这篇文献是比特币白皮书,区块链技术的原始论文,需要细品。本文是归纳核心内容的个人阅读笔记。
Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System
Author:Satoshi Nakamoto (中本聪)
Abstract
本文提出一种解决双花问题的P2P网络:该网络把 交易(transactions) 哈希结果记录到一个基于 PoW共识机制 不断增长的链上,用来给交易打上时间戳形成一条不可篡改的记录(如果不重做PoW)。 (The network timestamps transactions by hashing them into an ongoing chain of hash-based proof-of-work, forming a record that cannot be changed without redoing the proof-of-work)。
-
P2P的电子货币可以在无第三方金融机构的情况下进行在线支付。
-
数字签名技术可以用于防止双花(double-spending)。
-
最长链会作为已发生事件的载体,同时其自身也代表了最强大的CPU算力池。(The longest chain not only serves as proof of the sequence of events witnessed, but proof that it came from the largest pool of CPU power)。
-
只要大部分算力由节点控制而不是合作用于攻击网络,他们将始终创造比攻击者更长的链(也就是攻击该网络需要拿下 >50% 的算力)。
-
网络自身需要最小的结构单元(才能执行?)。
-
消息会尽可能广播。
-
节点可以随时加入和离开网络。
1 Introduction
- 基于信任的模型的固有缺点:交易可逆。可逆有纠纷成本,很难处理不可逆交易。
(评述:目前区块链技术的Gas费很高,没有实现原文中提到更方便小额支付的情况,同时信任关系更多的由信任第三方来处理,而不是交易对象,信任第三方需要对交易者进行KYC,相对确实没有区块链这样自由,但是区块链匿名性也没有让这个问题变的更好,反而助长了很多灰色行为,与白皮书的愿景一定程度上有相反的落地表现。另外,在链外/链下数据交互时也很难不需要第三方,目前更多是链上交互可以实现无第三方。)
2 Transactions
-
定义了一种基于一系列数字签名链条的电子货币/加密货币。发起人对上一笔交易的Hash和接收者的公钥整体的哈希进行签名(如图所示)即可进行电子货币的支付或转让。收款人可以通过验证签名来证明所有权(Ownership)。

到此还没有解决双花问题:The payee can’t verify that one of the owners did not double-spend the coin (收款人无法证实双花) -
【核心创新】在没有可信第三方的情况下,交易需要被广播(transactions must be publicly announced),同时还需要一个可以让参与者对他们接受到的信息达成一致历史顺序的系统(a system for participants to agree on a single history of the order in which they were received) 。收款人需要在每次交易时确保大多数节点认可他是第一次受到的。(The payee needs proof that at the time of each transaction, the majority of nodes agreed it was the first received.)[评述:分布式去中心化环境下由于通信时延/干扰等因素如何对事件顺序达成共识是本文献的核心创新]
3 Timestamp Server
(Timestamp在这里不知道怎么翻译比较合适,比起时间戳,理解为"打包"更合适)
时间戳服务器通过对要加时间戳的项目区块进行hash并且广播hash值来工作(A timestamp server works by taking a hash of a block of items to be timestamped and widely publishing the hash)。每个Timestamp包含了对上一个Timestamp的hash,如此循环形成链。

4 Proof-of-Work
为了在P2P上实现分布式时间戳服务器(distributed timestamp server)我们需要使用类似Adam Back的Hashcash的 proof-of-work 系统。工作量证明包括检测hash结果中的某个值,例如:SHA-256算法 hash值以一些0 bit开头(The proof-of-work involves scanning for a value that when hashed, such as with SHA-256, the hash begins with a number of zero bits)。【就是计算结果满足前缀有多少个0才满足PoW机制】平均所需工作量是0的位数的指数倍,但可以简单的通过hash来验证。
本文所述的timestamp network通过在block中增加一个nonce来实现,当block hash满足0比特数量的要求时即可。区块链满足PoW后不能被修改,除非修改从它开始之后的所有区块。

