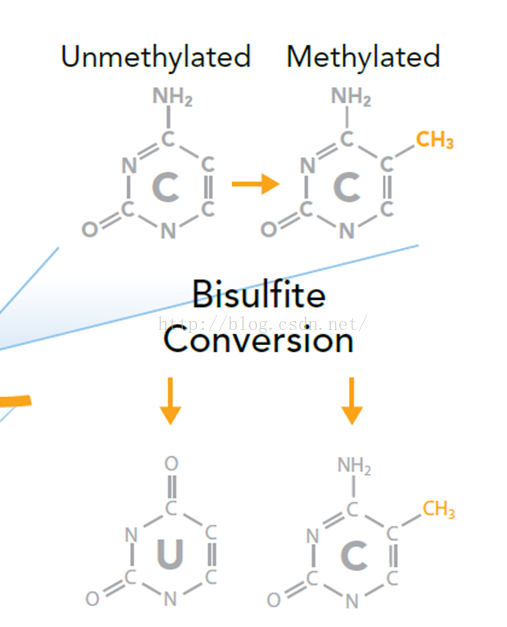
通过Bisulfite-Sequencing测量DNA甲基化程度
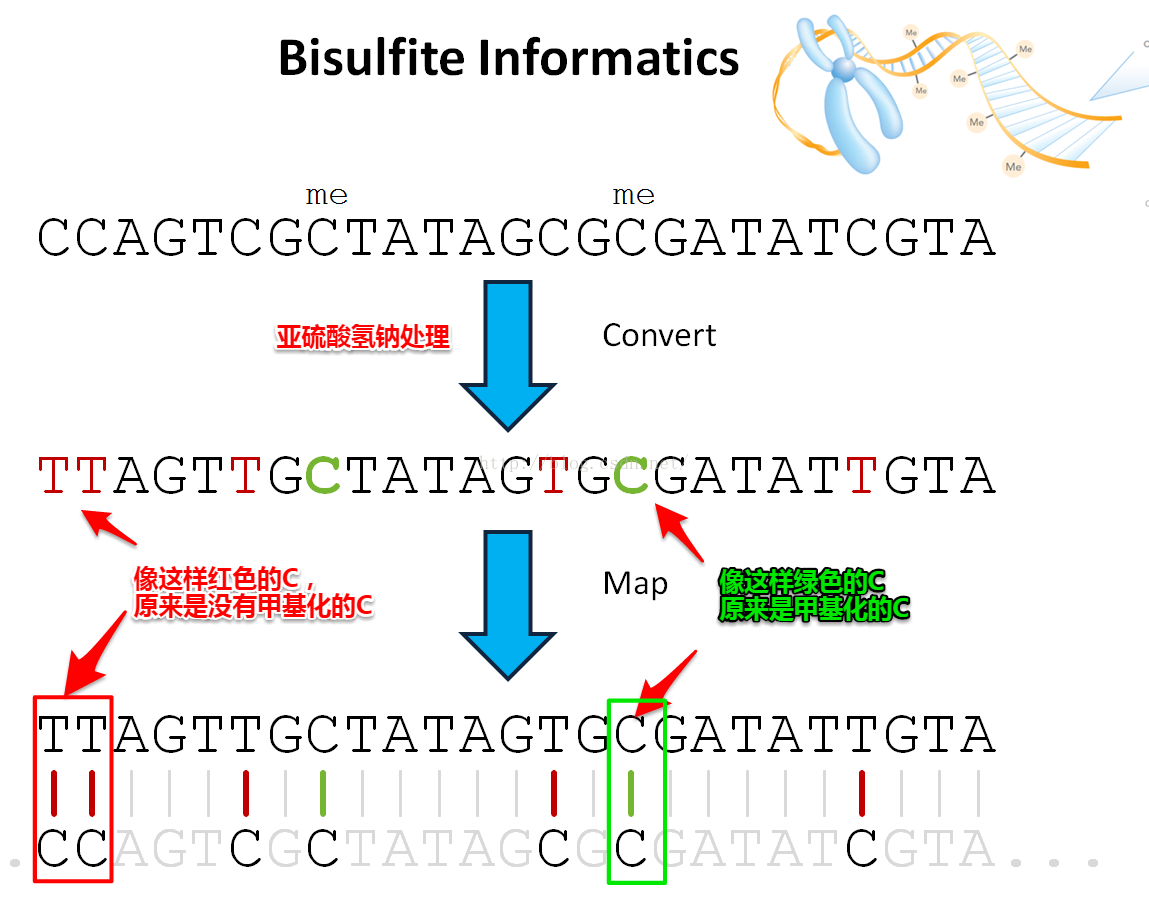
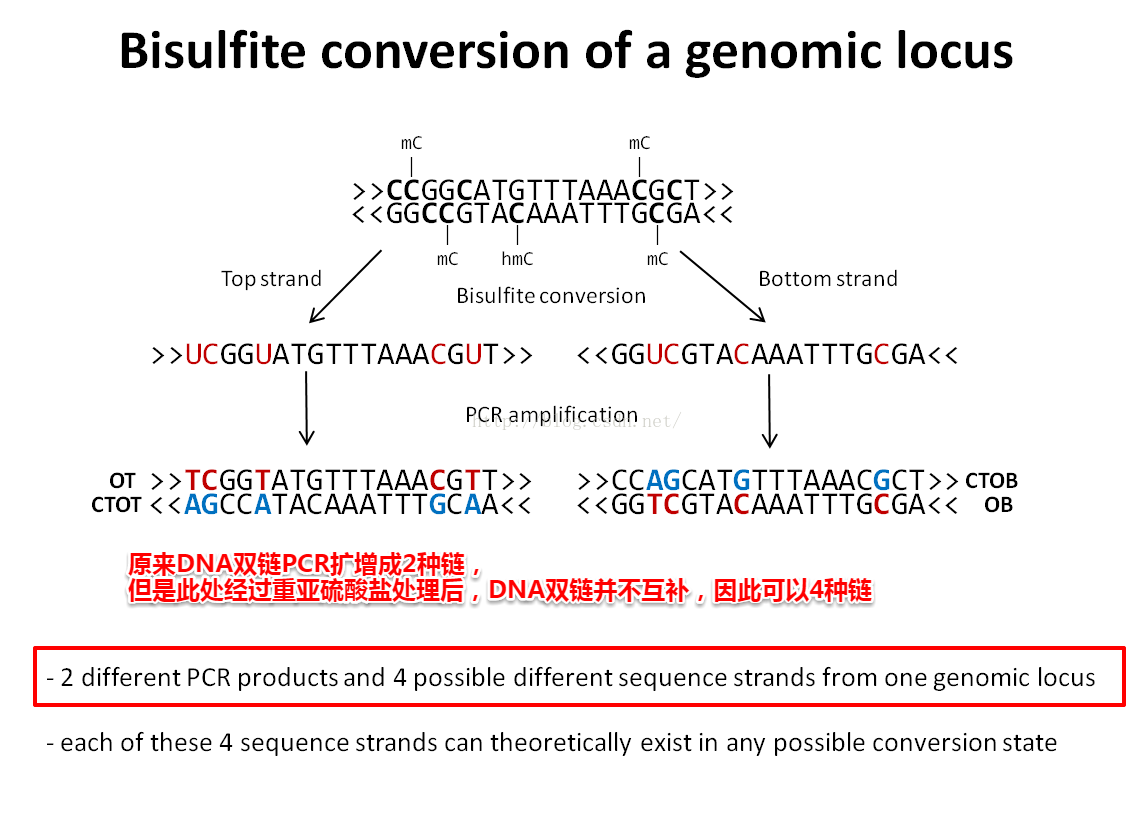
Bismark运行原理:
Bisulfite将序列正负链的C全部转换为T,所以也要将基因组序列进行转换。
基因组正负链转换很特别。
基因组的正链C->T,才能匹配原正链的reads
基因组的负链C->T相当于正链G->A,才能匹配原负链的reads
然后一条序列可以比对一个基因组的位置(即真实的基因组位置)
输出真实的基因组序列即可
How does Bismark work?
