所谓的原子操作,取的就是“原子是最小的、不可分割的最小个体”的意义,它表示在多个线程访问同一个全局资源的时候,能够确保所有其他的线程都不在同一时间内访问相同的资源。也就是他确保了在同一时刻只有唯一的线程对这个资源进行访问。这有点类似互斥对象对共享资源的访问的保护,但是原子操作更加接近底层,因而效率更高。
第一:创建四个线程,直接运行代码
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include "CELLTimestamp.hpp"
#include <atomic>
using namespace std;
mutex m;
const int tCount = 4;
int sum = 0;
void Funny(int index)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i <1000000; i++)
{
//m.lock();
//cout<<i << "other thread" << endl;
sum++;
//m.unlock();
}
}
int main(_In_ int argc, _In_reads_(argc) _Pre_z_ char** argv, _In_z_ char** envp)
{
thread t[tCount];
CELLTimestamp micTime;
for (int i = 0; i < tCount; i++)
{
t[i]= thread(Funny,i);
//cout << t[i].get_id() << endl;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < tCount; i++)
{
t[i].join();
}
cout <<micTime.getElapsedTimeInMicroSec()<<" "<< "main thread" << endl;
cout <<micTime.getElapsedTimeInMicroSec()<<" "<<sum << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}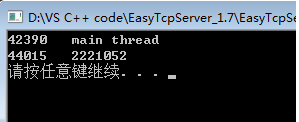
解析:创建多个线程如果不对线程进行上锁和解锁,造成输出数据错误,输出的sum应该是4000000.
第二、采用lock和unlock的方式,对全局变量限制访问
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include "CELLTimestamp.hpp"
#include <atomic>
using namespace std;
mutex m;
const int tCount = 4;
int sum = 0;
void Funny(int index)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i <1000000; i++)
{
m.lock();
//cout<<i << "other thread" << endl;
sum++;
m.unlock();
}
}
int main(_In_ int argc, _In_reads_(argc) _Pre_z_ char** argv, _In_z_ char** envp)
{
thread t[tCount];
CELLTimestamp micTime;
for (int i = 0; i < tCount; i++)
{
t[i]= thread(Funny,i);
//cout << t[i].get_id() << endl;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < tCount; i++)
{
t[i].join();
}
cout <<micTime.getElapsedTimeInMicroSec()<<" "<< "main thread" << endl;
cout <<micTime.getElapsedTimeInMicroSec()<<" "<<sum << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}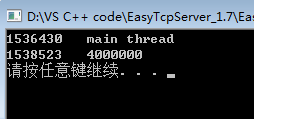
解析:采用lock和unlock对公用资源上锁,由于线程访问要不断上锁和解锁,所以消耗时间长(是方法一的35倍),但是输出的sum=4000000.
第三、采用原子操作
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include "CELLTimestamp.hpp"
#include <atomic>
using namespace std;
mutex m;
const int tCount = 4;
atomic_int sum = 0;
void Funny(int index)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i <1000000; i++)
{
//m.lock();
//cout<<i << "other thread" << endl;
sum++;
//m.unlock();
}
}
int main(_In_ int argc, _In_reads_(argc) _Pre_z_ char** argv, _In_z_ char** envp)
{
thread t[tCount];
CELLTimestamp micTime;
for (int i = 0; i < tCount; i++)
{
t[i]= thread(Funny,i);
//cout << t[i].get_id() << endl;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < tCount; i++)
{
t[i].join();
}
cout <<micTime.getElapsedTimeInMicroSec()<<" "<< "main thread" << endl;
cout <<micTime.getElapsedTimeInMicroSec()<<" "<<sum << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}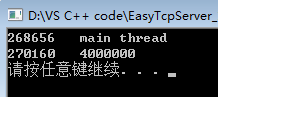
解析:原子操作 是C++11新增的内容,既安全有提高性能,是方法二的6倍多。






















 1263
1263











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