PoW还实现了多数决策的确定性实现(determining representation in majority decision making)。
- 工作量证明难度由根据每小时区块产生的平均值确定。如果它们生成得太快,则难度会增加。
5 Network
运行这个网络的步骤:
- 广播新交易到所有节点 New transactions are broadcast to all nodes.
- 每个节点都将新交易收集到一个区块 Each node collects new transactions into a block.
- 每个节点都为其区块进行工作量证明 Each node works on finding a difficult proof-of-work for its block.
- 当节点完成工作量证明时,它会将该区块广播到所有节点 When a node finds a proof-of-work, it broadcasts the block to all nodes.
- 仅当区块中的所有交易都有效且尚未使用时,节点才接受该区块 Nodes accept the block only if all transactions in it are valid and not already spent.
- 节点通过把接受的区块hash作为创建的新区块的previous hash来表示它们接受该区块 Nodes express their acceptance of the block by working on creating the next block in the chain, using the hash of the accepted block as the previous hash.
如果两个节点同时广播了两个不同区块,其他节点可以选择接收其中一个。在这种情形下,节点按接收到的第一个区块进行工作,但保存另一个作为分支,以防另一个链会变得更长。当完成下一个工作量证明并且这两个分支中的一个变长时,节点将切换到较长的链上工作。
新的交易不一定需要广播到所有节点,只要到达许大部分节点就行。区块广播允许消息丢包。如果一个节点没有收到一个区块,它会在收到下一个区块时发现它丢失了一个区块,并请求它。
6 Incentive
- 第一个区块比较特殊是创世区块。
- 通过transaction fees 同样可以获得激励。交易的输出与输入的差值作为区块奖励。
- 设计的最大数量货币进入流通时,奖励就完全由交易手续费构成,不再有通货膨胀。
7 Reclaiming Disk Space
- 一旦这笔钱的最新交易被埋在足够多的区块下,之前的花费过的交易(spent transactions)可以在磁盘空间中被丢弃来节省磁盘空间(Once the latest transaction in a coin is buried under enough blocks, the spent transactions before it can be discarded to save disk space)。
【评述:比特币采用的是UTXO模型,即要花掉一笔钱需要用上一个unspend transaction,如果对这个tx的spent被足够多的区块确认,那么unspend tx就可以认为被spent了,于是可以做磁盘压缩】 - 为了在不破坏block hash的情况下实现(丢弃算法),交易以Merkle树的方式进行哈希,只有树的根节点包含在区块哈希中。旧有的区块可以通过剪枝来压缩。内部hash值不用存储(即下图虚线部分)。
【评述:如果不用Merkle树,而是线性计算hash并存储,这种情况下验证任一笔交易,需要所有交易数据。】
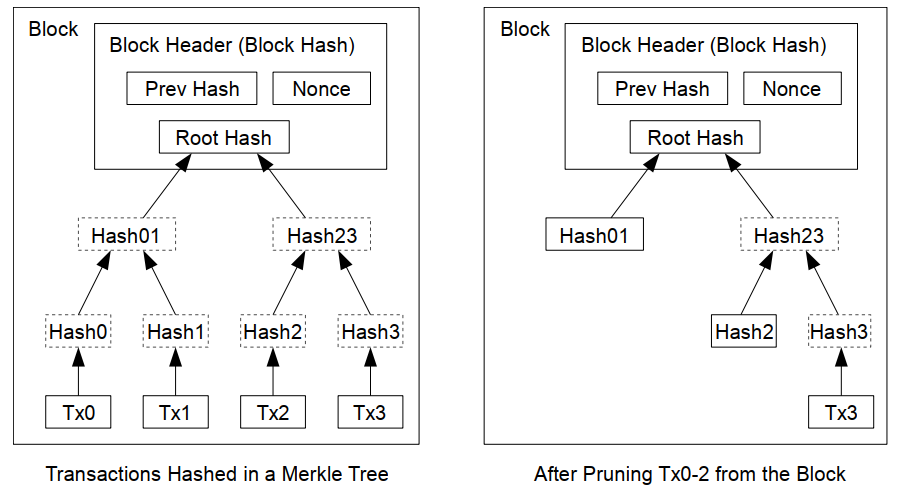
- 没有交易的区块头大概80bytes。我们假设每10min出块一次,
80 bytes * 6 * 24 * 365 = 4.2MB/year,每年新增内容为4.2MB。在2008年计算机内存为2GB且摩尔定律预测每年增长1.2GB,即使区块头需要全部存在内存中,存储也不成问题。
【评述:在有交易记录的情况下,平均每个交易至少250字节,按平均每个区块包含2000个交易来估算,包含完整交易记录的区块大小相当于区块头的数千倍。】
【评述:目前实践中,回收算法应该还没有真正使用】
8 Simplified Payment Verification
可以不用跑完网络所有节点来验证支付。用户只需保留最长工作证明链的区块头的副本(可以通过网络查询来确认拥有最长的链),并获得对应于打包交易区块的Merkle树(and obtain the Merkle branch linking the transaction to the block it’s timestamped in)。用户不能自己验证交易,但是可以通过网络看到其他节点接受了这笔交易,并在其后追加了新的区块来进一步确认网络接受了这笔交易。