Sequence reads are first transformed into fully bisulfite-converted forward (C->T) and reverse read (G->A conversion of the forward strand) versions, before they are aligned to similarly converted versions of the genome (also C->T and G->A converted). Sequence reads that produce a unique best alignment from the four alignment processes against the bisulfite genomes (which are running in parallel) are then compared to the normal genomic sequence and the methylation state of all cytosine positions in the read is inferred. For use with Bowtie 1, a read is considered to align uniquely if one alignment exists that has with fewer mismatches to the genome than any other alignment (or if there is no other alignment). For Bowtie 2, a read is considered to align uniquely if an alignment has a unique best alignment score (as reported by the Bowtie 2 AS:i field). If a read produces several alignments with the same number of mismatches or with the same alignment score (AS:i field), a read (or a read-pair) is discarded altogether.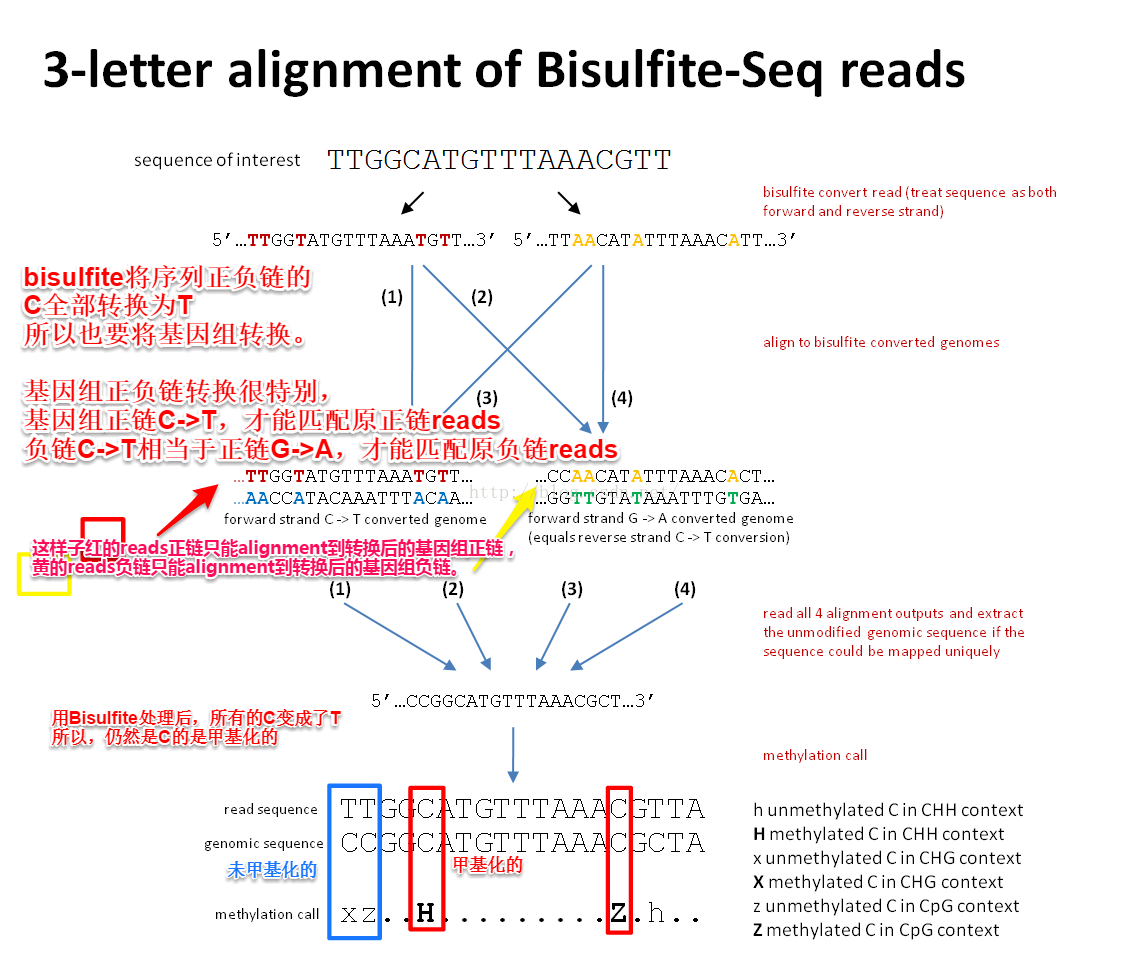

Bismark alignment and methylation call report
Upon completion, Bismark produces a run report containing information about the following: - Summary of alignment parameters used - Number of sequences analysed - Number of sequences with a unique best alignment (mapping efficiency) - Statistics summarising the bisulfite strand the unique best alignments came from - Number of cytosines analysed - Number of methylated and unmethylated cytosines - Percentage methylation of cytosines in CpG, CHG or CHH context (where H can be either A, T or C). This percentage is calculated individually for each context following the equation:
% methylation (context) = 100 * methylated Cs (context) / (methylated Cs (context) + unmethylated Cs (context)).
It should be stressed that the percent methylation value (context) is just a very rough calculation performed directly at the mapping step. Actual methylation levels after post-processing or filtering have been applied may vary.
Directional BS-Seq libraries (default)
Bisulfite treatment of DNA and subsequent PCR amplification can give rise to four (bisulfite converted) strands for a given locus. Depending on the adapters used, BS-Seq libraries can be constructed in two different ways:
- If a library is directional, only reads which are (bisulfite converted) versions of the original top strand (OT) or the original bottom strand (OB) will be sequenced. Even though the strands complementary to OT (CTOT) and OB (CTOB) are generated in the BS-PCR step they will not be sequenced as they carry the wrong kind of adapter at their 5’-end. By default, Bismark performs only 2 read alignments to the OT and OB strands, thereby ignoring alignments coming from the complementary strands as they should theoretically not be present in the BS-Seq library in question.
