Self-Supervised Adversarial Hashing Networks for Cross-Modal Retrieval
from CVPR 2018
abstract
本文采用2个对抗网络来影响不同模态之间的相关性,并将标签作为训练样本,放入生成器生成对应的语义来供其他网络学习。本文采用multi-label的形式来表述label与对象之间的关系(即一个对象可能有多个label)。
network and loss
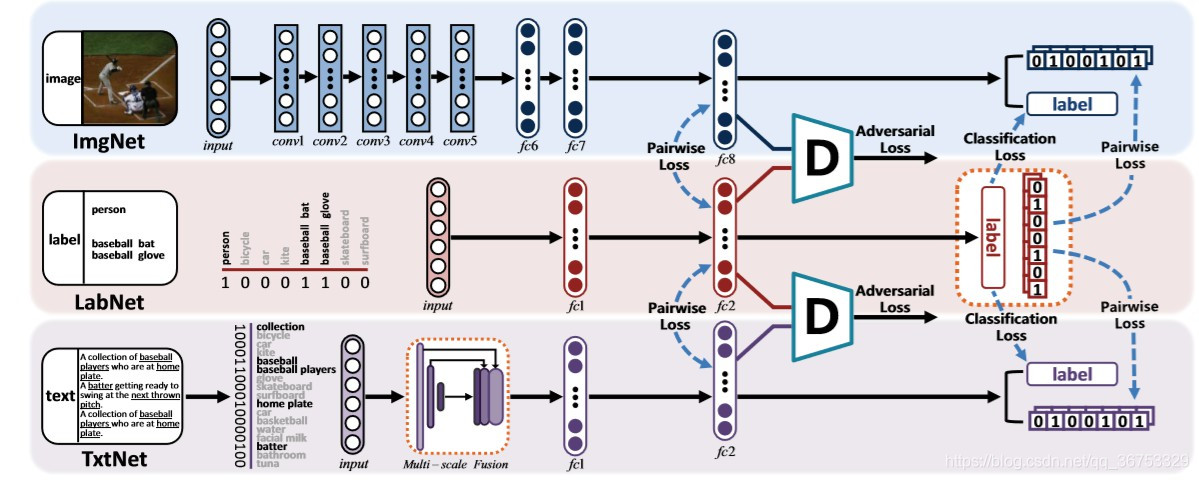
本文为了说明结果,采用了图像模态和文本模态的双模态分类。网络结构如上图,其中包含了两个特征提取网络:图像特征提取网络ImgNet与文本特征提取网络TxtNet。以及用来将label用于语义生成的labNet,还有结合ImgNet与labNet输出的辨别器D1,和结合TxtNet输出与LabNet输出的辨别器D2。
network struct
网络结构采用了目前CMH常见的网络模型。
ImgNet采用CNN-F模型,将最后的全连接层改为hash输出层,结构如下
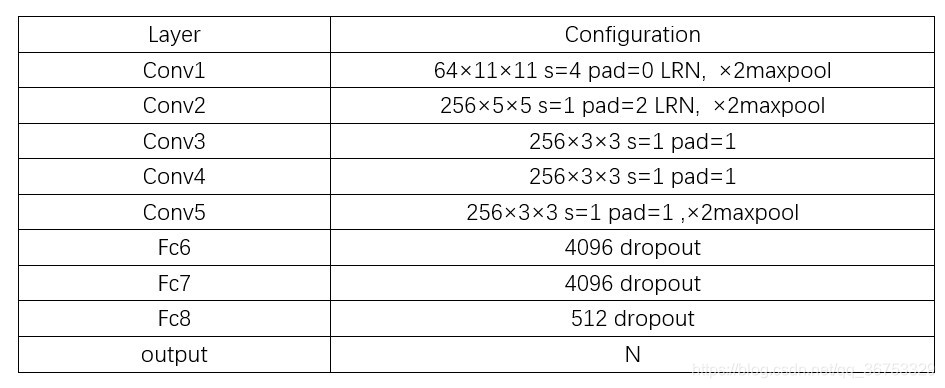
这里采用了其他论文中的描述,但与实际有些许不服,即最后fch8应为N,这里的N为hash code长度+分类标签个数,后续相同。
TxtNet使用了融合标签(MS),每一层MS由一个average pooling + 1×1的conv构成,结构如下
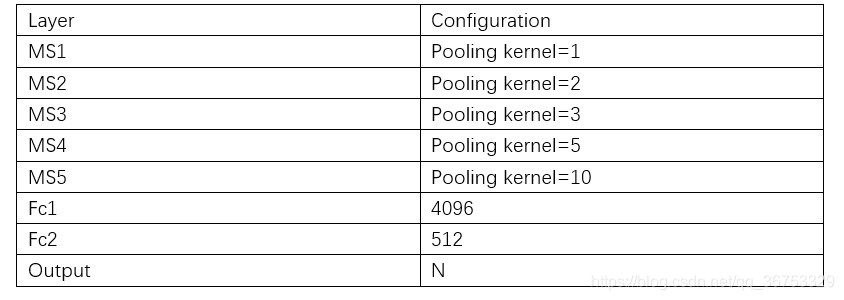
特征提取网络(ImgNet and TxtNet)均采用relu作为激活函数
LabNet采用全连接层的方式,即(label -> 4096 -> 512 -> N),采用sigmoid作为激活函数
对抗网络D(D1,D2相同)也是采用全连接层的方式,即(feature -> 4096 -> 4096 -> 1),采用tanh作为激活函数
loss
首先我们定义两个实例的相似度Si,j,由于是多标签情况,所以只要两个实例有一个共同的标签,即表示两个实例是相似的,Si,j=1,否之Si,j=0.
其次,labNet的输入标签我们称为inputLabel,输出的分类标签label,其中label的维度在1×N ,与inputLabel的表示含义及其维度不同