- 只要网络不超过50%的算力被攻击者控制,这种方式就是有效的。
9 Combining and Splitting Value
- 尽管可以独立(无信任第三方)去处理每个货币(bitcoin)但如果交易中的每一分钱都分开转移效率会很低。交易支持多重输入和输出(如下图所示,至多2输出,一个输出用于转让,一个用于找零)。

交易可能彼此依赖,但不用对每笔交易从头开始清算到现在。
【更多细节参考上面的超链接关于UTXO模型的介绍】
10 Privacy
由于公钥的匿名性(与人无关,公钥可以随意生成)起到了对用户的隐私保护。
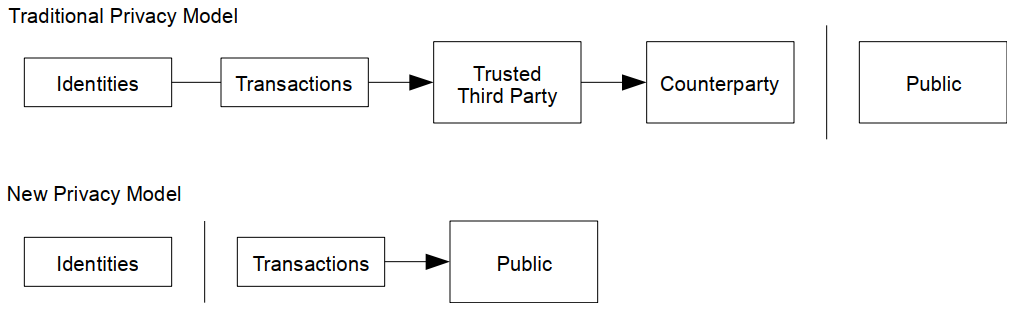
【评述:但要进行链下操作的话容易被抓住马脚】
As an additional firewall, a new key pair should be used for each transaction to keep them from being linked to a common owner. Some linking is still unavoidable with multi-input transactions, which necessarily reveal that their inputs were owned by the same owner. The risk is that if the owner of a key is revealed, linking could reveal other transactions that belonged to the same owner.
11 Calculations
略。可以参见ref。
本节主要讲安全性的计算
12 Conclusion
略。
Reference
[1] W. Dai, “b-money,” http://www.weidai.com/bmoney.txt, 1998.
[2] H. Massias, X.S. Avila, and J.-J. Quisquater, “Design of a secure timestamping service with minimal
trust requirements,” In 20th Symposium on Information Theory in the Benelux, May 1999.
[3] S. Haber, W.S. Stornetta, “How to time-stamp a digital document,” In Journal of Cryptology, vol 3, no
2, pages 99-111, 1991.
[4] D. Bayer, S. Haber, W.S. Stornetta, “Improving the efficiency and reliability of digital time-stamping,”
In Sequences II: Methods in Communication, Security and Computer Science, pages 329-334, 1993.
[5] S. Haber, W.S. Stornetta, “Secure names for bit-strings,” In Proceedings of the 4th ACM Conference
on Computer and Communications Security, pages 28-35, April 1997.
[6] A. Back, “Hashcash - a denial of service counter-measure,”
http://www.hashcash.org/papers/hashcash.pdf, 2002.
[7] R.C. Merkle, “Protocols for public key cryptosystems,” In Proc. 1980 Symposium on Security and
Privacy, IEEE Computer Society, pages 122-133, April 1980.
[8] W. Feller, “An introduction to probability theory and its applications,” 1957.
历史的评述
在 Metaverse 或者 Web3 兴起的窗口,该技术被发掘出了更多关于 如何在数字世界建立所有权 的意义。
Reference
参考已有的翻译:



























 3170
3170

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