- Alternatively, BS-Seq libraries can be constructed so that all four different strands generated in the BS-PCR can and will end up in the sequencing library with roughly the same likelihood. In this case all four strands (OT, CTOT, OB, CTOB) can produce valid alignments and the library is called non- directional. Specifying --non_directional instructs Bismark to use all four alignment outputs.
To summarise again: alignments to the original top strand or to the strand complementary to the original top strand (OT and CTOT) will both yield methylation information for cytosines on the top strand. Alignments to the original bottom strand or to the strand complementary to the original bottom strand (OB and CTOB) will both yield methylation information for cytosines on the bottom strand, i.e. they will appear to yield methylation information for G positions on the top strand of the reference genome.
For more information about how to extract methylation information of the four different alignment strands please see below in the section on the Bismark methylation extractor.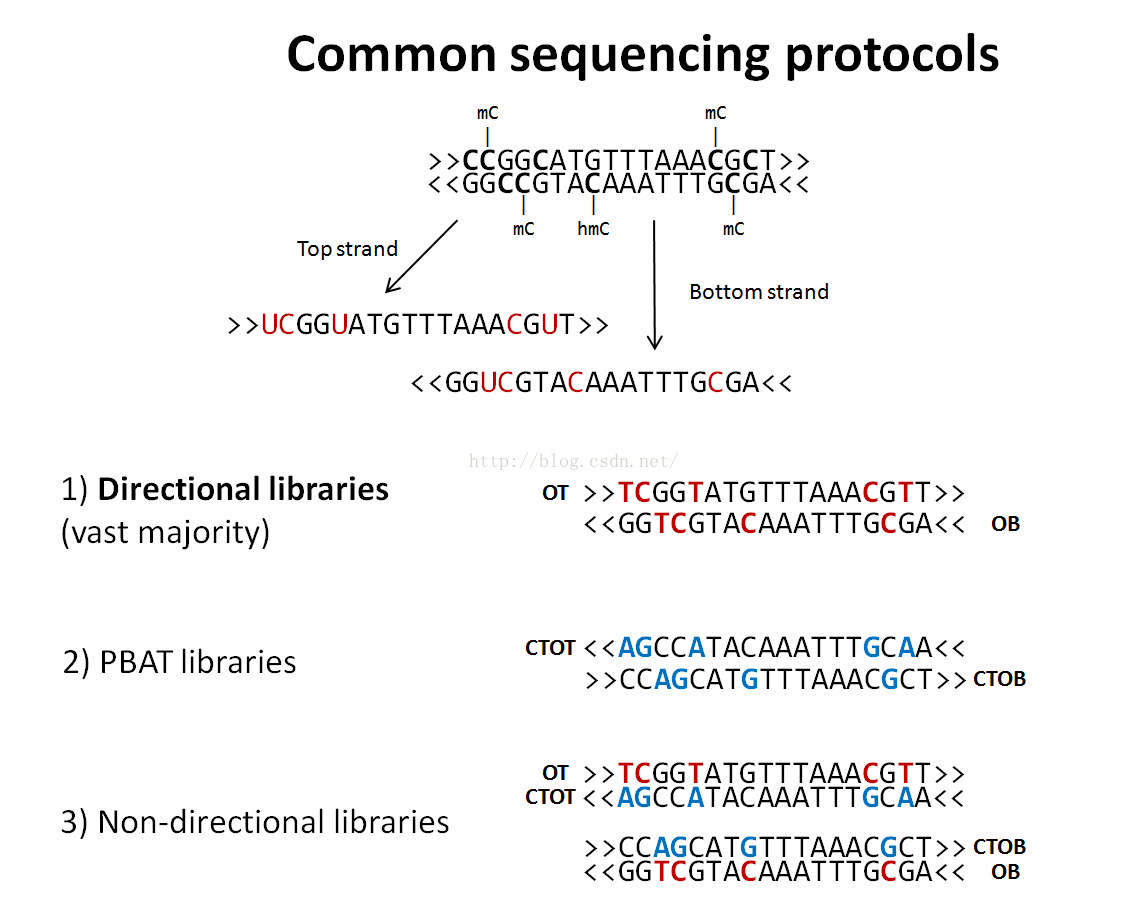

Bismark在线甲基化分析资料:http://www.bioinformatics.bbsrc.ac.uk/training.html
Bismark原理英文PPT:
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