我 们 用 F l 表 示 L a b N e t 的 特 征 , F v 表 示 I m g N e t 输 出 的 特 征 , F t 表 示 T x t N e t 输 出 的 特 征 我们用F^l表示LabNet的特征,F^v表示ImgNet输出的特征,F^t表示TxtNet输出的特征 我们用Fl表示LabNet的特征,Fv表示ImgNet输出的特征,Ft表示TxtNet输出的特征
我 们 用 H l 表 示 L a b N e t 的 h a s h , H v 表 示 I m g N e t 输 出 的 h a s h , H t 表 示 T x t N e t 输 出 的 h a s h 我们用H^l表示LabNet的hash,H^v表示ImgNet输出的hash,H^t表示TxtNet输出的hash 我们用Hl表示LabNet的hash,Hv表示ImgNet输出的hash,Ht表示TxtNet输出的hash
对 于 h a s h 的 学 习 , 我 们 定 义 B v , t ∈ { − 1 , 1 } K , 这 里 K 为 h a s h 的 长 度 对于hash的学习,我们定义B^{v,t}\in\{-1, 1\}^K,这里K为hash的长度 对于hash的学习,我们定义Bv,t








 本文介绍了CVPR 2018年提出的自监督对抗哈希网络(SSAH),用于跨模态检索。通过两个对抗网络影响不同模态的相关性,使用多标签表示对象与标签的关系。网络结构包括图像和文本特征提取网络,以及语义生成和判别器网络。损失函数包括语义生成、特征、对抗损失,优化过程中采用分步更新策略。实验表明SSAH结构相对于其他方法有显著提升,未来可考虑改进相似矩阵和哈明距离。
本文介绍了CVPR 2018年提出的自监督对抗哈希网络(SSAH),用于跨模态检索。通过两个对抗网络影响不同模态的相关性,使用多标签表示对象与标签的关系。网络结构包括图像和文本特征提取网络,以及语义生成和判别器网络。损失函数包括语义生成、特征、对抗损失,优化过程中采用分步更新策略。实验表明SSAH结构相对于其他方法有显著提升,未来可考虑改进相似矩阵和哈明距离。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 2601
2601

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








